Introduction
Primary hypogonadism, a condition characterized by the inadequate production of testosterone and sperm due to testicular dysfunction, presents significant challenges to male reproductive health. In the United States, this condition affects a notable portion of the male population, leading to concerns over fertility and overall well-being. This article delves into the clinical outcomes and treatment options for American males grappling with primary hypogonadism, aiming to enhance understanding and guide effective management strategies.
Understanding Primary Hypogonadism
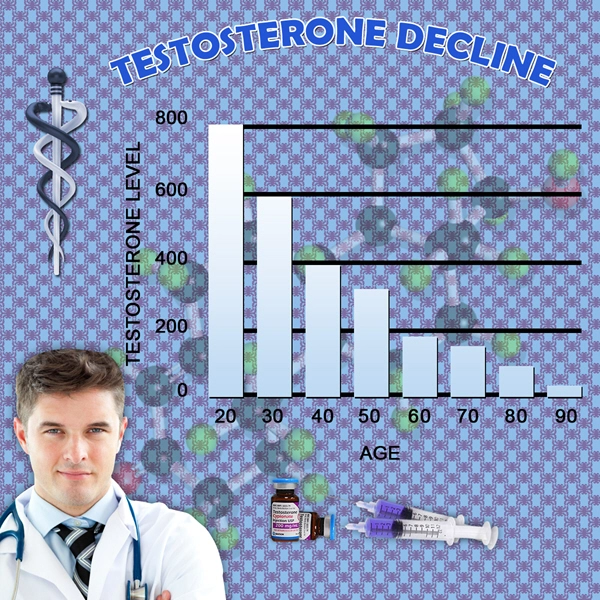
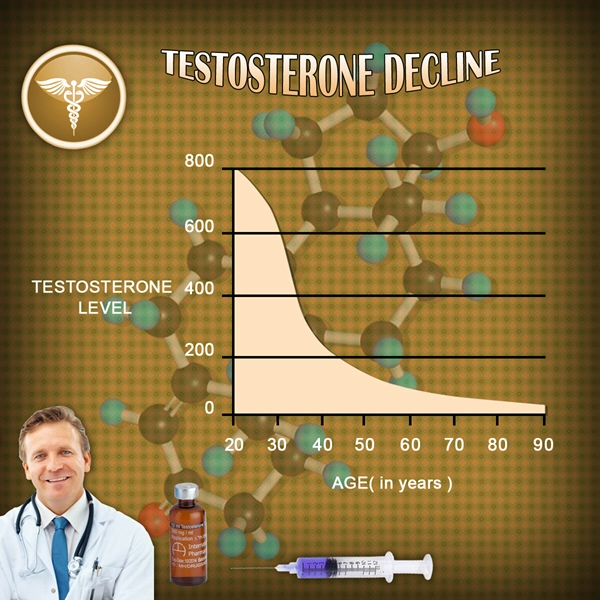
Primary hypogonadism, also known as hypergonadotropic hypogonadism, arises from intrinsic testicular failure. This can be attributed to various causes, including genetic disorders like Klinefelter syndrome, testicular injury, or infections such as mumps orchitis. The resultant low levels of testosterone and impaired spermatogenesis not only affect fertility but also contribute to a range of symptoms such as decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, and reduced muscle mass.
Clinical Outcomes and Fertility Implications
The clinical manifestations of primary hypogonadism in American males are multifaceted. Infertility is a primary concern, with affected individuals often facing challenges in achieving conception due to low sperm count or azoospermia. Beyond fertility, patients may experience psychological effects such as depression and anxiety, further compounded by physical symptoms like fatigue and osteoporosis due to low testosterone levels.
In the context of fertility, the impact of primary hypogonadism is profound. Studies have shown that men with this condition have a significantly reduced chance of natural conception. The emotional toll of infertility can be substantial, necessitating a holistic approach to patient care that addresses both the physical and psychological aspects of the condition.
Diagnostic Approaches
Diagnosing primary hypogonadism involves a thorough evaluation of clinical symptoms, hormonal assays, and genetic testing where applicable. Serum testosterone levels, along with follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) levels, are critical in confirming the diagnosis. Elevated FSH and LH levels in the presence of low testosterone are indicative of primary testicular failure.
Treatment Modalities and Their Efficacy
The management of primary hypogonadism focuses on two main objectives: restoring testosterone levels and addressing fertility issues. Testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) is a cornerstone of treatment, effectively alleviating symptoms related to low testosterone. However, TRT does not improve fertility and may, in fact, suppress spermatogenesis further.
