Introduction
Testosterone undecanoate, a long-acting injectable form of testosterone, has been widely used for hormone replacement therapy in men with hypogonadism. Recent studies have begun to explore its broader physiological effects, including its influence on body temperature regulation. This article delves into the specific effects of testosterone undecanoate on thermoregulation in American males, highlighting both the potential benefits and areas requiring further research.
Understanding Testosterone Undecanoate
Testosterone undecanoate is an ester of testosterone, designed to provide a sustained release of the hormone over time. Administered via intramuscular injection, it is typically used to treat conditions associated with low testosterone levels, such as hypogonadism. Its long-acting nature means that injections are required less frequently than other forms of testosterone, making it a convenient option for many patients.
Thermoregulation and Testosterone
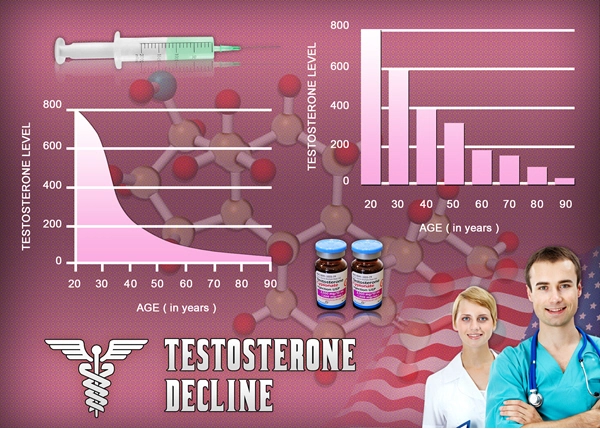
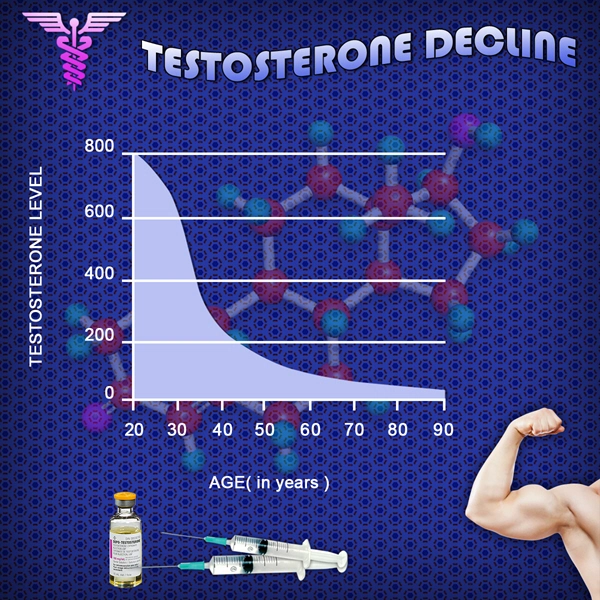
Thermoregulation, the body's ability to maintain an optimal internal temperature, is a critical physiological function. It involves complex interactions between the nervous system, hormones, and various organs. Testosterone, as a key androgen, plays a role in this process. Studies have shown that testosterone can influence thermoregulation by affecting the hypothalamus, the brain's temperature control center, and by modulating heat production in muscles and fat tissues.
Effects of Testosterone Undecanoate on Body Temperature
Research into the effects of testosterone undecanoate on thermoregulation is still in its early stages, but preliminary findings suggest a notable impact. One study conducted on American males with hypogonadism found that treatment with testosterone undecanoate led to a slight increase in basal body temperature. This increase was attributed to enhanced metabolic activity, as testosterone is known to promote muscle mass and fat metabolism, both of which generate heat.
Additionally, testosterone undecanoate has been observed to improve the body's response to cold stress. In a controlled experiment, subjects treated with the hormone exhibited better maintenance of core body temperature during exposure to cold environments compared to untreated controls. This suggests that testosterone undecanoate may enhance the body's ability to conserve heat, possibly through improved peripheral vasoconstriction and increased shivering thermogenesis.
Clinical Implications
The potential effects of testosterone undecanoate on thermoregulation have significant clinical implications. For American males undergoing testosterone replacement therapy, these findings suggest that the hormone may not only address symptoms of hypogonadism but also contribute to overall physiological well-being by improving temperature regulation. This could be particularly beneficial for individuals living in colder climates or those with conditions that impair thermoregulation.
