Introduction to Urethral Health Challenges
Urethral epithelial atrophy is a lesser-known but significant medical condition that affects a subset of the male population, particularly those experiencing androgen deficiency. Androgens, including testosterone, play a crucial role in maintaining the structure and function of the urethral epithelium, the inner lining of the urethra. Deficiency in these hormones can lead to various urological health issues, including atrophy of the urethral lining.
The Impact of Androgen Deficiency
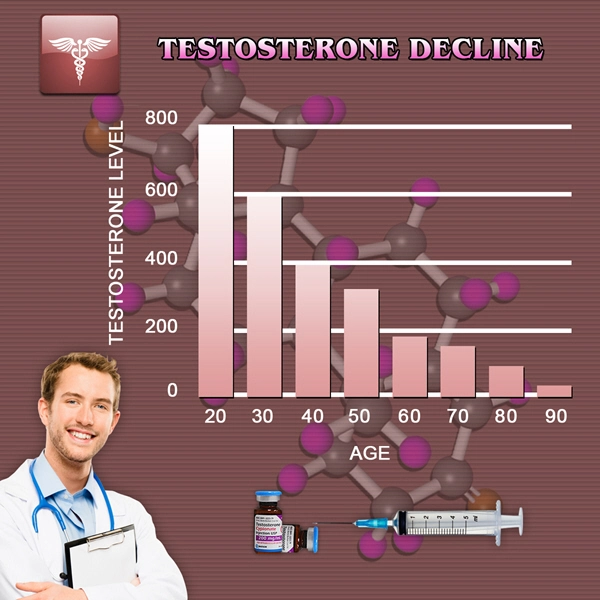
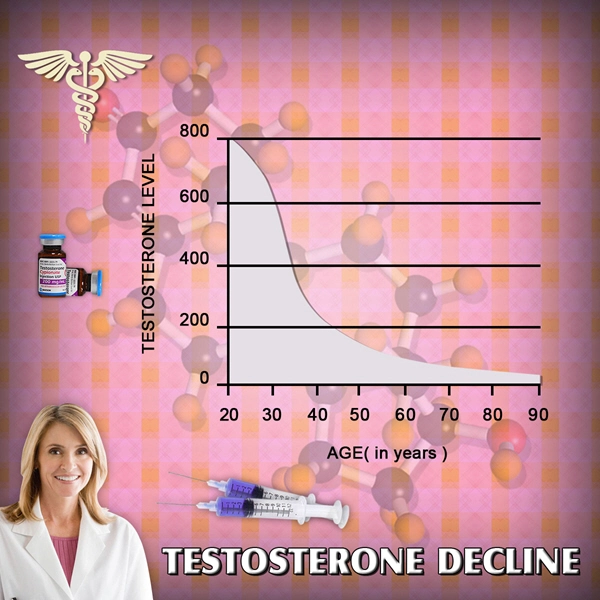
Androgen deficiency in men, often resulting from hypogonadism or hormonal therapy for prostate cancer, can lead to a range of symptoms from reduced muscle mass and energy levels to more specific complications such as urethral epithelial atrophy. This condition is characterized by the thinning of the urethral lining, which can lead to discomfort, increased susceptibility to infections, and problems with urinary function.
Histopathological Insights
Histopathological assessment, the microscopic examination of tissue to study the manifestations of disease, plays a pivotal role in diagnosing urethral epithelial atrophy. Tissue samples, typically obtained through a biopsy, are examined for signs of thinning epithelium and other cellular changes indicative of atrophy. This method provides a definitive diagnosis and helps in understanding the extent of tissue damage.
Treatment Responses to Hormone Replacement Therapy
One of the primary treatments for androgen deficiency and its complications, including urethral atrophy, is hormone replacement therapy (HRT). This treatment involves supplementing the body with external hormones, predominantly testosterone, to restore hormonal levels to a more normal range.
Clinical studies have shown that hormone replacement can significantly mitigate the symptoms of androgen deficiency and can lead to the regeneration of the urethral epithelium. Men undergoing HRT often report improvements in urinary function and a decrease in discomfort, highlighting the effectiveness of this approach in managing urethral epithelial atrophy.
Clinical Implications and Future Directions
For healthcare providers, recognizing the signs of androgen deficiency and its potential impact on urethral health is crucial. Early diagnosis and treatment are key in preventing the progression of urethral epithelial atrophy and in maintaining overall urological health.
Future research should aim to further elucidate the mechanisms by which androgen levels influence urethral epithelial health and to optimize hormone replacement therapies to minimize side effects while maximizing benefits. Additionally, exploring alternative therapeutic options that can complement or substitute hormone therapy could be beneficial for patients who are unable or unwilling to undergo HRT.
Conclusion
Urethral epithelial atrophy in androgen-deficient men is a condition that, although underrecognized, can significantly affect a patient’s quality of life. Through proper histopathological assessment and the judicious use of hormone replacement therapy, men suffering from this condition can achieve substantial relief from symptoms and improvements in urinary function. As research advances, the hope is to develop more tailored and effective treatments to address this and other androgen-related conditions, enhancing the health and well-being of affected individuals.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Testosterone's Impact on Bladder Health: Insights from Electron Microscopy Studies [Last Updated On: March 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 7th, 2025]
- Testosterone's Impact on Prostatic Stroma: Implications for Prostate Health and Therapy [Last Updated On: March 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 9th, 2025]
Word Count: 466