Introduction
Testosterone deficiency syndrome (TDS), also known as hypogonadism, is a condition that affects a significant number of American men, leading to a variety of health concerns. While the impact of TDS on sexual health, muscle mass, and mood is well-documented, emerging research suggests a potential link between testosterone deficiency and pancreatic health. This article explores the relationship between TDS and pancreatic function, highlighting the importance of early detection and management for American men.
Understanding Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome
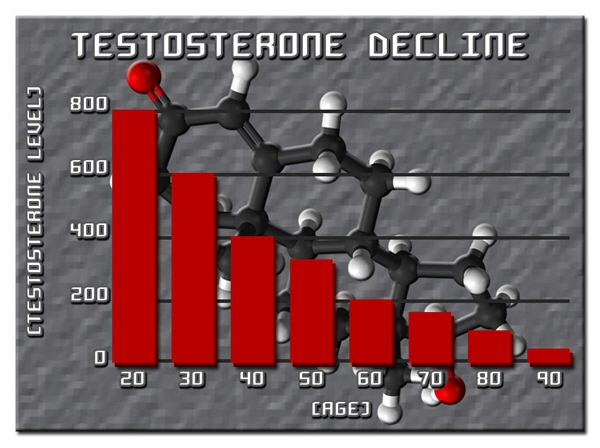
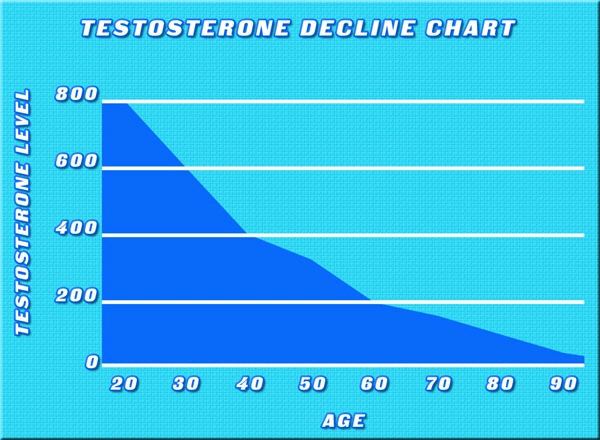
Testosterone deficiency syndrome occurs when the body fails to produce adequate levels of testosterone, the primary male sex hormone. This condition can result from various factors, including aging, obesity, chronic diseases, and genetic predispositions. Symptoms of TDS may include reduced libido, erectile dysfunction, fatigue, and decreased muscle mass. However, the effects of testosterone deficiency extend beyond these well-known symptoms, potentially impacting other organ systems, such as the pancreas.
The Pancreas and Its Role in Health
The pancreas is a vital organ responsible for regulating blood sugar levels and aiding in digestion. It produces insulin, a hormone that allows cells to absorb glucose from the bloodstream, and digestive enzymes that break down food in the small intestine. Any disruption in pancreatic function can lead to serious health conditions, such as diabetes and pancreatitis.
Emerging Evidence: Testosterone and Pancreatic Health
Recent studies have begun to uncover a potential connection between testosterone levels and pancreatic health. Research suggests that testosterone may play a role in maintaining the integrity of pancreatic beta cells, which are responsible for insulin production. Low testosterone levels have been associated with impaired glucose metabolism and an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes, a condition closely linked to pancreatic dysfunction.
Furthermore, animal studies have demonstrated that testosterone deficiency can lead to pancreatic inflammation and reduced insulin sensitivity. These findings raise concerns about the potential impact of TDS on pancreatic health in American men, particularly as the prevalence of both conditions continues to rise.
Implications for American Men
The potential link between testosterone deficiency and pancreatic health has significant implications for American men. Given the high rates of obesity, sedentary lifestyles, and aging populations in the United States, the prevalence of TDS is likely to increase. This, in turn, may contribute to a higher incidence of pancreatic-related disorders, such as diabetes and pancreatitis.
American men, particularly those over the age of 40, should be aware of the symptoms of TDS and consider regular screening for testosterone levels. Early detection and treatment of testosterone deficiency may help mitigate the risk of developing pancreatic health issues and improve overall well-being.
Management and Treatment Options
For men diagnosed with TDS, various treatment options are available, including testosterone replacement therapy (TRT). TRT can help restore testosterone levels to normal ranges, potentially improving symptoms and reducing the risk of associated health conditions. However, the decision to pursue TRT should be made in consultation with a healthcare professional, as it may not be suitable for all individuals.
In addition to medical interventions, lifestyle modifications can play a crucial role in managing TDS and supporting pancreatic health. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and weight management can help improve testosterone levels and reduce the risk of developing diabetes and other pancreatic-related disorders.
