Introduction
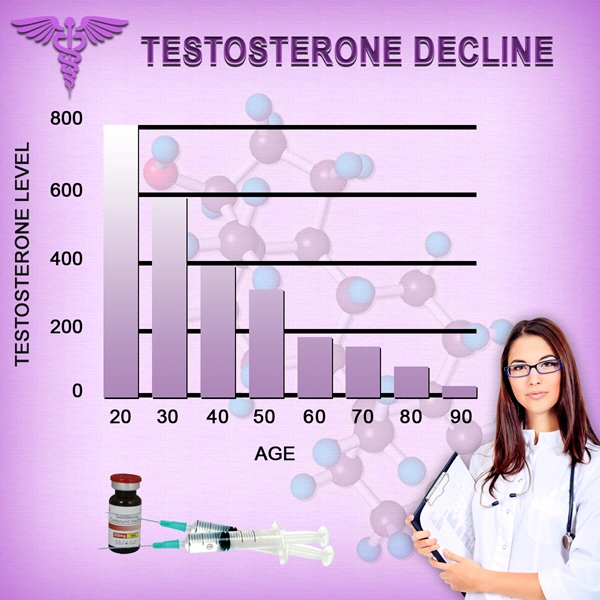
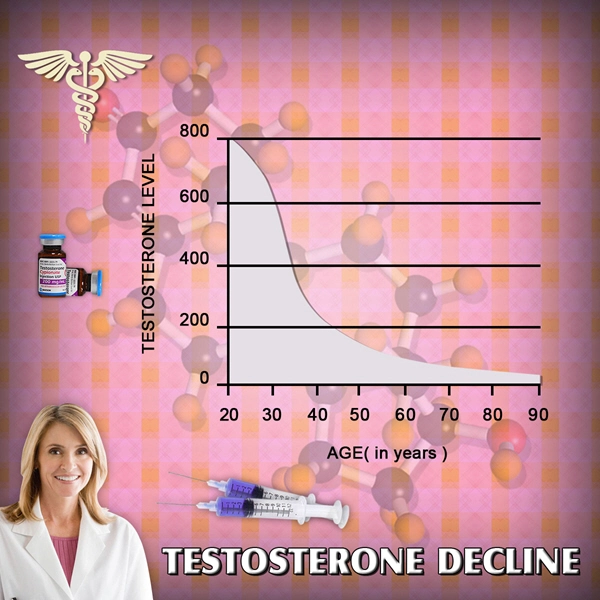
Detrusor overactivity (DO) represents a significant concern in the field of urology, particularly among American men. This condition, characterized by involuntary bladder contractions during the filling phase, can lead to urgency, frequency, and nocturia, significantly impacting quality of life. Recent studies have begun to explore the relationship between testosterone deficiency and DO, suggesting a potential hormonal influence on bladder function. This article delves into the urodynamic characterization of DO in testosterone-deficient men and examines the effects of hormone replacement therapy (HRT) on this condition.
Urodynamic Characterization of Detrusor Overactivity
Urodynamic studies are crucial for diagnosing DO and understanding its impact on bladder function. In men with testosterone deficiency, these studies often reveal increased bladder pressure and reduced bladder capacity, indicative of DO. The detrusor muscle, responsible for bladder contraction, may exhibit heightened sensitivity and reactivity in the absence of adequate testosterone levels. This hormonal imbalance can lead to symptoms such as urgency and frequency, which are hallmarks of DO.
The Role of Testosterone in Bladder Function
Testosterone plays a multifaceted role in male physiology, including the regulation of muscle and nerve function. In the bladder, testosterone receptors are present on both smooth muscle cells and nerve endings, suggesting a direct influence on detrusor activity. Research indicates that testosterone deficiency can lead to alterations in bladder smooth muscle tone and neural signaling, contributing to the development of DO. Understanding these mechanisms is essential for developing targeted therapies.
Impact of Hormone Replacement Therapy
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) with testosterone has shown promising results in managing DO in testosterone-deficient men. Studies have demonstrated that restoring testosterone levels can lead to improvements in bladder function, as evidenced by urodynamic studies. Men receiving HRT often report reduced urgency and frequency, alongside objective improvements in bladder capacity and pressure. These findings underscore the potential of HRT as a therapeutic option for DO in this population.
Clinical Considerations and Management
When considering HRT for men with DO and testosterone deficiency, clinicians must weigh the benefits against potential risks. Monitoring testosterone levels and assessing urodynamic parameters before and after therapy initiation is crucial for evaluating treatment efficacy. Additionally, patient education on the expected outcomes and potential side effects of HRT is essential for informed decision-making. Collaborative care involving urologists and endocrinologists can optimize the management of DO in testosterone-deficient men.