For men desiring fertility, alternative treatments such as gonadotropin therapy are employed. Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) and recombinant FSH have been used to stimulate spermatogenesis, with varying degrees of success. Clinical trials have demonstrated that a significant proportion of men with primary hypogonadism can achieve improved sperm counts and, subsequently, successful conception with these treatments.
Innovative Approaches and Future Directions
Recent advancements in reproductive medicine offer hope for more effective treatments. Techniques such as testicular sperm extraction (TESE) combined with intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) have revolutionized fertility outcomes for men with severe sperm production issues. Additionally, ongoing research into stem cell therapy and gene editing holds promise for future therapeutic interventions.
Conclusion
Primary hypogonadism poses significant challenges to fertility and reproductive health among American males. Through a comprehensive understanding of its clinical outcomes and the implementation of tailored treatment strategies, healthcare providers can significantly improve the quality of life for affected individuals. As research progresses, the future holds potential for even more effective solutions, offering hope to those navigating the complexities of this condition.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Primary Hypogonadism: Understanding, Overcoming Stigma, and Seeking Support in American Males [Last Updated On: February 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 21st, 2025]
- Exercise and Nutrition: Managing Primary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options for American Men [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Obesity and Primary Hypogonadism: A Vicious Cycle in American Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Management, and Advocacy for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in Aging Men: Symptoms, Treatment, and Lifestyle Management [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Navigating Challenges with Robust Support Networks [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Navigating the Emotional Journey of Primary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Diet and Nutrition Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Impact on Work and Strategies for Enhanced Productivity in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Current Treatments and Future Innovations for American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Financial Impact of Primary Hypogonadism on American Men: Costs and Planning [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Testosterone's Role and Replacement Therapy Benefits [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism and Diabetes: Dual Challenge in American Men's Health Management [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Innovative Treatments for Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Body Image and Masculinity in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Holistic Management [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Diagnosis, Challenges, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- American Males' Resilience and Mental Fortitude in Managing Primary Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Community Support Enhances Life for Men with Primary Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Navigating U.S. Healthcare [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Family Support Crucial for American Males with Primary Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Holistic Management and Treatment Strategies [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism's Impact on Muscle Mass in American Males: Diagnosis and Management [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Impact on Sleep Quality and Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Integrating Mental Health for Holistic Care in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Males: Causes, Impacts, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Understanding, Managing, and Supporting American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Males: Causes, Effects, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Males: Importance of Regular Medical Check-ups [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism's Impact on Social Life and Relationships in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Impacts on American Men's Self-Esteem and Well-being [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Support [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Peer Support's Vital Role in Managing Primary Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Genetic Testing for Primary Hypogonadism: Diagnosis and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Understanding, Impact, and Advocacy for Better Care [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Diagnosis, Challenges, and Multidisciplinary Management [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Variability, Impact, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism's Impact on Career Aspirations in American Males: Insights and Strategies [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Males: Awareness, Impact, and Urgent Action Needed [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism's Impact on Physical Activity in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: TRT Benefits, Risks, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Understanding, Impact, and Early Intervention for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Treatment, Healthcare, and Insurance Navigation in the U.S. [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Nutritionists' Vital Role in Managing Primary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Emotional Impacts and Holistic Management Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options for American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Exercise Physiology's Crucial Role in Managing Primary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Addressing Emotional Support Needs in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Symptoms, Management, and Continuous Monitoring [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Impacts and Family Planning Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Endocrinologists' Vital Role in Managing Primary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Overcoming Psychological Barriers to Primary Hypogonadism Treatment in American Males [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Managing Stress and Anxiety in American Men [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Symptoms, Prevalence, and Lifestyle Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Social Impacts on American Males' Relationships and Professional Life [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Financial Assistance and Support Options for American Men [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Males: The Vital Role of Patient Education [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Males: Challenges and Strategies for Treatment Adherence [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Holistic Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Technology's Role in Managing Primary Hypogonadism for American Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Support Groups: Vital for Managing Primary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Treatment, and Healthcare Navigation for American Men [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Multidisciplinary Care [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Health, Emotions, and Daily Life in American Males [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Mental Health Apps: Support for American Males with Primary Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Impact, Advocacy, and Workplace Support for American Men [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Importance of Regular Follow-ups for American Men [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Dietitians' Role in Managing Primary Hypogonadism with Tailored Nutrition Plans for American Males [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Overcoming Travel Challenges for American Males [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism's Impact on American Men's Hobbies and Well-being [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Physical Therapy's Role in Managing Primary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Managing Primary Hypogonadism: A Comprehensive Healthcare Team Approach for American Men [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Personalized Care and Treatment Strategies [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism's Impact on Educational Achievement in American Males [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options for American Males [Last Updated On: April 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 22nd, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Impacts, Diagnosis, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: April 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 22nd, 2025]
Word Count: 537