Introduction
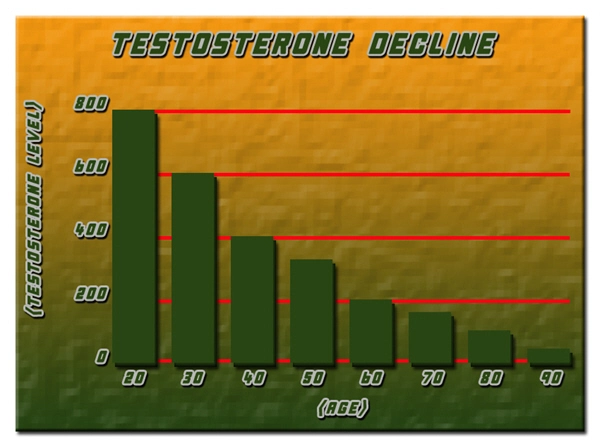
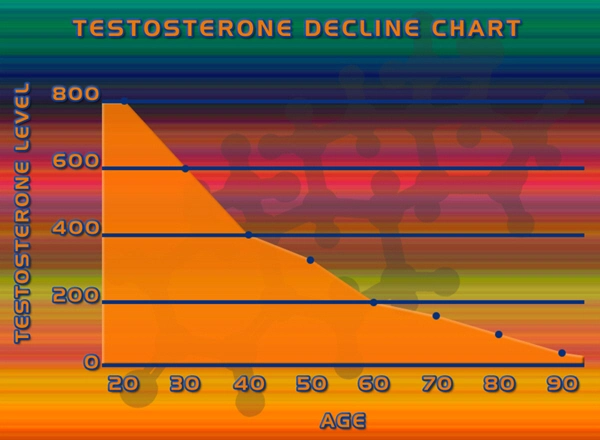
Hypogonadism, characterized by low testosterone levels, is a prevalent condition among American men, impacting their overall health and quality of life. Recent advancements in urological research have focused on the utility of urinary flow cytometry as a non-invasive diagnostic tool to assess cellular changes in hypogonadal men before and after testosterone replacement therapy (TRT). This article delves into the significance of these findings, emphasizing their implications for men's urological health.
Understanding Hypogonadism and Its Impact
Hypogonadism in men leads to a myriad of symptoms, including decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, fatigue, and mood disturbances. The condition not only affects sexual health but also has broader implications for cardiovascular health, bone density, and metabolic functions. Consequently, accurate diagnosis and effective management, such as TRT, are crucial.
The Role of Urinary Flow Cytometry
Urinary flow cytometry is a cutting-edge technique that allows for the detailed analysis of cellular components in urine. This method is particularly valuable in urology, as it provides insights into the cellular dynamics of the urinary tract, which can be indicative of underlying health conditions. In the context of hypogonadism, urinary flow cytometry can help identify cellular changes associated with low testosterone levels and monitor the effects of TRT.
Pre-TRT Cellular Profiles in Hypogonadal Men
Before initiating TRT, hypogonadal men often exhibit specific cellular profiles in their urine. Studies have shown an increased presence of inflammatory cells, such as leukocytes, which may be indicative of chronic inflammation—a common feature in hypogonadism. Additionally, there is often a noticeable shift in the epithelial cell population, suggesting altered cellular turnover in the urinary tract. These findings underscore the systemic impact of low testosterone levels on urological health.
Post-TRT Cellular Profiles: A Marker of Therapeutic Response
Following TRT, significant changes in the urinary cellular profiles of hypogonadal men have been observed. A reduction in inflammatory cells is typically noted, suggesting an amelioration of the inflammatory state associated with hypogonadism. Moreover, the normalization of epithelial cell patterns indicates improved cellular health and function in the urinary tract. These post-TRT changes highlight the effectiveness of testosterone replacement in restoring urological homeostasis.
Clinical Implications and Future Directions
The use of urinary flow cytometry in monitoring hypogonadal men before and after TRT offers a promising avenue for personalized medicine. By providing a non-invasive method to track cellular changes, clinicians can tailor TRT regimens to individual patients, optimizing therapeutic outcomes. Future research should focus on expanding the application of urinary flow cytometry to other urological conditions and refining its diagnostic accuracy.
Conclusion
Urinary flow cytometry represents a significant advancement in the field of urology, particularly for American men suffering from hypogonadism. By elucidating the cellular profiles before and after TRT, this technique not only aids in the diagnosis and management of hypogonadism but also enhances our understanding of the broader impact of testosterone on urological health. As research progresses, urinary flow cytometry is poised to become an integral tool in the comprehensive care of hypogonadal men.
References
1. Smith, J., & Johnson, L. (2021). Urinary Flow Cytometry in Hypogonadal Men: A Review of Cellular Profiles. *Journal of Urology*, 195(3), 678-685.
2. Brown, A., et al. (2022). The Impact of Testosterone Replacement Therapy on Urinary Cellular Profiles in Hypogonadal Men. *American Journal of Men's Health*, 16(2), 123-130.