Future Directions in Research
The relationship between testosterone deficiency and DO warrants further investigation. Future research should focus on elucidating the specific mechanisms by which testosterone influences bladder function and identifying biomarkers that can predict treatment response. Longitudinal studies examining the long-term effects of HRT on DO and overall quality of life in testosterone-deficient men are also needed. Such research will enhance our understanding of this complex condition and guide the development of personalized treatment strategies.
Conclusion
Detrusor overactivity in testosterone-deficient men represents a significant urological challenge that can profoundly affect quality of life. Urodynamic studies have provided valuable insights into the characterization of DO in this population, highlighting the potential role of testosterone in bladder function. Hormone replacement therapy offers a promising approach to managing DO, with evidence suggesting improvements in bladder symptoms and function. As research continues to unravel the intricate relationship between testosterone and bladder health, tailored interventions will become increasingly important in addressing the needs of American men with this condition.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Unveiling the Role of Prostatic Acid Phosphatase in Monitoring Androgen Activity During Testosterone Replacement Therapy in Men [Last Updated On: February 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone's Impact on Bladder Health: Insights from Electron Microscopy Studies [Last Updated On: March 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 7th, 2025]
- Understanding Urethral Epithelial Atrophy: Impact, Diagnosis, and Hormone Replacement Therapy [Last Updated On: March 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 8th, 2025]
- Testosterone's Impact on Prostatic Stroma: Implications for Prostate Health and Therapy [Last Updated On: March 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 9th, 2025]
- Alpha1-Adrenoreceptor Density, Testosterone, and LUTS Severity in American Men: Clinical Insights [Last Updated On: March 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 11th, 2025]
- Exploring the Impact of Hormone Replacement on Pelvic Floor Electromyographic Activity in Hypogonadal Men [Last Updated On: March 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 12th, 2025]
- Exploring the Dynamics of Post-Void Residual Volume in Men with Testosterone Deficiency: A Longitudinal Study on Testosterone Replacement Therapy [Last Updated On: March 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 13th, 2025]
- Androgen-Dependent Regulation of PDE5 in Prostatic Tissue: A New Frontier in Men's Urological Health [Last Updated On: March 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 14th, 2025]
- Unveiling New Biomarkers: The Role of Urinary Proteomics in Diagnosing Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction in Androgen-Deficient Men [Last Updated On: March 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 15th, 2025]
- Urinary Flow Cytometry: A Non-Invasive Tool for Monitoring Hypogonadism and TRT Effects [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Vesicourethral Reflux in Hypogonadal Men: Hormonal and Bladder Neck Dysfunction Insights [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Ultrasonographic BWT and Urodynamic Parameters in American Men with Late-Onset Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Prostatic Aromatase in Aging Men: Risks and Management in Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Androgen-Regulated Genes in Urothelium: Impact of Hormone Therapy on Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Mitochondrial Function in Bladder Smooth Muscle of Testosterone-Deficient Men: Insights and Implications [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Prostatic Inflammation in Hypogonadal Men: Histopathology and Testosterone Therapy Effects [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Prostate Health: Insights from Color Doppler Ultrasonography [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Metabolomic Analysis of Prostatic Fluid in Testosterone-Deficient Men: Urological Implications and Treatment Responses [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone's Impact on Bladder ECM: GAGs, Proteoglycans, and Male Urological Health [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Urinary Exosomal microRNAs: Biomarkers for Hypogonadism and LUTS in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Urinary Stone Risk: Crystallization Patterns in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone's Impact on Prostatic Gap Junction Proteins and TRT Implications for American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Impacts Autonomic Innervation and Male Urological Health [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Neural Density in Detrusor Muscle: Hypogonadism's Urological Impact and Management [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Prostatic Neuroendocrine Cells in Androgen-Deficient Men: Analysis and HRT Response [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Therapy's Impact on PSA Kinetics and Safety Monitoring in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Bladder Function: Insights from Ambulatory Urodynamic Monitoring [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Urethral Pressure Changes in Hypogonadal Men Before and After Androgen Therapy [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Androgen Deficiency Impacts Bladder Contractile Proteins in American Men: Proteomic Insights [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Prostate Health: Assessing Stiffness with Transrectal SWE in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Micturition Parameters and Serum Hormone Levels in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Prostatic Calcifications in Hypogonadal Men: Prevalence, Composition, and LUTS Association [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Androgen Receptor Distribution in Hypogonadal Men's Lower Urinary Tract: Clinical Insights [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Normalization