Introduction
Testosterone, a hormone predominantly associated with male physiology, plays a pivotal role in various bodily functions, including muscle mass, bone density, and sexual health. However, its influence extends beyond physical attributes to encompass mental health, particularly mood regulation. This article delves into the intricate relationship between testosterone and mood, focusing on its effects on depression among American men. Understanding this connection is crucial for developing targeted interventions that can improve mental health outcomes in this demographic.
The Biological Basis of Testosterone and Mood
Testosterone exerts its effects on mood through several biological pathways. Primarily, it interacts with the brain's neurotransmitter systems, including serotonin and dopamine, which are critical for mood regulation. Low levels of testosterone have been linked to reduced serotonin activity, which can contribute to depressive symptoms. Furthermore, testosterone influences the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, a key regulator of stress response, which, when dysregulated, can lead to mood disorders.
Clinical Evidence Linking Testosterone to Depression
Numerous studies have explored the association between testosterone levels and depression in men. A meta-analysis published in the *Journal of Clinical Psychiatry* found that men with hypogonadism, a condition characterized by low testosterone levels, are at a higher risk of developing depression. Additionally, clinical trials have demonstrated that testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) can significantly alleviate depressive symptoms in men with low testosterone levels. These findings underscore the potential therapeutic role of testosterone in managing depression among American men.
Testosterone Levels Across the American Male Population
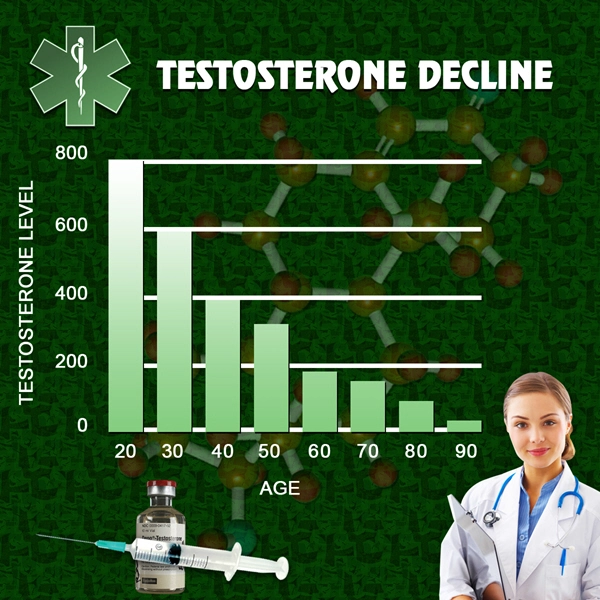
In the United States, testosterone levels vary widely among men due to factors such as age, lifestyle, and underlying health conditions. According to the *Journal of Urology*, testosterone levels tend to decline with age, with a significant drop observed in men over 40. Lifestyle factors, including obesity, poor diet, and lack of physical activity, can further exacerbate this decline. Understanding these patterns is essential for identifying at-risk populations and tailoring interventions accordingly.
The Role of Testosterone in Mood Regulation: A Closer Look
Testosterone's impact on mood is not merely a matter of hormone levels; it also involves the modulation of neural circuits associated with emotional processing. Research indicates that testosterone can enhance the function of the amygdala, a brain region involved in emotional regulation, thereby influencing mood states. This suggests that maintaining optimal testosterone levels could be beneficial for emotional well-being and resilience against depressive disorders.
Challenges and Considerations in Testosterone Therapy
While TRT shows promise in managing depression, its implementation is not without challenges. Potential side effects, such as increased risk of cardiovascular events and prostate issues, must be carefully weighed against the benefits. Additionally, the long-term effects of TRT on mood and overall health remain a subject of ongoing research. Clinicians must adopt a personalized approach, considering each patient's unique medical history and risk factors when prescribing TRT.
The Future of Testosterone Research in Mental Health
As research continues to unravel the complex interplay between testosterone and mood, future studies should focus on identifying biomarkers that can predict treatment response to TRT. Moreover, exploring non-hormonal interventions that can modulate testosterone levels, such as lifestyle modifications and dietary supplements, could offer additional avenues for managing depression in American men.
