Introduction to Secondary Hypogonadism
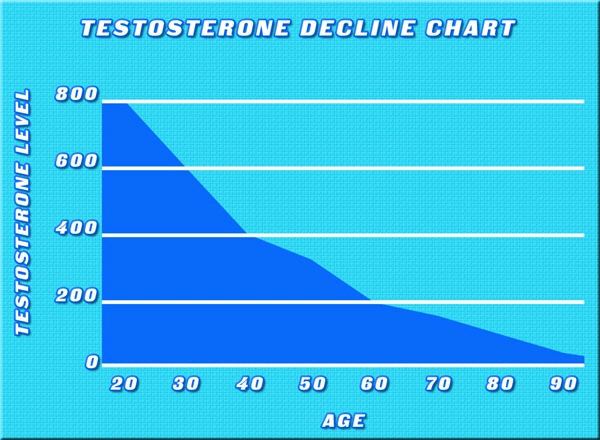
Secondary hypogonadism, also known as hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, is a condition in which the body does not produce enough testosterone due to a problem with the pituitary gland or hypothalamus. These glands are responsible for signaling the testes to produce testosterone, a crucial hormone for male health. When these signals are disrupted, it can lead to a variety of symptoms, including reduced libido, fatigue, and muscle loss. For American males, understanding this condition is essential, particularly in relation to another common concern: hair loss.
The Link Between Secondary Hypogonadism and Hair Loss
Hair loss, or androgenetic alopecia, is a prevalent issue among American men, affecting approximately 50% of men by the age of 50. While genetics play a significant role, hormonal imbalances, such as those caused by secondary hypogonadism, can exacerbate this condition. Testosterone is converted into dihydrotestosterone (DHT) by the enzyme 5-alpha reductase. DHT is a more potent androgen that can shrink hair follicles, leading to hair thinning and eventual baldness. In cases of secondary hypogonadism, the body may attempt to compensate for low testosterone levels by increasing the conversion to DHT, thereby accelerating hair loss.
Diagnosing Secondary Hypogonadism
Diagnosing secondary hypogonadism involves a comprehensive evaluation of symptoms and hormone levels. American males experiencing hair loss alongside symptoms such as decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, and fatigue should consult a healthcare provider. Blood tests measuring testosterone, luteinizing hormone (LH), and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) levels can help confirm the diagnosis. Low testosterone levels accompanied by low or normal LH and FSH levels are indicative of secondary hypogonadism.
Treatment Options for Secondary Hypogonadism
Treatment for secondary hypogonadism typically focuses on restoring testosterone levels to normal. Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is a common approach, involving the administration of testosterone through injections, gels, or patches. This can help alleviate symptoms and potentially slow down hair loss. However, it is crucial for American males to work closely with their healthcare providers to monitor hormone levels and adjust treatment as necessary.
Managing Hair Loss Associated with Secondary Hypogonadism
While HRT can help manage the underlying hormonal imbalance, additional treatments may be necessary to address hair loss directly. Medications such as finasteride and minoxidil are commonly used to treat androgenetic alopecia. Finasteride works by inhibiting the conversion of testosterone to DHT, while minoxidil is thought to prolong the growth phase of hair follicles. In some cases, hair transplant surgery may be considered for those seeking a more permanent solution.
Lifestyle Factors and Prevention
In addition to medical treatments, American males can take proactive steps to manage secondary hypogonadism and hair loss. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and adequate sleep, can support overall hormonal health. Stress management is also crucial, as chronic stress can exacerbate hormonal imbalances and contribute to hair loss. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help monitor hormone levels and catch any issues early.
Conclusion
Secondary hypogonadism is a condition that can significantly impact the quality of life for American males, particularly in relation to hair loss. Understanding the link between these two issues is crucial for effective management and treatment. By working closely with healthcare providers and adopting a holistic approach to health, men can address the symptoms of secondary hypogonadism and mitigate the effects of hair loss. Awareness and proactive management are key to maintaining both physical and emotional well-being.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Cardiovascular Health and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: February 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: Importance of Regular Check-ups for Early Detection and Management [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Genetic Insights into Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Diagnosis and Treatment [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Exercise Regimens for Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Sleep: Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Stress-Induced Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Energy and Treatment Options in American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Body Composition in American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Comprehensive Support for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Mental Health and Treatment Approaches in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Cognitive Function in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Understanding Impacts and Managing Prostate Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Testing, and Treatment for American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Immune System and Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Mood Disorders: Impact and Clinical Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Diabetes: Prevalence, Link, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Exploring Alternative Therapies for Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Anemia: Causes, Symptoms, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Fat Distribution in American Men: Risks and Management [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Kidney Function in American Males: Symptoms, Treatment, and Management [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Causes, and Management Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Support [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Skin Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Nutrition's Role in Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Key Nutrients and Dietary Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Understanding Its Profound Social Impact on American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Bone Density in American Men: Diagnosis and Management [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Environmental Factors and Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: Impacts and Interventions [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Lifestyle Impact on Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Prevention and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Fatigue: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Thyroid Function's Impact on Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Diagnosis and Management [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Libido and Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Sleep Disorders and Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Health and Treatment Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Cognitive Function in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts, Mental Health Needs, and Integrated Care Solutions for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Psychological Impact on American Men: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Stress, Strategies, and Support for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Autoimmune Diseases: A Rising Concern in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Exercise Boosts Testosterone and Alleviates Secondary Hypogonadism Symptoms in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Emotional Well-being in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Liver Health: Impacts and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Physical Performance and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Cardiovascular Risks in American Males: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Muscle Strength in American Men: Diagnosis and Treatment [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Symptoms, Monitoring, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Comprehensive Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
Word Count: 554