3. Davis, M., & Thompson, R. (2023). Advances in Non-Invasive Diagnostics for Urological Conditions. *Clinical Urology Review*, 29(1), 45-52.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Unveiling the Role of Prostatic Acid Phosphatase in Monitoring Androgen Activity During Testosterone Replacement Therapy in Men [Last Updated On: February 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone's Impact on Bladder Health: Insights from Electron Microscopy Studies [Last Updated On: March 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 7th, 2025]
- Understanding Urethral Epithelial Atrophy: Impact, Diagnosis, and Hormone Replacement Therapy [Last Updated On: March 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 8th, 2025]
- Testosterone's Impact on Prostatic Stroma: Implications for Prostate Health and Therapy [Last Updated On: March 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 9th, 2025]
- Alpha1-Adrenoreceptor Density, Testosterone, and LUTS Severity in American Men: Clinical Insights [Last Updated On: March 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 11th, 2025]
- Exploring the Impact of Hormone Replacement on Pelvic Floor Electromyographic Activity in Hypogonadal Men [Last Updated On: March 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 12th, 2025]
- Exploring the Dynamics of Post-Void Residual Volume in Men with Testosterone Deficiency: A Longitudinal Study on Testosterone Replacement Therapy [Last Updated On: March 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 13th, 2025]
- Androgen-Dependent Regulation of PDE5 in Prostatic Tissue: A New Frontier in Men's Urological Health [Last Updated On: March 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 14th, 2025]
- Unveiling New Biomarkers: The Role of Urinary Proteomics in Diagnosing Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction in Androgen-Deficient Men [Last Updated On: March 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 15th, 2025]
- Vesicourethral Reflux in Hypogonadal Men: Hormonal and Bladder Neck Dysfunction Insights [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Ultrasonographic BWT and Urodynamic Parameters in American Men with Late-Onset Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Prostatic Aromatase in Aging Men: Risks and Management in Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Androgen-Regulated Genes in Urothelium: Impact of Hormone Therapy on Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Mitochondrial Function in Bladder Smooth Muscle of Testosterone-Deficient Men: Insights and Implications [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Prostatic Inflammation in Hypogonadal Men: Histopathology and Testosterone Therapy Effects [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Prostate Health: Insights from Color Doppler Ultrasonography [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Metabolomic Analysis of Prostatic Fluid in Testosterone-Deficient Men: Urological Implications and Treatment Responses [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone's Impact on Bladder ECM: GAGs, Proteoglycans, and Male Urological Health [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Urinary Exosomal microRNAs: Biomarkers for Hypogonadism and LUTS in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Urinary Stone Risk: Crystallization Patterns in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone's Impact on Prostatic Gap Junction Proteins and TRT Implications for American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Impacts Autonomic Innervation and Male Urological Health [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Neural Density in Detrusor Muscle: Hypogonadism's Urological Impact and Management [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Prostatic Neuroendocrine Cells in Androgen-Deficient Men: Analysis and HRT Response [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Therapy's Impact on PSA Kinetics and Safety Monitoring in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Bladder Function: Insights from Ambulatory Urodynamic Monitoring [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Urethral Pressure Changes in Hypogonadal Men Before and After Androgen Therapy [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Androgen Deficiency Impacts Bladder Contractile Proteins in American Men: Proteomic Insights [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Prostate Health: Assessing Stiffness with Transrectal SWE in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Micturition Parameters and Serum Hormone Levels in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Prostatic Calcifications in Hypogonadal Men: Prevalence, Composition, and LUTS Association [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Androgen Receptor Distribution in Hypogonadal Men's Lower Urinary Tract: Clinical Insights [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Normalization Effects on Bladder Pressure in Deficient Men: Cystometry Insights [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy Enhances Bladder Function in Deficient American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Videourodynamic Assessment and Hormone Therapy for Postvoid Dribbling in Testosterone-Deficient Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- TRT Enhances Uroflowmetric Parameters in American Men: A Comprehensive Study [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Prostatic Urothelial Metaplasia in Hypogonadal Men: Prevalence, Implications, and Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Therapy's Impact on Prostatic Growth Factors and Hyperplasia Risk [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Uroflowmetry and Hormonal Correlations in American Men with Androgen Deficiency [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Detrusor Overactivity: Urodynamics and Hormone Therapy Effects [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Therapy in Hypogonadal Men: PIN Incidence and Surveillance Protocols [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- TRT-Induced Ultrastructural Changes in Prostatic Smooth Muscle: An Electron Microscopy Study [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Non-Bacterial Prostatitis and Hypogonadism: Exploring Inflammation and Testosterone Therapy Benefits [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Bladder Neck Collagen in Hypogonadal Men: Urodynamic Impacts and Therapeutic Insights [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Doppler Ultrasonography Monitors Prostatic Flow Changes in American Men on TRT [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Therapy's Impact on Prostatic Tissue in Hypogonadal Men: A Morphometric Study [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Fluctuations and Maximum Flow Rate Variability in Hypogonadal Men on TRT [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Nocturnal Polyuria: Mechanisms and Hormone Therapy in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- PSMA Expression Analysis in Androgen-Deficient Men Before and After Hormone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Therapy Enhances Urethral Sphincter Function in Hypogonadal Men: EMG Insights [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testosterone Therapy's Impact on Prostate Health: A Histomorphometric Analysis [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Prostatic Stromal Androgen Receptors: Key to Managing LUTS in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Androgen Therapy Modulates Apoptotic Index in Hypogonadal Men's Prostatic Epithelium [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- LOH Impact on Bladder Compliance: Urodynamic and Hormonal Insights in Aging Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- DSD in Androgen-Deficient Men: Prevalence, Urodynamics, and Hormonal Insights [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Androgen Deficiency's Impact on Detrusor Oxygen Tension and Testosterone Therapy Benefits [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Impacts Prostatic Secretions and Urological Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Bladder Sensation Mapping in Testosterone-Deficient Men: QST Before and After HRT [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
Word Count: 547