Introduction to Low Libido
Low libido, or a reduced interest in sexual activity, is a common yet often overlooked issue among American men. While societal pressures and psychological factors are frequently discussed, the medical side of low libido remains less explored. Understanding the physiological causes can be crucial for effective treatment and improved quality of life.
Hormonal Imbalances
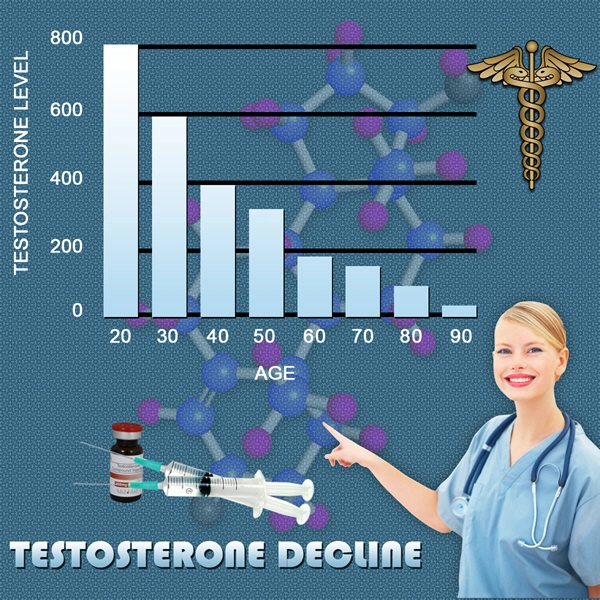
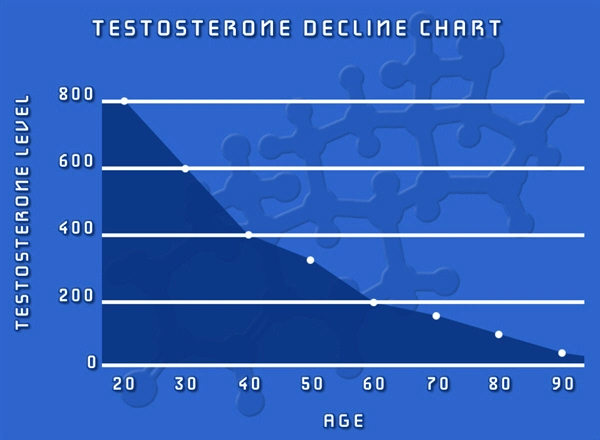
One of the primary medical causes of low libido in men is hormonal imbalance, particularly involving testosterone. Testosterone is the key hormone responsible for male sexual drive. As men age, testosterone levels naturally decline, which can lead to a decrease in libido. However, low testosterone levels can also be caused by conditions such as hypogonadism, where the body does not produce enough testosterone. Symptoms of low testosterone include fatigue, depression, and reduced muscle mass, in addition to decreased sexual desire.
Thyroid Disorders
The thyroid gland, which regulates metabolism, can also impact libido. Both hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) and hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) can lead to changes in sexual desire. Hypothyroidism can cause fatigue and weight gain, which may indirectly affect libido, while hyperthyroidism can lead to anxiety and irritability, further complicating sexual interest.
Medications and Low Libido
Certain medications can have a significant impact on libido. Antidepressants, particularly selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), are known to decrease sexual desire as a side effect. Other medications, such as those used to treat high blood pressure, can also affect libido. It is essential for men to discuss potential side effects with their healthcare providers to explore alternative treatments if necessary.
Chronic Illnesses
Chronic illnesses such as diabetes, heart disease, and kidney disease can contribute to low libido. These conditions can affect blood flow, nerve function, and overall energy levels, all of which are crucial for maintaining sexual desire. Managing these chronic conditions effectively can help mitigate their impact on libido.
Neurological Disorders
Neurological disorders, including multiple sclerosis and Parkinson's disease, can also lead to low libido. These conditions can affect the brain's signaling pathways and the body's ability to respond to sexual stimuli. Addressing the neurological aspects of these disorders through medication and therapy can sometimes improve sexual function.