Effects on Bladder Pressure in Deficient Men: Cystometry Insights [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy Enhances Bladder Function in Deficient American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Videourodynamic Assessment and Hormone Therapy for Postvoid Dribbling in Testosterone-Deficient Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- TRT Enhances Uroflowmetric Parameters in American Men: A Comprehensive Study [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Prostatic Urothelial Metaplasia in Hypogonadal Men: Prevalence, Implications, and Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Therapy's Impact on Prostatic Growth Factors and Hyperplasia Risk [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Uroflowmetry and Hormonal Correlations in American Men with Androgen Deficiency [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Therapy in Hypogonadal Men: PIN Incidence and Surveillance Protocols [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- TRT-Induced Ultrastructural Changes in Prostatic Smooth Muscle: An Electron Microscopy Study [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Non-Bacterial Prostatitis and Hypogonadism: Exploring Inflammation and Testosterone Therapy Benefits [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Bladder Neck Collagen in Hypogonadal Men: Urodynamic Impacts and Therapeutic Insights [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Doppler Ultrasonography Monitors Prostatic Flow Changes in American Men on TRT [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Therapy's Impact on Prostatic Tissue in Hypogonadal Men: A Morphometric Study [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Fluctuations and Maximum Flow Rate Variability in Hypogonadal Men on TRT [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Nocturnal Polyuria: Mechanisms and Hormone Therapy in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- PSMA Expression Analysis in Androgen-Deficient Men Before and After Hormone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Therapy Enhances Urethral Sphincter Function in Hypogonadal Men: EMG Insights [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testosterone Therapy's Impact on Prostate Health: A Histomorphometric Analysis [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Prostatic Stromal Androgen Receptors: Key to Managing LUTS in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Androgen Therapy Modulates Apoptotic Index in Hypogonadal Men's Prostatic Epithelium [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- LOH Impact on Bladder Compliance: Urodynamic and Hormonal Insights in Aging Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- DSD in Androgen-Deficient Men: Prevalence, Urodynamics, and Hormonal Insights [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Neurogenic Bladder in Hypogonadal Men with Metabolic Syndrome: Urodynamics and Hormonal Insights [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Androgen Deficiency's Impact on Detrusor Oxygen Tension and Testosterone Therapy Benefits [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Impacts Prostatic Secretions and Urological Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Bladder Sensation Mapping in Testosterone-Deficient Men: QST Before and After HRT [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- 3D Ultrasonography: Monitoring Prostate Health in Men on Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Impacts Bladder Capacity: HRT Benefits in American Males [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Prostatic Aromatase Activity and Estrogen's Role in LUTS Among Aging American Men [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Computerized Urethral Pressure Analysis in Hypogonadal Men Pre- and Post-TRT [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Androgen Receptor Sensitivity: Predicting Testosterone Therapy Outcomes in Men's Urological Health [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Bladder Health: Suburothelial Myofibroblast Insights for American Men [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Bladder Wall Fibrosis in Men: Grading, Testosterone Deficiency, and Hormone Therapy Benefits [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Prostatic Elastography: Assessing Tissue Stiffness in Men on Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Diurnal LUTS Variations in Hypogonadal Men Linked to Testosterone Rhythms [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- TRT Modulates Prostatic Epithelial Cell Autophagy in Hypogonadal Men: A Review [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- OAB in Androgen-Deficient Men: Prevalence, Symptoms, and Testosterone Therapy Benefits [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- TRT Enhances Periurethral Vascularity in American Men: Power Doppler Insights [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Differentiating and Treating Prostatitis-like Symptoms in Hypogonadal Men with Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Intraprostatic Hormone Levels in American Men: Testosterone Therapy Impacts and Management [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Mathematical Modeling Predicts Prostatic Growth in TRT for American Men [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
- Electrophysiological Insights into Bladder Nerve Activity in Testosterone-Deficient American Males [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
- Neurourological Assessment Protocol for Autonomic Neuropathy in Testosterone-Deficient American Men [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Urinary GAG Levels: Biochemical Insights and Clinical Implications [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Testosterone Therapy Enhances VUJ Functionality in Androgen-Deficient Men: Videourodynamic Insights [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Urinary NGF as Biomarker for LUTS in Testosterone-Deficient Men: Diagnostic Potential [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- CEUS: A Novel Approach to Assess Urethral Mucosal Vasocongestion in Hypogonadal Men [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
Word Count: 548