Conclusion
The emerging evidence linking testosterone deficiency to pancreatic health underscores the importance of addressing TDS in American men. By raising awareness of this potential connection and promoting early detection and management of testosterone deficiency, healthcare professionals can help mitigate the risk of pancreatic-related health issues. American men should prioritize regular health check-ups, maintain a healthy lifestyle, and work closely with their healthcare providers to optimize their overall well-being. As research continues to unravel the complex relationship between testosterone and pancreatic health, it is crucial for men to stay informed and proactive in managing their health.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Understanding Testosterone Deficiency: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: February 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 20th, 2025]
- Stress-Induced Testosterone Decline in American Males: Causes and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Hormone Therapy Benefits and Holistic Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency in American Men: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Energy-Boosting Treatments [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency in American Men: Impacts on Mood and Mental Health [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impact, Diagnosis, and Management in Aging American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Environmental Toxins Linked to Rising Testosterone Deficiency in U.S. Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency in American Men: Impacts on Muscle Mass and Treatment Strategies [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impacts on Prostate Health and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Importance of Regular Monitoring and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Smoking's Impact on Testosterone Levels and TDS Risk in American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Vitamin D's Role in Managing Testosterone Deficiency in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Chronic Illnesses and Their Impact on Testosterone Deficiency in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Alcohol's Impact on Testosterone and Risk of TDS in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Zinc's Vital Role in Combating Testosterone Deficiency in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Magnesium's Role in Managing Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Understanding Its Impact on Hair Loss in Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impacts on Immune Function in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Cognitive Decline in American Men: Impacts and Interventions [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Impacts Muscle, Fat, and Bone Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency in American Men: Impacts on Libido and Holistic Management [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: A Promising Approach to Managing Testosterone Deficiency in Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Soy Consumption and Testosterone Levels in American Men with TDS: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Depression: Exploring the Link in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Ashwagandha: A Natural Remedy for Testosterone Deficiency in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Shift Work's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males: A Growing Concern [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impacts on Skin Health and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Blue Light Exposure Linked to Testosterone Deficiency in American Men: Mitigation Strategies [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Sleep Apnea: A Bidirectional Health Concern for American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Anemia: Understanding Links and Managing Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Weight Training Boosts Testosterone: A Solution for American Men with TDS [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Joint Health in American Males: Impacts and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency in American Male Athletes: Symptoms, Impact, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency in American Men: Impacts on Dental Health and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Air Pollution's Impact on Testosterone Levels and TDS in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Boron Supplementation: A Promising Approach to Managing Testosterone Deficiency in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impacts on Vision Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Pesticide Exposure Linked to Testosterone Deficiency in American Men: Risks and Reduction Strategies [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Diet Soda Consumption Linked to Lower Testosterone Levels in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- EMF Exposure and Testosterone Levels: Implications for TDS in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Chronic Stress and Testosterone Deficiency in American Males: Impacts and Management [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- High-Fat Diets and Testosterone: Impacts and Dietary Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impacts on Liver Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Linked to Hearing Loss in American Males: Insights and Implications [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency in American Males: Impacts on Memory and Cognitive Health [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Heavy Metal Exposure and Testosterone Deficiency in American Men: Impacts and Mitigation [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impacts on Kidney Function and Holistic Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Plasticizers Linked to Testosterone Deficiency in American Men: Emerging Research and Risks [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Adrenal Health: A Holistic Approach for American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Thyroid Health: Interconnections and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Fenugreek: A Natural Solution for Testosterone Deficiency in American Males [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Linked to Increased Gallbladder Disease Risk in American Males [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Noise Pollution Linked to Testosterone Deficiency in American Males: A Growing Concern [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome in American Men: Pituitary Role, Symptoms, and Management [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Tribulus Terrestris: A Promising Aid for Testosterone Deficiency in American Men [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impact, Diagnosis, and Treatment in American Men [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Fluoride Exposure and Testosterone Levels in American Men: A Potential Link Explored [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Pineal Gland: Impacts and Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- DHEA Supplementation: A Promising Approach to Managing Testosterone Deficiency in American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impacts on Parathyroid Health and Holistic Management [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Phthalates Exposure Linked to Testosterone Deficiency in American Males: A Public Health Concern [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency in American Males: Impacts on Respiratory Health and COPD [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Bisphenol A Exposure Linked to Testosterone Deficiency in American Men [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Ginseng's Potential in Managing Testosterone Deficiency in American Males [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- PFC Exposure Linked to Testosterone Deficiency in American Males: A Public Health Concern [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Gastrointestinal Impacts and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Urinary Health in American Men: Impacts and Management [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
- Understanding and Managing Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome in American Males [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
- Shilajit: A Natural Remedy for Testosterone Deficiency in American Males [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impacts on Metabolic Health and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency in American Males: Impacts and Autoimmune Disorder Links [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Triclosan Exposure Linked to Lower Testosterone in American Men with TDS [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Phytoestrogens' Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Men with TDS [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impact of Endocrine Disruptors on American Males [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Parabens in Personal Care Products Linked to Testosterone Deficiency in American Males [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Cordyceps: A Natural Supplement for Managing Testosterone Deficiency in American Men [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: Impacts on Neurological Health in American Males [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
Word Count: 626