Lifestyle Factors
While not strictly medical, lifestyle factors such as obesity, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption can have a medical impact on libido. Obesity can lead to hormonal imbalances and reduced blood flow, while smoking and excessive alcohol can impair vascular health and nerve function. Adopting a healthier lifestyle can improve overall health and potentially boost libido.
Psychological Factors
Although this article focuses on the medical side of low libido, it is important to acknowledge the interplay between psychological and physiological factors. Stress, anxiety, and depression can exacerbate medical conditions that affect libido. A holistic approach to treatment, addressing both psychological and medical aspects, is often the most effective.
Seeking Medical Advice
Men experiencing low libido should consult with a healthcare provider to explore potential medical causes. A thorough medical evaluation can help identify underlying conditions that may be contributing to decreased sexual desire. Treatment options may include hormone therapy, medication adjustments, or lifestyle changes, depending on the specific cause.
Conclusion
Low libido in American men is a multifaceted issue with significant medical underpinnings. From hormonal imbalances and thyroid disorders to chronic illnesses and the side effects of medications, understanding the medical causes is essential for effective treatment. By addressing these medical factors, men can take proactive steps towards improving their sexual health and overall well-being.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Physical Causes of Low Libido in American Males: Hormones, Illnesses, and Lifestyle [Last Updated On: February 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 20th, 2025]
- Unraveling the Link Between Anxiety and Diminished Sexual Desire in American Men [Last Updated On: March 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 1st, 2025]
- Revitalizing Desire: Strategies for Overcoming Low Libido in Long-term Relationships Among American Males [Last Updated On: March 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 1st, 2025]
- Decoding Medical Science: A Comprehensive Approach To Low Libido Issues [Last Updated On: March 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 2nd, 2025]
- Comprehensive Overview of Male Libido Issues: Causes, Treatments, and Lifestyle Interventions [Last Updated On: March 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 3rd, 2025]
- Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Managing Low Libido in Men [Last Updated On: March 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 4th, 2025]
- Exploring Hormonal Influences on Male Libido: Testosterone, Thyroid, and Prolactin [Last Updated On: March 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 5th, 2025]
- Understanding and Managing Low Libido in American Men: Causes and Treatments [Last Updated On: March 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 6th, 2025]
- Understanding Post-Menopausal Libido: Hormonal, Physical, and Emotional Factors Impacting Sexual Desire [Last Updated On: March 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 7th, 2025]
- Understanding Low Libido in Men: Causes, Impacts, and Effective Treatment Strategies [Last Updated On: March 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 8th, 2025]
- Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Managing Low Libido in Men: Psychological Perspectives and Solutions [Last Updated On: March 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 9th, 2025]
- Navigating the Impact of Chronic Diseases on Male Libido: A Comprehensive Medical Insight [Last Updated On: March 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 12th, 2025]
- Revitalizing Intimacy: Exploring Medical Therapies for Low Libido in Postpartum American Women [Last Updated On: March 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 13th, 2025]
- Revitalizing Desire: Cutting-Edge Medical Treatments for Low Libido in American Males [Last Updated On: March 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 15th, 2025]
- Psychological Causes of Low Libido in American Men: Stress, Depression, and More [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Low Libido in American Males: Health Risks and the Importance of Seeking Help [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Understanding Low Libido in American Males: Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Medication-Induced Low Libido in American Males: Causes and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Understanding and Treating Low Libido in Men: Causes and Comprehensive Solutions [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Diabetes and Male Libido: Understanding and Managing Low Sexual Desire [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Chronic Illness Impact on Male Libido: Physiological, Psychological, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Medications Impacting Male Libido: Insights and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Natural Supplements for Low Libido in Men: Efficacy, Safety, and Holistic Approaches [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Low Libido and Depression in American Males: Understanding and Treating the Connection [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Advancements in Treating Low Libido in American Males: A Comprehensive Approach [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Hyperthyroidism's Impact on Libido in American Males: Hormonal and Psychological Effects [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Understanding Low Libido in Women Over 50: Insights for American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Understanding and Managing Low Libido in American Males: Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Understanding and Addressing Low Libido in American Males: Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Post-Pregnancy Low Libido in American Males: Causes and Solutions [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Low Libido in American Males During Partner's Lactation: Causes and Solutions [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Managing Low Libido in Male Surgical