Introduction to Migraines and Testosterone
Migraines are a debilitating neurological condition characterized by throbbing pain on one side of the head, often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light and sound. In the United States, migraines affect a significant portion of the male population, impacting their quality of life and productivity. Recent research has begun to explore the role of hormonal treatments, such as testosterone undecanoate, in managing this condition. Testosterone undecanoate, a long-acting injectable form of testosterone, has been traditionally used for testosterone replacement therapy in men with hypogonadism. However, its potential benefits in migraine management are gaining attention.
The Link Between Testosterone and Migraines
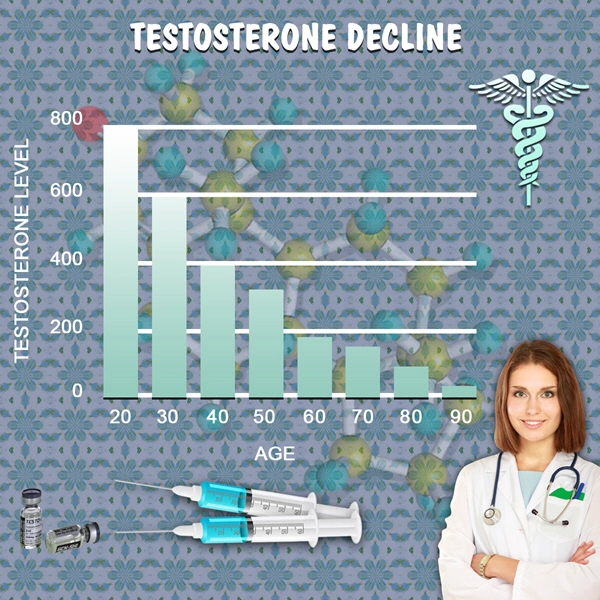
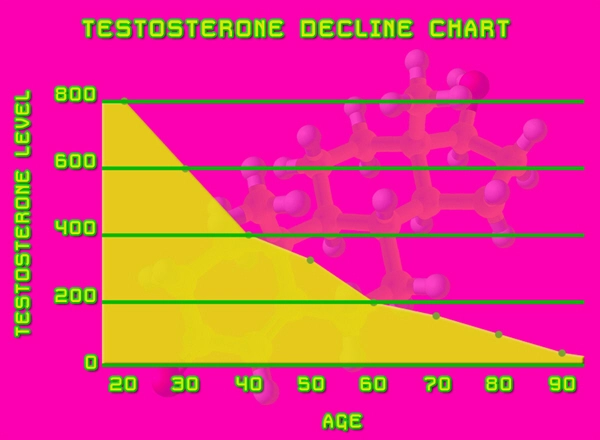
Testosterone, a key male sex hormone, plays a crucial role in various physiological processes, including vascular health and pain modulation. Studies have suggested that low testosterone levels may be associated with an increased frequency and severity of migraines. This correlation has led researchers to investigate whether testosterone supplementation could serve as a therapeutic option for migraine sufferers. Testosterone undecanoate, due to its sustained release profile, offers a stable and consistent increase in testosterone levels, potentially mitigating migraine symptoms.
Clinical Evidence Supporting Testosterone Undecanoate
Emerging clinical data have begun to shed light on the efficacy of testosterone undecanoate in managing migraines. A pilot study conducted on American males with chronic migraines and low testosterone levels demonstrated a significant reduction in migraine frequency and intensity following testosterone undecanoate treatment. Participants reported an average decrease of 50% in migraine days per month, alongside improvements in overall well-being and energy levels. These findings suggest that testosterone undecanoate could be a promising adjunct therapy for men struggling with migraines.
Mechanisms of Action
The exact mechanisms by which testosterone undecanoate may alleviate migraines are not fully understood but are thought to involve multiple pathways. Testosterone is known to have anti-inflammatory properties, which could help reduce the neuroinflammatory processes implicated in migraines. Additionally, testosterone may enhance the function of the endothelium, the inner lining of blood vessels, thereby improving blood flow and reducing the vascular component of migraines. Furthermore, testosterone's role in pain modulation could contribute to its migraine-relieving effects by altering the perception and processing of pain signals in the brain.
Considerations and Potential Side Effects
While the potential benefits of testosterone undecanoate in migraine management are promising, it is essential to consider the treatment's safety profile. Common side effects of testosterone therapy include acne, fluid retention, and changes in mood or libido. More serious risks, such as an increased likelihood of cardiovascular events, have also been reported in some studies. Therefore, testosterone undecanoate should be prescribed and monitored by a healthcare professional, with regular assessments of hormone levels and cardiovascular health.
