Introduction to Testosterone Enanthate Therapy
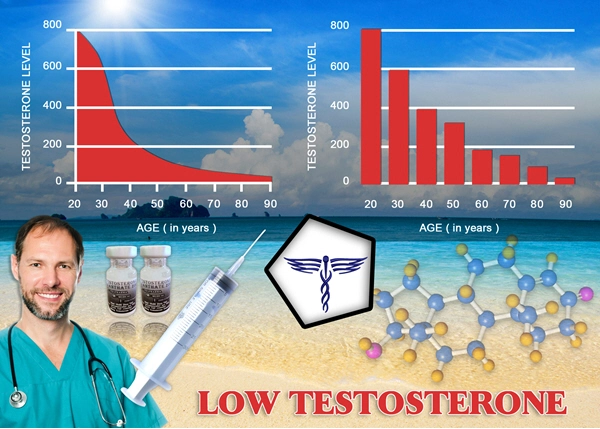
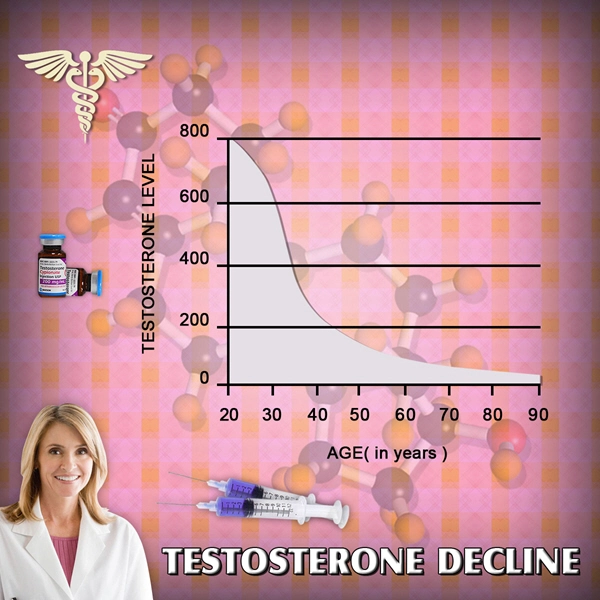
Testosterone Enanthate is a widely used form of testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) among American men suffering from hypogonadism, a condition characterized by low testosterone levels. This therapy is administered through intramuscular injections, typically on a weekly or bi-weekly basis, to restore testosterone levels to a normal range. While TRT can significantly improve symptoms such as decreased libido, fatigue, and mood disturbances, it is crucial to understand its impact on the male reproductive system.
Impact on Spermatogenesis
One of the primary concerns associated with Testosterone Enanthate therapy is its potential to suppress spermatogenesis, the process of sperm production. The exogenous administration of testosterone can lead to a negative feedback loop on the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis. This feedback results in decreased production of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), which are essential for spermatogenesis. Studies have shown that up to 90% of men on TRT may experience some degree of spermatogenic suppression, which can lead to reduced fertility.
Effects on Testicular Size and Function
Alongside the impact on sperm production, Testosterone Enanthate therapy can also affect testicular size and function. Prolonged use of TRT can lead to testicular atrophy, a condition where the testes shrink due to reduced stimulation from LH and FSH. This atrophy can further exacerbate fertility issues and may require additional interventions to restore testicular function. It is essential for men considering or undergoing TRT to be aware of these potential changes and discuss them with their healthcare provider.
Hormonal Imbalances and Their Consequences
The use of Testosterone Enanthate can lead to various hormonal imbalances beyond the suppression of LH and FSH. Elevated testosterone levels can convert to estradiol, a form of estrogen, through the process of aromatization. This conversion can result in symptoms such as gynecomastia (enlarged breast tissue in men) and may necessitate the use of aromatase inhibitors to manage estrogen levels. Additionally, the suppression of natural testosterone production can lead to a dependency on exogenous testosterone, making it challenging to discontinue therapy without experiencing withdrawal symptoms.
