Introduction to Hypopituitarism
Hypopituitarism is a medical condition characterized by the diminished production of one or more of the hormones secreted by the pituitary gland. This gland, often referred to as the "master gland," plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions through its hormonal secretions. When these hormones are deficient, a cascade of health issues can ensue, affecting not only the immediate hormonal targets but also distant systems such as the cardiovascular system.
The Cardiovascular System and Hormonal Influence
The cardiovascular system, responsible for the circulation of blood and the delivery of nutrients and oxygen to tissues, is intricately linked to the endocrine system. Hormones such as growth hormone (GH), adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), all produced by the pituitary gland, have direct and indirect effects on heart function and vascular health. For instance, GH influences cardiac muscle mass and function, while ACTH affects blood pressure regulation through its impact on cortisol production.
Hypopituitarism's Impact on Cardiovascular Health
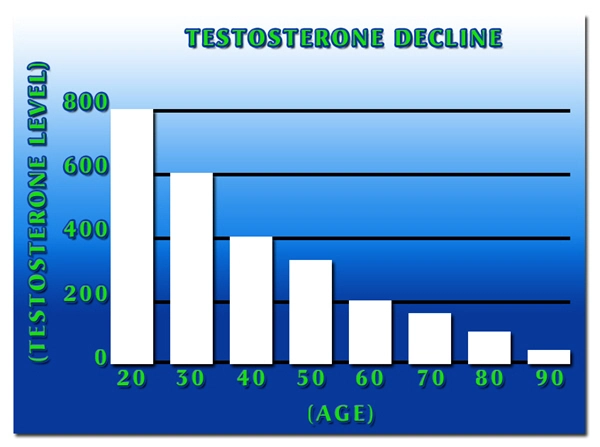
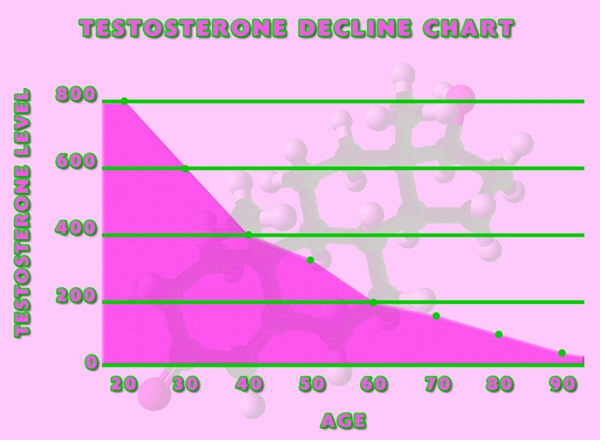
In American males, hypopituitarism can manifest in several ways that compromise cardiovascular health. A deficiency in GH, for example, has been associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease due to changes in body composition, lipid profiles, and insulin sensitivity. Similarly, a lack of ACTH can lead to hypotension and an inability to respond adequately to stress, both of which can precipitate cardiovascular events.
Research Findings and Clinical Observations
Recent studies have begun to shed light on the specific cardiovascular risks associated with hypopituitarism. Research published in the *Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism* indicates that men with hypopituitarism have a higher prevalence of atherosclerosis, a condition that significantly increases the risk of heart attacks and strokes. Moreover, clinical observations suggest that these individuals often present with altered lipid profiles, characterized by elevated levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and decreased levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, further exacerbating their cardiovascular risk.
Management and Treatment Strategies
Effective management of hypopituitarism in American males necessitates a multifaceted approach that addresses both the hormonal deficiencies and the resultant cardiovascular risks. Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is a cornerstone of treatment, aimed at restoring hormonal balance and mitigating the associated health risks. For instance, GH replacement therapy has been shown to improve cardiovascular risk factors such as insulin resistance and lipid profiles.
In addition to HRT, lifestyle modifications play a critical role in managing cardiovascular health in men with hypopituitarism. Regular physical activity, a heart-healthy diet, and smoking cessation are all essential components of a comprehensive management plan. Furthermore, regular monitoring of cardiovascular health through blood pressure checks, lipid panels, and electrocardiograms can help in the early detection and management of cardiovascular complications.
Conclusion and Future Directions
The connection between hypopituitarism and cardiovascular health in American males is a complex and evolving field of study. As research continues to unravel the intricate interplay between hormonal deficiencies and cardiovascular disease, it is imperative that healthcare providers remain vigilant in screening and managing these patients. Future studies may focus on the long-term outcomes of HRT and the potential benefits of novel therapeutic approaches, ultimately aiming to improve the quality of life and longevity of men living with hypopituitarism.