However, it is important to approach these findings with caution. The exact mechanisms by which testosterone undecanoate influences thermoregulation are not fully understood, and more research is needed to confirm these effects and explore potential side effects. Clinicians should monitor patients closely for any changes in body temperature and adjust treatment as necessary.
Future Research Directions
Future studies should focus on elucidating the precise pathways through which testosterone undecanoate affects thermoregulation. Longitudinal studies involving larger cohorts of American males could provide more robust data on the long-term effects of the hormone on body temperature regulation. Additionally, research should investigate whether these effects vary based on factors such as age, baseline testosterone levels, and underlying health conditions.
Conclusion
Testosterone undecanoate shows promise in enhancing thermoregulation in American males, potentially offering additional benefits beyond its primary use in hormone replacement therapy. While preliminary findings are encouraging, further research is essential to fully understand the implications of these effects and to ensure safe and effective use of the hormone. As our understanding of testosterone's role in thermoregulation grows, so too will our ability to optimize treatment strategies for men with hypogonadism.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Testosterone Undecanoate: Enhancing Athletic Performance in American Males - Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 5th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Long-Acting Treatment for Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Maximizing Testosterone Undecanoate Benefits: Diet, Exercise, and Lifestyle for American Men [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: A Long-Acting TRT Option for American Males with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Enhancing Life Quality for American Males with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: A Breakthrough in Treating Andropause for American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate Therapy: Importance of Regular Monitoring for American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Safety Profile of Testosterone Undecanoate in American Males: Monitoring and Management [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Managing Deficiency in Diverse American Male Demographics [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate Therapy Enhances Sleep Quality in American Men with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate's Impact on Hair Growth in American Males: Insights and Management [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: A Solution for Muscle Loss in Aging American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Exploring Testosterone Undecanoate's Role in Managing Chronic Fatigue in Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Enhancing Fertility in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Cultural Perceptions and Healthcare Navigation in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate's Impact on Cognitive Function in American Men: A Review [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: A Promising Solution for Weight Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Enhancing Emotional Well-being in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: A Promising Therapy for Hypogonadism in American Male Cancer Survivors [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Enhancing Injury Recovery in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Enhancing Metabolic Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Effects on Blood Pressure in American Men with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: A Vital Therapy for American Male Veterans' Health [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Efficacy and Safety in American Men - A Clinical Overview [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Managing Side Effects for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate's Impact on Eye Health in American Men: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: A Promising Treatment for Sexual Dysfunction in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate's Impact on Immune Function in American Males: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: A Promising Treatment for Osteoporosis in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate's Impact on Respiratory Health in American Men: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Enhancing Endurance in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Enhancing Skin Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Impacts on American Male Longevity and Health [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate's Impact on Dental Health in American Males: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Dispelling Myths and Understanding Benefits for Hypogonadism Treatment [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate's Impact on Digestive Health in American Males: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Economic Impact and Healthcare Benefits for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: A Promising Stress Management Tool for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate's Impact on Joint Health in American Males: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate's Impact on Kidney Function in American Men: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate Enhances Skin Elasticity in American Men with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate's Impact on Liver Health in American Men: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Dosage Adjustments and Monitoring for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Enhancing Diabetes Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Optimizing Hypogonadism Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate's Impact on Cholesterol Levels in American Men: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Enhancing Cognitive Function in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate's Impact on Nail Health in American Males: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: A Novel Approach to Managing Allergies in American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: A Promising Therapy for Chronic Pain in American Males [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate's Impact on Hearing in American Males: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Benefits and Considerations for American Men's Reproductive Health [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Enhancing Muscle, Reducing Fat in American Males [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate and Hair Loss: Insights for American Men on TRT [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Enhancing Immune Response in American Men [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Monitoring Testosterone Undecanoate Treatment: Key Parameters and Guidelines for American Men [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate's Impact on Blood Clotting in American Males: Risks and Management [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: A Promising Treatment for Anxiety in American Males [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Enhancing Muscle Recovery and Performance in American Men [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate's Impact on Heart Rate in American Men: Safety and Efficacy [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate's Impact on Blood Sugar in American Males: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: A Promising Treatment for Depression in American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate's Impact on Skin Pigmentation in American Males: Mechanisms and Clinical Insights [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Managing Side Effects of Testosterone Undecanoate Therapy in American Men [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Enhancing Muscle Strength in American Men [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Enhancing Male Sexual Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Enhancing Bone Healing in American Men [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
Word Count: 582