Patients: Causes, Impacts, and Strategies [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Understanding and Treating Low Libido in American Males: Causes and Solutions [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Postpartum Libido in Men: Medical Tips and Strategies for Enhancement [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Understanding and Addressing Low Libido in American Men: A Comprehensive Approach [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Alcohol's Impact on Male Libido: Physiological Effects and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Revitalizing Male Sexual Desire: Understanding and Treating Low Libido Holistically [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Understanding and Addressing Low Libido in American Males: Causes, Impacts, and Solutions [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Understanding and Addressing Low Libido in American Men: Medical and Lifestyle Approaches [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Effective Interventions for Low Libido in American Men: A Comprehensive Guide [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Revitalizing Sexual Desire in Middle-Aged Men: A Holistic Approach [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Low Libido in American Women: Causes, Impacts, and Multifaceted Treatment Approaches [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Exploring Risks and Side Effects of Low Libido Treatments in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Post-Surgical Libido Recovery: Medical Tips for American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Understanding Low Libido in Men: Causes, Impacts, and Holistic Solutions [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Understanding and Addressing Low Libido in American Men: Causes and Solutions [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Chronic Pain and Low Libido: Understanding the Medical Connection in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Managing Low Libido in Male Athletes: Hormonal, Nutritional, and Psychological Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Understanding and Overcoming Low Libido in American Males: A Comprehensive Guide [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Sudden Low Libido in American Males: Medical, Psychological, and Lifestyle Factors [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Addressing Low Libido in American Males: Psychological, Physiological, and Lifestyle Factors [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Understanding and Treating Low Libido in American Men: A Holistic Approach [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Strategies to Boost Low Libido in American Males: Medical and Lifestyle Approaches [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Low Libido in American Men: Causes, Treatments, and Lifestyle Impacts [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Exploring Low Libido in Men: Causes, Treatments, and Personalized Approaches [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Exploring Medical Patterns of Low Libido in Young American Males: Causes and Treatments [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Exploring the Link Between Low Libido and Weight Gain in American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Hypertension's Impact on Libido in American Men: Causes and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Low Libido in American Males: Causes, Risks, and Medical Importance [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Chronic Low Libido in American Males: Medical Signs and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Age-Related Low Libido in Men: Causes, Treatments, and Future Innovations [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Low Libido and Unhappiness in American Men: Medical Insights and Interventions [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Lifestyle Changes to Boost Libido in American Males: A Medical Perspective [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Managing Low Libido in American Males Post-Chemotherapy: Medical and Lifestyle Approaches [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Revitalizing Sexual Health: Understanding and Overcoming Low Libido in American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Understanding and Treating Low Libido in Men: A Holistic Approach [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Exploring Medical Causes and Solutions for Low Libido in American Men [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Antidepressants and Low Libido in American Males: Causes, Impacts, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Understanding Low Libido in Women: Medical Insights for American Males [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Exploring Causes and Solutions for Low Libido in American Men [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Understanding and Addressing Low Libido in American Men: Medical Insights and Solutions [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Understanding and Addressing Low Libido in American Males: Causes, Impacts, and Solutions [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Medical Procedures Impacting Libido in American Men: Causes and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Medical Factors Impacting Low Libido in Women Under 40: Insights and Solutions [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Addressing Low Libido in Men: Causes, Diagnosis, and Multifaceted Treatment Approaches [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Medical Causes and Management of Low Libido in American Men [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Managing Low Libido in American Males: Causes, Impacts, and Holistic Approaches [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Understanding and Addressing Low Libido in American Males: A Holistic Approach [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Understanding and Treating Low Libido in Men: Causes and Solutions [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Understanding and Treating Low Libido in American Males: Symptoms, Causes, and Recovery [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
Word Count: 569