In conclusion, hypopituitarism presents a significant challenge to cardiovascular health in American males. Through a combination of hormone replacement therapy, lifestyle modifications, and vigilant monitoring, it is possible to mitigate the risks and enhance the well-being of those affected by this condition.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- What is Hypopituitarism [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 18th, 2021]
- Is There Such a Thing as Too Much HGH? [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: August 22nd, 2023]
- Hypopituitarism in American Men: Impacts and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 10th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Metabolic Syndrome: Unraveling the Connection in American Males [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Unveiling the Cardiovascular Risks: The Link Between Hypopituitarism and Heart Disease in American Males [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Unraveling the Connection: Hypopituitarism and Uterine Fibroids in American Males [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Exploring Hypopituitarism's Impact on Vaginal Health and the Female Reproductive System [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Unraveling the Hormonal Link: Hypopituitarism and Breast Cancer in American Males [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Autoimmune Disorders: Critical Insights for American Males [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Obesity in American Males: Hormonal Impacts and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism in American Males: Hormonal Imbalances and Sleep Disorder Connections [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Surgical Interventions for Hypopituitarism and Pituitary Tumors in American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Mental Health in American Males: Depression, Anxiety, and Treatment [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Multidisciplinary Care Essential for Managing Hypopituitarism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism in American Males: Cancer Risks and Monitoring Strategies [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Anemia in American Males: The Critical Role of EPO Deficiency [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Male Hair Loss: Hormonal Mechanisms and Treatment Strategies [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Kidney Function in American Males: Monitoring and Management [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Immune Function in American Men: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Management [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism in American Males: Cognitive Impacts and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism in American Males: Impact on Eye Health and Visual Impairments [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism in Aging American Males: Impact, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Liver Health in American Males: Hormonal Deficiencies and Management [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Joint Health in American Males: Diagnosis and Management [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on GI Health in American Males: Digestion and Nutrient Absorption [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Skin Health in American Males: Symptoms and Management [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Seizure Disorders in American Males: Clinical Insights and Management [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Migraines: Hormonal Links and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Hypertension: Impact on Blood Pressure in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Link to Gout and Uric Acid in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Muscle Strength in American Males: Management and Insights [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Autoimmune Link: Hypopituitarism and Rheumatoid Arthritis in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Exploring the Link Between Hypopituitarism and MS in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Autoimmune Link Between Hypopituitarism and Celiac Disease in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Diabetes: Impact on Glucose Metabolism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Kidney Health in American Males: Monitoring and Management [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Hearing Loss: Exploring Links and Implications for American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism in American Males: Cardiovascular Risks and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Asthma in American Males: Hormonal Insights and Management [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Allergies: Hormonal Impacts on Immune Response in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Role in Accelerating Parkinson's Disease in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Liver Cirrhosis: Impacts and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and CFS Overlap in American Males: Symptoms, Mechanisms, and Clinical Insights [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Fibromyalgia: Overlapping Symptoms and Impact on American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism, Hormonal Imbalances, and Alzheimer's Risk in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Sjögren's Syndrome: Effects on Exocrine Glands in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Dyslipidemia: Impacts on American Males' Health and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Prostate Cancer in American Males: Diagnosis and Management [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Exploring the Link Between Hypopituitarism and Lupus in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Pituitary Cancer: Early Detection and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism in American Males: Monitoring Hormones to Reduce Stroke Risk [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and IBD: Gastrointestinal Links and Impacts on American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Adrenal Cancer: Endocrine Links in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Osteoarthritis: Impact on Joint Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Gallbladder Disease: Exploring Links in American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Pancreatitis: Risks and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Breast Cancer Link in American Males: Hormonal Insights and Clinical Implications [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Hormonal Imbalances in Hypopituitarism and Thyroid Cancer: Impacts on American Males [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Testicular Cancer: Impacts and Fertility Preservation Strategies [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Ovarian Cancer: Exploring Hormonal Links in American Males [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism in American Males: Hormonal Imbalances and Benign Tumor Risks [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and PCOS: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Hormonal Links Between Hypopituitarism and Endometriosis in American Males Explored [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Erectile Dysfunction: Hormonal Links and Holistic Management in American Males [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism: Effects on Male Reproductive and Penile Health [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism, Hormonal Imbalance, and Cervical Cancer Risk in Men [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Female Reproductive and Vaginal Health: Diagnosis and Management [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Premature Ejaculation: Exploring Hormonal Links in American Males [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Miscarriage Risk and Male Fertility in America [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Preeclampsia in Pregnancy: Monitoring and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Ectopic Pregnancy: Impacts and Management in Women's Health [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Male Infertility: Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism and Gestational Diabetes: Metabolic Links in American Males [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Lactation: Support Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Hypopituitarism's Impact on Mental Health and Postpartum Depression in American Males [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
Word Count: 565