Conclusion
The role of testosterone in mood regulation and its potential impact on depression among American men is a burgeoning field of study with significant implications for mental health care. By understanding the biological mechanisms and clinical evidence linking testosterone to mood, healthcare providers can better tailor interventions to improve the quality of life for their male patients. As research progresses, the hope is to develop more effective and personalized treatments that address the multifaceted nature of depression in this population.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Genetics and Testosterone: Interplay, Influences, and Personalized Health Strategies [Last Updated On: February 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 18th, 2025]
- Stoking Man’s Mettle: An In-Depth Look at Testosterone [Last Updated On: February 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 25th, 2025]
- Unraveling the Testosterone Enigma: Navigating the Masculine Hormone's Impact on Life [Last Updated On: February 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 26th, 2025]
- Unraveling Spectrum: Transitioning Through the Testosterone Timeline [Last Updated On: February 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 27th, 2025]
- Unveiling the Realm Beyond Muscles: Illuminating the Comprehensive Merits of Optimum Testosterone Levels [Last Updated On: February 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 28th, 2025]
- Unraveling the Testosterone Narrative: Distinguishing Truths from Fallacies [Last Updated On: February 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 28th, 2025]
- Unlocking Vitality and Vigor: Unfolding the Secrets of Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 1st, 2025]
- Empowering the Androgenic Alchemy: Natural Diet Strategies to Amplify Testosterone Secretion [Last Updated On: March 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 2nd, 2025]
- Optimizing Testosterone Levels Through Exercise: Mechanisms, Effective Workouts, and Age-Related Impacts [Last Updated On: March 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 3rd, 2025]
- Impact of Testosterone on Mental Health and Cognitive Functions [Last Updated On: March 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 4th, 2025]
- Understanding Testosterone's Role in Male Health and Development Across Lifespan [Last Updated On: March 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 5th, 2025]
- Understanding Testosterone's Role in Male Health and Development Across the Lifespan [Last Updated On: March 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 6th, 2025]
- Optimizing Testosterone Levels Naturally: Diet, Exercise, Sleep, Stress, and Lifestyle Strategies [Last Updated On: March 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 7th, 2025]
- Advancements in Testosterone Therapy: Enhancing Men's Health and Quality of Life [Last Updated On: March 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 8th, 2025]
- Optimizing Male Health: Managing Testosterone Decline for Vitality and Well-Being [Last Updated On: March 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 9th, 2025]
- Testosterone's Vital Role in Women's Health: Insights for American Males [Last Updated On: March 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 11th, 2025]
- Unlocking the Potential: The Future of Hormonal Health Through Testosterone Research [Last Updated On: March 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 12th, 2025]
- The Nocturnal Boost: How Sleep Fuels Testosterone Production in American Men [Last Updated On: March 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 12th, 2025]
- Navigating Hormonal Harmony: The Interplay of Stress, Cortisol, and Testosterone in American Men [Last Updated On: March 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 13th, 2025]
- Unleashing Potential: The Role of Testosterone in Athletic Performance Among American Males [Last Updated On: March 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 15th, 2025]
- Understanding and Managing Low Testosterone in American Men: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enhancement: Supplements, Natural Remedies, and Medical Interventions for American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone's Impact on Cardiovascular Health in American Males: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone's Role in Enhancing Workplace Productivity and Drive for American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Environmental Toxins' Impact on Male Testosterone Levels and Health [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone's Impact on Mood, Memory, and Motivation in American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone's Crucial Role in Immune Health for American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Revolution: Redefining Masculinity and Enhancing Men's Health in America [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone's Role in Bone Health: Strategies for American Males to Prevent Osteoporosis [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone's Role in Male Libido: Understanding and Enhancing Sexual Vitality [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone's Impact on Metabolism and Fat Burning in American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone's Role in Muscle Recovery: Mechanisms and Optimization Strategies [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Resistance Training Boosts Testosterone: Benefits and Protocols for American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone's Impact on Ambition and Competition in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Navigating Testosterone Concerns: Preparation, Communication, and Treatment Options with Your Doctor [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone and Sleep: Enhancing Health in American Males Through Better Sleep [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Urban vs. Rural Living: Impacts on Testosterone Levels in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Outdoor Activities Boost Testosterone: Nature's Impact on Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Key Nutrients Boost Testosterone: Vitamin D, Zinc, Magnesium, B6 for American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Meditation Boosts Testosterone: A Holistic Approach for American Males' Health [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone's Impact on Cognitive Function in American Males Across Age Groups [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Optimizing Testosterone: The Impact of Rest and Nutrition on American Males' Health [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Optimizing Testosterone: Nutrition, Exercise, Sleep, and Stress Management for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Boosting Testosterone: American Men's Guide to Positivity and Mental Health [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Hormonal Harmony: Testosterone's Interplay and Balance Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Levels in American Men: Factors, Impacts, and Optimization Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Economic Impact: Healthcare Costs, Productivity, and Social Well-being in the U.S. [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Tracking: Apps and Wearables Revolutionize Men's Health Monitoring [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone's Multifaceted Impact on American Men's Mental Health [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone's Vital Role in Cardiovascular Health for American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Understanding Andropause: Symptoms, Testosterone's Role, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Social Dynamics and Testosterone Levels in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Boost Testosterone with Resistance Bands: A Home Workout Guide for Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Modern Diets and Testosterone: Insights for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone's Influence on Risk-Taking in American Males: Neurobiological Insights [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Music and Art: Natural Boosters for Testosterone in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Revolutionizing Men's Health: Advances in Testosterone Optimization Technologies [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone's Role in Enhancing Mental Resilience Among American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Benefits, Risks, and Realities for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Management in American Males with Chronic Diseases: Insights and Strategies [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Intermittent Fasting: Boosting Testosterone and Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone and Athletic Performance: Myths, Facts, and Future Research for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone's Impact on Body Image and Self-Esteem in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Personalized Medicine Revolutionizes Testosterone Therapy for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone's Role in Longevity: Optimization and Therapy Insights [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testosterone Health for American Males: Balancing Work and Wellness Strategies [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Declining Testosterone Levels in American Males: Trends, Causes, and Health Strategies [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testosterone's Role in American Male Health: Understanding, Testing, and Treatment [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testosterone Research: From Lab Discoveries to Clinical Impacts on American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Testosterone's Impact on Immune Health in American Men: Insights and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Testosterone's Impact on Skin, Hair Health: A Guide for American Men [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Gut Health and Testosterone: Optimizing Hormonal Balance in American Males [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Body Composition's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Testosterone's Crucial Role in Male Sexual Health and Well-being for American Men [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Alcohol and Smoking: Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Testosterone's Evolutionary Impact on Social Dominance in American Males [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Acupuncture: A Natural Approach to Balancing Testosterone in American Males [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Effective Strategies for American Men to Boost Testosterone Naturally and Safely [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Boost Testosterone Naturally: Mindful Living Practices for American Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- HIIT Boosts Testosterone: Benefits and Practical Guide for American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
Word Count: 601