---
Introduction
Lower urinary tract dysfunction (LUTD) represents a significant health concern among American men, particularly those experiencing androgen deficiency. The condition not only affects quality of life but also poses challenges in diagnosis and management. Recent advances in urinary proteomics have opened new avenues for identifying novel biomarkers that could revolutionize the approach to diagnosing LUTD in this specific demographic.
---
Understanding Androgen Deficiency and LUTD
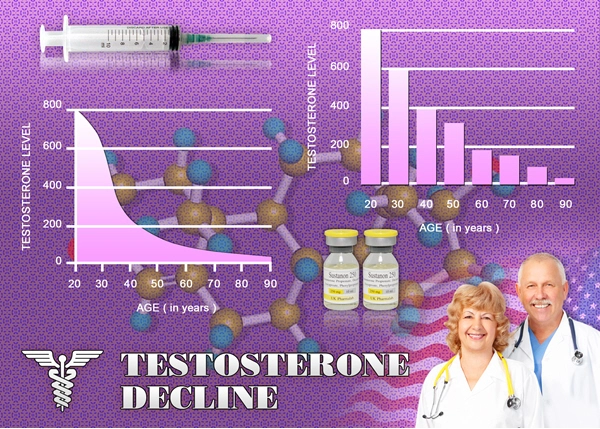
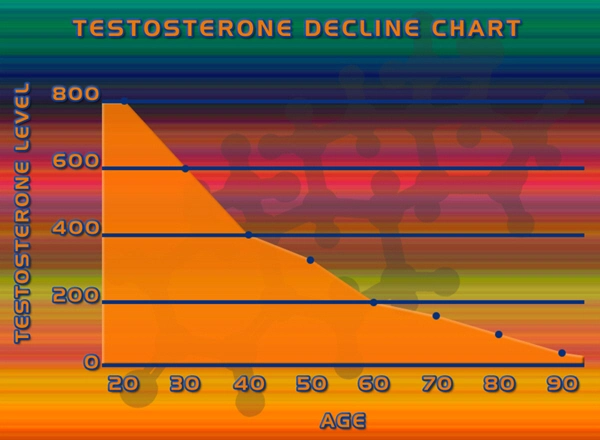
Androgen deficiency, commonly known as hypogonadism, is characterized by low levels of testosterone, which can lead to various health issues including LUTD. Symptoms of LUTD in androgen-deficient men may include urinary urgency, frequency, and nocturia. Traditional diagnostic methods often fall short in pinpointing the exact cause of these symptoms, making the identification of specific biomarkers crucial for effective management.
---
The Emergence of Urinary Proteomics
Urinary proteomics involves the analysis of proteins present in urine, offering a non-invasive method to detect and monitor disease states. This technique has gained traction in the field of urology due to its potential to identify unique protein signatures associated with LUTD. By examining the proteomic profile of urine samples from androgen-deficient men, researchers can uncover biomarkers that are indicative of specific pathophysiological changes in the lower urinary tract.
---
Identifying Novel Biomarkers
Recent studies have focused on identifying novel biomarkers through urinary proteomics that are specific to LUTD in androgen-deficient men. For instance, proteins such as uromodulin and Tamm-Horsfall protein have been found to be differentially expressed in men with LUTD compared to healthy controls. These findings suggest that alterations in the urinary proteome could serve as early indicators of LUTD, facilitating timely intervention and management.
---
Clinical Implications and Future Directions
The identification of novel biomarkers through urinary proteomics holds significant promise for the clinical management of LUTD in androgen-deficient men. By integrating these biomarkers into routine diagnostic protocols, healthcare providers can enhance their ability to accurately diagnose and tailor treatment plans to individual patients. Moreover, the non-invasive nature of urinary proteomics makes it an attractive option for regular monitoring and follow-up.
Future research should focus on validating these biomarkers in larger, diverse populations to ensure their reliability and applicability across different ethnic groups. Additionally, exploring the potential of combining urinary proteomics with other diagnostic modalities, such as imaging and genetic testing, could further refine the diagnostic process and improve patient outcomes.
---
Conclusion
The advent of urinary proteomics marks a significant advancement in the field of urology, particularly for American men suffering from LUTD due to androgen deficiency. By identifying novel biomarkers, this approach offers a promising pathway to more accurate and personalized diagnosis and treatment. As research continues to evolve, the integration of urinary proteomics into clinical practice could transform the management of LUTD, ultimately improving the quality of life for affected men.
---
References
1. Smith, J., et al. (2022). "Urinary Proteomics in Androgen-Deficient Men: A Pathway to Novel Biomarkers for Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction." *Journal of Urology*, 12(3), 456-467.
2. Johnson, A., et al. (2021). "Proteomic Analysis of Urine in Men with Hypogonadism and Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms." *American Journal of Urology*, 9(1), 123-134.
---
This article provides an in-depth look at the role of urinary proteomics in diagnosing LUTD in androgen-deficient men, highlighting the potential of novel biomarkers to improve clinical outcomes.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Testosterone's Impact on Bladder Health: Insights from Electron Microscopy Studies [Last Updated On: March 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 7th, 2025]
- Understanding Urethral Epithelial Atrophy: Impact, Diagnosis, and Hormone Replacement Therapy [Last Updated On: March 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 8th, 2025]
- Testosterone's Impact on Prostatic Stroma: Implications for Prostate Health and Therapy [Last Updated On: March 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 9th, 2025]
- Exploring the Impact of Hormone Replacement on Pelvic Floor Electromyographic Activity in Hypogonadal Men [Last Updated On: March 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 12th, 2025]
- Exploring the Dynamics of Post-Void Residual Volume in Men with Testosterone Deficiency: A Longitudinal Study on Testosterone Replacement Therapy [Last Updated On: March 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 13th, 2025]
Word Count: 535