Managing Reproductive Health During TRT
To mitigate the impact of Testosterone Enanthate on reproductive health, several strategies can be employed. One approach is the use of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), which mimics the action of LH and can help maintain spermatogenesis and testicular function. Another strategy involves the use of selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) to counteract the effects of increased estrogen levels. Regular monitoring of hormone levels and fertility markers is also crucial to ensure that any adverse effects are identified and managed promptly.
Conclusion and Recommendations
Testosterone Enanthate therapy offers significant benefits for American men with hypogonadism, but it is not without its challenges, particularly concerning reproductive health. Men considering or currently undergoing TRT should have open discussions with their healthcare providers about the potential risks and management strategies. By staying informed and proactive, men can navigate the complexities of TRT while safeguarding their reproductive health.
In summary, while Testosterone Enanthate therapy can be a vital tool in managing low testosterone levels, it is essential to weigh its benefits against the potential impact on fertility and testicular function. With the right approach and medical guidance, men can achieve a balance that supports both their overall well-being and reproductive health.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Athletic Performance and Associated Risks in the US [Last Updated On: February 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 18th, 2025]
- Long-Term Health Risks of Testosterone Enanthate Use in American Men [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Benefits, Risks, and Management for Low Testosterone Treatment [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Sleep Quality in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Treatment for Sexual Dysfunction in American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Dispelling Myths and Understanding Facts for American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Muscle, Reducing Fat for Weight Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Treatment for Depression in American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Cognitive Function in Aging American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Benefits, Prostate Risks, and Monitoring for American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Therapy for Chronic Pain in American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Cycle: Enhancing Performance and Managing Risks in Athletes [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Treatment for Osteoporosis in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Therapy: Personalization, Monitoring, and Lifestyle Integration for American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Blood Sugar Levels in American Men: A Review [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Withdrawal: Symptoms and Management Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Male Fertility: Insights for American Patients [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Therapy for Obesity in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Ethical Dilemmas of Testosterone Enanthate Use Among American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Therapy: Enhancing Veteran Health and Vitality [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Effects on Hair Growth and Loss in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Mental Clarity in American Males: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Appetite and Digestion in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Emotional Well-being in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Potential New Treatment for Allergies in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Injury Recovery in American Male Athletes [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Impacts on Joint Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Treatment for Anemia in Hypogonadal American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Immune Function in American Men - Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Cardiovascular Endurance in American Men: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Cultural Perceptions and Masculinity in American Society [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Combating Age-Related Decline in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Solution for Muscle Wasting in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Therapy: Benefits, Process, and Risks for Men Over 50 [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Stress Management Tool for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Boosts Skin Elasticity in American Males: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Potential Treatment for Chronic Fatigue Syndrome in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Endurance in American Male Athletes - Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Therapy: Benefits, Limitations, and Management for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Muscle, Reducing Fat, Boosting Performance in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Dental Health in American Males: Risks and Recommendations [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Vision and Eye Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Benefits, Costs, and Risks for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Optimizing Testosterone Enanthate Therapy: Dosage, Monitoring, and Lifestyle for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Therapy: Impacts on Life Expectancy and Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Post-Surgical Recovery in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Respiratory Function in American Men [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Treatment for Autoimmune Disorders in American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Role in Managing Diabetes in American Men: Benefits and Considerations [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Therapy: Kidney Function Impact in American Males [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Hearing Health in American Men: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Liver Health in American Men: Risks and Monitoring [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Therapy for Hypertension in American Males [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Impacts on Male Reproductive Health and Fertility in America [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Potential Treatment for Gastrointestinal Disorders in American Males [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Neurological Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Adrenal Health in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Enhancing Muscle and Bone Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Thyroid Function in American Men: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Benefits, Risks, and Endocrine Impact in American Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Immune Function in American Males: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Therapy for Respiratory Disorders in American Men [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Gastrointestinal Health in American Males [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Cardiovascular Health in American Males: Risks and Benefits [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Emerging Role in Dermatology for American Men: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate Boosts Hematological Health in American Men: Benefits and Monitoring [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Therapy for Metabolic Disorders in American Males [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: A Promising Therapy for Neurological Disorders in American Males [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate's Impact on Respiratory Health in American Males: An Analysis [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Testosterone Enanthate: Potential Benefits for Musculoskeletal Disorders in American Men [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
Word Count: 535