Introduction
Testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) is a widely used treatment for hypogonadism in American males, aimed at restoring normal testosterone levels and improving quality of life. However, the impact of TRT on erythropoiesis, the process of red blood cell production, remains a topic of significant clinical interest. This article explores the effects of TRT on hematological parameters, focusing on its potential to influence erythropoiesis in American men.
Background on Testosterone and Erythropoiesis
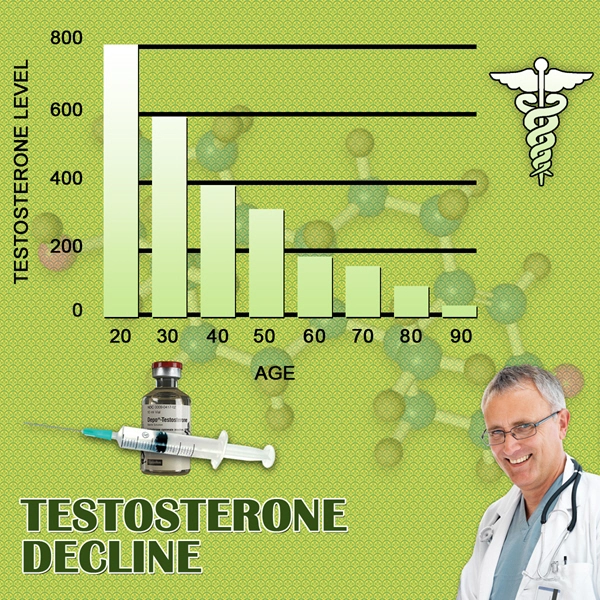
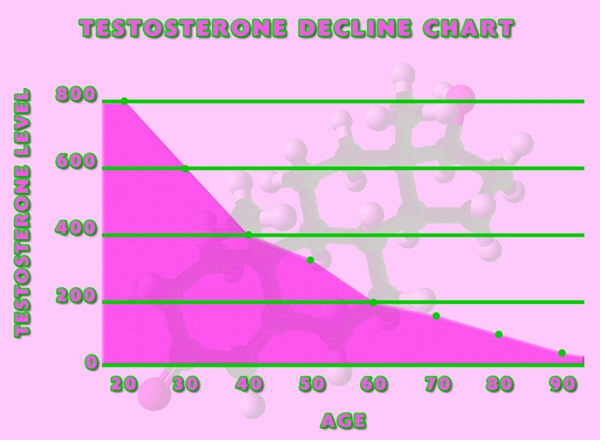
Testosterone, the primary male sex hormone, plays a crucial role in various physiological processes, including the regulation of erythropoiesis. Erythropoiesis is the process by which red blood cells are produced in the bone marrow, and testosterone has been shown to stimulate this process by increasing the production of erythropoietin, a hormone that promotes red blood cell formation. Understanding the relationship between testosterone and erythropoiesis is essential for managing the hematological effects of TRT.
Clinical Studies on TRT and Erythropoiesis
Several clinical studies have investigated the impact of TRT on erythropoiesis in American males. A notable study conducted by the National Institutes of Health found that men receiving TRT experienced a significant increase in hematocrit levels, a measure of the volume percentage of red blood cells in blood. This increase was attributed to the stimulatory effect of testosterone on erythropoiesis. Another study published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism reported similar findings, with TRT leading to elevated hemoglobin levels, another indicator of red blood cell concentration.
Potential Risks and Benefits
While the increase in red blood cell production can be beneficial for some patients, particularly those with anemia, it also poses potential risks. Elevated hematocrit levels can lead to a condition known as erythrocytosis, which increases the risk of blood clots, strokes, and heart attacks. Therefore, monitoring hematological parameters is crucial for patients undergoing TRT. Clinicians must balance the benefits of improved testosterone levels with the potential risks of excessive red blood cell production.
Management and Monitoring Strategies
To mitigate the risks associated with TRT-induced erythropoiesis, healthcare providers should implement regular monitoring of hematocrit and hemoglobin levels. The Endocrine Society recommends checking these parameters every three to six months during the first year of TRT and annually thereafter. If erythrocytosis develops, adjustments to the TRT regimen, such as dose reduction or temporary discontinuation, may be necessary. Additionally, patients should be educated about the signs and symptoms of erythrocytosis and encouraged to report any concerns promptly.
Future Research Directions
Further research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms by which testosterone influences erythropoiesis and to identify factors that may predispose certain individuals to erythrocytosis. Longitudinal studies that track hematological parameters over extended periods could provide valuable insights into the long-term effects of TRT. Additionally, investigating the role of genetic factors and comorbidities in modulating the erythropoietic response to TRT could help tailor treatment strategies to individual patients.
