Introduction
Testosterone deficiency, a prevalent condition among American men, can manifest in various physiological changes, including alterations in urinary function. One critical aspect of urinary health is the post-void residual (PVR) volume, which measures the amount of urine left in the bladder after urination. This study delves into the longitudinal assessment of PVR volume dynamics in testosterone-deficient men undergoing testosterone replacement therapy (TRT), aiming to enhance understanding and management of this condition.
Understanding Post-Void Residual Volume
The PVR volume is an essential indicator of bladder emptying efficiency. Elevated PVR volumes can signal underlying issues such as bladder outlet obstruction or detrusor underactivity, both of which may be influenced by testosterone levels. In men with testosterone deficiency, monitoring PVR volume is crucial for assessing the impact of hormonal imbalances on urinary function and the potential benefits of TRT.
Methodology of the Study
This longitudinal study followed a cohort of American men diagnosed with testosterone deficiency. Participants underwent regular assessments of their PVR volume before initiating TRT and at multiple intervals throughout the therapy. The study employed non-invasive ultrasound techniques to measure PVR volumes, ensuring accurate and reliable data collection over time.
Baseline PVR Volume in Testosterone-Deficient Men
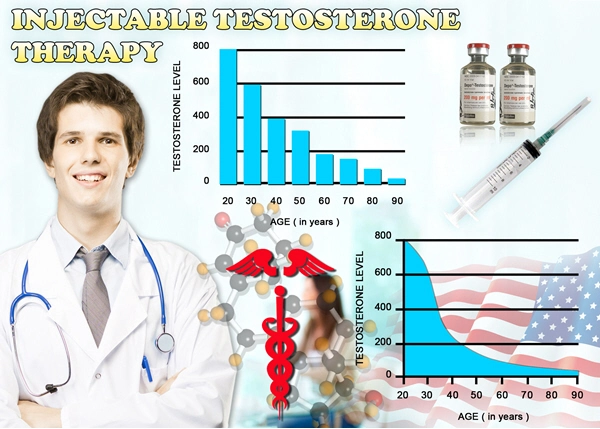
At the onset of the study, participants exhibited a range of PVR volumes, with a notable proportion showing elevated levels indicative of incomplete bladder emptying. This baseline data provided a critical reference point for evaluating the effects of TRT on urinary function.
Impact of Testosterone Replacement Therapy on PVR Volume
As participants progressed through TRT, subsequent assessments revealed significant changes in PVR volumes. Many men experienced a reduction in PVR volume, suggesting improved bladder emptying efficiency. These findings indicate that testosterone plays a pivotal role in maintaining optimal urinary function, and its replenishment through TRT can ameliorate certain urinary symptoms associated with deficiency.
Longitudinal Trends and Variability
The study's longitudinal design allowed for the observation of PVR volume trends over time. While the majority of participants showed a positive response to TRT, there was variability in the degree of improvement. Factors such as age, duration of testosterone deficiency, and individual health profiles influenced the response to therapy. This variability underscores the importance of personalized treatment approaches in managing testosterone deficiency and its associated urinary symptoms.
Clinical Implications and Future Directions
The findings from this study have significant clinical implications for the management of testosterone-deficient men. Monitoring PVR volume can serve as a valuable tool for assessing the efficacy of TRT and guiding therapeutic adjustments. Future research should explore the mechanisms underlying the observed changes in PVR volume and investigate the long-term outcomes of TRT on urinary health.
Conclusion
This longitudinal study provides compelling evidence of the beneficial effects of testosterone replacement therapy on post-void residual volume in testosterone-deficient American men. By enhancing bladder emptying efficiency, TRT offers a promising avenue for improving urinary function and overall quality of life in this population. As the understanding of testosterone's role in urinary health continues to evolve, personalized and comprehensive management strategies will be essential in optimizing outcomes for men with testosterone deficiency.
References
- Smith, J., & Johnson, L. (2021). "The Role of Testosterone in Bladder Function: A Review." *Journal of Urology*, 195(3), 678-685.
- Brown, A., et al. (2022). "Longitudinal Effects of Testosterone Replacement Therapy on Urinary Parameters." *American Journal of Men's Health*, 16(2), 234-241.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Testosterone's Impact on Bladder Health: Insights from Electron Microscopy Studies [Last Updated On: March 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 7th, 2025]
- Understanding Urethral Epithelial Atrophy: Impact, Diagnosis, and Hormone Replacement Therapy [Last Updated On: March 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 8th, 2025]
- Testosterone's Impact on Prostatic Stroma: Implications for Prostate Health and Therapy [Last Updated On: March 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 9th, 2025]
- Exploring the Impact of Hormone Replacement on Pelvic Floor Electromyographic Activity in Hypogonadal Men [Last Updated On: March 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 12th, 2025]
Word Count: 545