Future Directions and Research
The use of testosterone undecanoate for migraine management is still in its early stages, and further research is needed to establish its efficacy and safety definitively. Future studies should focus on larger, more diverse populations to validate the preliminary findings and explore optimal dosing regimens. Additionally, investigating the long-term effects of testosterone supplementation on migraine patterns and overall health will be crucial in determining its place in clinical practice.
Conclusion
Testosterone undecanoate represents a novel approach to managing migraines in American males, particularly those with low testosterone levels. While the initial clinical evidence is encouraging, more comprehensive research is required to fully understand its potential and limitations. As the medical community continues to explore the intricate relationship between hormones and neurological conditions, testosterone undecanoate may emerge as a valuable tool in the comprehensive management of migraines.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Testosterone Undecanoate: Enhancing Athletic Performance in American Males - Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 5th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Long-Acting Treatment for Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Maximizing Testosterone Undecanoate Benefits: Diet, Exercise, and Lifestyle for American Men [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: A Long-Acting TRT Option for American Males with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Enhancing Life Quality for American Males with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: A Breakthrough in Treating Andropause for American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate Therapy: Importance of Regular Monitoring for American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Safety Profile of Testosterone Undecanoate in American Males: Monitoring and Management [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Managing Deficiency in Diverse American Male Demographics [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate Therapy Enhances Sleep Quality in American Men with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate's Impact on Hair Growth in American Males: Insights and Management [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: A Solution for Muscle Loss in Aging American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Exploring Testosterone Undecanoate's Role in Managing Chronic Fatigue in Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Enhancing Fertility in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Cultural Perceptions and Healthcare Navigation in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate's Impact on Cognitive Function in American Men: A Review [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: A Promising Solution for Weight Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Enhancing Emotional Well-being in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: A Promising Therapy for Hypogonadism in American Male Cancer Survivors [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Enhancing Injury Recovery in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Enhancing Metabolic Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Effects on Blood Pressure in American Men with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: A Vital Therapy for American Male Veterans' Health [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Efficacy and Safety in American Men - A Clinical Overview [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Managing Side Effects for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate's Impact on Eye Health in American Men: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: A Promising Treatment for Sexual Dysfunction in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate's Impact on Immune Function in American Males: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: A Promising Treatment for Osteoporosis in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate's Impact on Respiratory Health in American Men: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Enhancing Endurance in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Enhancing Skin Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Impacts on American Male Longevity and Health [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate's Impact on Dental Health in American Males: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Dispelling Myths and Understanding Benefits for Hypogonadism Treatment [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate's Impact on Digestive Health in American Males: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Economic Impact and Healthcare Benefits for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: A Promising Stress Management Tool for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate's Impact on Joint Health in American Males: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate's Impact on Kidney Function in American Men: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate Enhances Skin Elasticity in American Men with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate's Impact on Liver Health in American Men: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Dosage Adjustments and Monitoring for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Enhancing Diabetes Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Optimizing Hypogonadism Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate's Impact on Cholesterol Levels in American Men: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Enhancing Cognitive Function in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate's Impact on Nail Health in American Males: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: A Novel Approach to Managing Allergies in American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: A Promising Therapy for Chronic Pain in American Males [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate's Impact on Hearing in American Males: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Benefits and Considerations for American Men's Reproductive Health [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Enhancing Muscle, Reducing Fat in American Males [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate and Hair Loss: Insights for American Men on TRT [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Enhancing Immune Response in American Men [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Monitoring Testosterone Undecanoate Treatment: Key Parameters and Guidelines for American Men [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate's Impact on Blood Clotting in American Males: Risks and Management [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: A Promising Treatment for Anxiety in American Males [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Enhancing Muscle Recovery and Performance in American Men [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate's Impact on Heart Rate in American Men: Safety and Efficacy [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate's Impact on Blood Sugar in American Males: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: A Promising Treatment for Depression in American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate's Impact on Skin Pigmentation in American Males: Mechanisms and Clinical Insights [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Managing Side Effects of Testosterone Undecanoate Therapy in American Men [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Enhancing Muscle Strength in American Men [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Enhancing Male Sexual Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Enhancing Bone Healing in American Men [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate Enhances Wound Healing in American Men: Clinical Insights and Implications [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate's Impact on Appetite in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate's Impact on Thermoregulation in American Males: Benefits and Research Needs [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate's Impact on Sleep Quality in American Men: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate's Impact on Skin Sensitivity in American Males: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate Therapy: Lifestyle Adjustments for American Men [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate Enhances Skin Hydration in American Males: A Comprehensive Study [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate: Enhancing Aesthetics in American Men Through Muscle and Fat Optimization [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate's Impact on Vascular Health in American Men: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Testosterone Undecanoate's Impact on Blood Viscosity in American Men: Risks and Management [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
Word Count: 582