Conclusion
Testosterone replacement therapy has a significant impact on erythropoiesis in American males, leading to increased red blood cell production. While this can be beneficial for some patients, it also poses risks, necessitating careful monitoring and management. By understanding the relationship between TRT and erythropoiesis, healthcare providers can optimize treatment outcomes and minimize potential complications. Ongoing research will continue to refine our understanding of this complex interplay and guide the development of safer and more effective TRT protocols.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- TRT's Impact on Mental Health in American Men: Depression, Anxiety, and Cognition [Last Updated On: February 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 21st, 2025]
- Economic Impact of Testosterone Replacement Therapy on U.S. Healthcare System [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- TRT: Understanding Impacts on Prostate Health and Cancer Risk in American Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: American Men's Experiences and Impact on Quality of Life [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Optimizing TRT: Diet, Exercise, and Holistic Health for American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Navigating Insurance for Testosterone Replacement Therapy: A Guide for American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Benefits, Risks, and Management for American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Dosage, Administration, and Lifestyle Integration for American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Enhancing TRT Outcomes with Alternative Therapies: A Holistic Approach for American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Future of TRT: Innovations and Impacts on American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Benefits and Risks for Young American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- TRT Improves Sleep Quality in American Males with Hypogonadism: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- TRT: Managing Hypogonadism in American Males - Benefits, Risks, and Future Trends [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Combating Fatigue in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- TRT Boosts Bone Health in American Males: Benefits, Evidence, and Lifestyle Integration [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Cultural Attitudes and Masculinity in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Managing Side Effects in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Enhancing Muscle Mass in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Immune Function: Benefits, Risks, and Monitoring in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Benefits, Risks, and Process for American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Optimizing Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Monitoring, Adjustments, and Lifestyle Integration for American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Impacts on Cardiovascular Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- TRT in American Men: Balancing Benefits with Hair Loss Risks [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: A Promising Treatment for Depression in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Benefits, Risks, and Management for Aging American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- TRT Enhances Mood and Vitality in American Males: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- TRT: Benefits and Risks for Vision Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- TRT's Potential in Enhancing Cognitive Function in American Men with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- TRT: Enhancing Joint Health in American Males Through Hormone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- TRT: Enhancing Weight Management in American Males with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Enhancing Cognitive Function in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- TRT Impact on Male Fertility: Risks, Alternatives, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Benefits, Risks, and Realistic Expectations for Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Cost-Benefit Analysis and Accessibility in the U.S. [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- TRT: Enhancing Stamina and Vitality in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- TRT's Role in Enhancing Injury Recovery Among American Males: Benefits and Considerations [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- TRT: A Promising Approach to Managing Chronic Pain in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- TRT: A Promising Approach to Stress Management in American Males with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Kidney Health: Benefits, Risks, and Monitoring for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Benefits, Risks, and Holistic Approaches for Low Libido [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- TRT and Liver Health: Risks, Monitoring, and Mitigation Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Diabetes: Benefits, Risks, and Personalized Management for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Benefits, Risks, and Management for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- TRT: Enhancing Emotional Well-being in Men with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- TRT Benefits for American Males: Enhancing Skin Health and Vitality [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- TRT Boosts Confidence and Vitality in American Males: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testosterone Therapy: Benefits, Risks, and Side Effects for American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Respiratory Health in American Men: Benefits and Considerations [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Digestive Health: Insights for American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Enhancing Effects with Lifestyle Changes for American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Choosing the Right TRT Clinic: A Guide for American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Blood Pressure: Risks, Benefits, and Management for American Men [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Cholesterol: Essential Insights for American Males [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Restoring Vitality in American Males with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Thyroid Function: Monitoring and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Blood Sugar: Insights for American Men Considering Therapy [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Navigating Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Understanding and Interpreting Lab Results [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Enhancing Athletic Performance Safely and Ethically [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Benefits, Allergic Risks, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Dental Health: Insights and Recommendations for American Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Maximizing TRT Benefits: Integrating Therapy with Lifestyle and Supplements for American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- TRT and Hearing Health: Considerations for American Males [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Legal Aspects of Testosterone Replacement Therapy for American Males [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Guide to Managing Testosterone Replacement Therapy While Traveling [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Enhancing Social Life and Health in American Males [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Eye Health: Benefits for American Men [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Male Fertility: Risks, Evidence, and Mitigation Strategies [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Nail Health: Benefits, Risks, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Hand Health in American Men: Strength, Dexterity, and Joints [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Exploring Social Implications of Testosterone Replacement Therapy in American Males [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- TRT: Enhancing Work Performance in American Males - Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Enhancing Artistic Expression in American Males [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Neck Health: Considerations for American Men [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- TRT: Enhancing Foot Health in American Males Through Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Ethical Considerations in Testosterone Replacement Therapy for American Men [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- TRT Impact on Chest Health: Benefits, Risks, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Psychological Benefits and Risks for American Men [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- TRT: Enhancing Back Health in American Males with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- TRT Enhances Glycemic Control in American Men with Type 2 Diabetes: Cohort Study [Last Updated On: April 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Enhancing Male Health and Addressing Low Testosterone in American Men [Last Updated On: April 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 21st, 2025]
Word Count: 547