Introduction to Secondary Hypogonadism
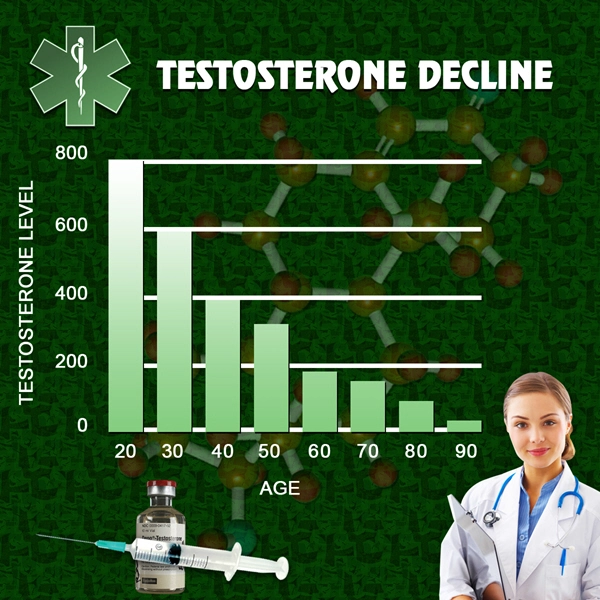
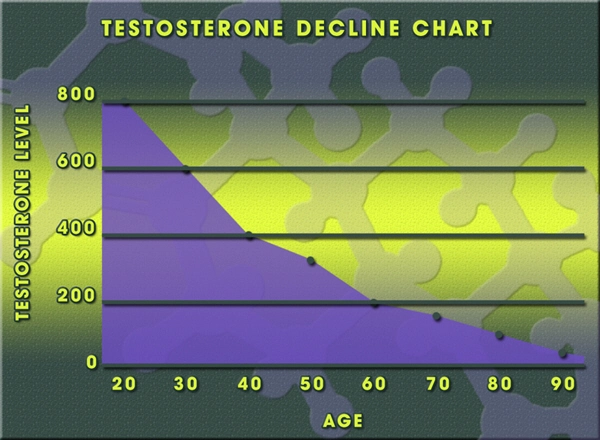
Secondary hypogonadism, a condition where the body does not produce enough testosterone due to a problem with the pituitary gland or hypothalamus, is increasingly recognized as a significant health issue among American men. This condition can lead to a variety of symptoms including decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, fatigue, and mood disturbances. Understanding and addressing secondary hypogonadism is essential for maintaining men's health and quality of life.
The Prevalence of Secondary Hypogonadism
Recent studies have shown that secondary hypogonadism is more common than previously thought, affecting a significant portion of the male population in the United States. Factors such as obesity, chronic illnesses, and certain medications can contribute to the development of this condition. As awareness grows, it is crucial for men to be educated about the signs and symptoms of secondary hypogonadism to seek timely medical intervention.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Men with secondary hypogonadism may experience a range of symptoms that can impact their daily lives. These include reduced sexual desire, difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection, decreased muscle mass, increased body fat, and emotional changes such as depression or irritability. Diagnosis typically involves a thorough medical history, physical examination, and blood tests to measure testosterone levels and other hormones. Early detection and diagnosis are key to managing the condition effectively.
Treatment Options
Treatment for secondary hypogonadism varies depending on the underlying cause. Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is a common approach, where testosterone is administered through injections, gels, patches, or pellets. This can help alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life. In cases where the condition is caused by a tumor or other structural issue in the pituitary gland or hypothalamus, surgical intervention or other targeted treatments may be necessary. It is important for men to work closely with their healthcare providers to determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
The Role of Lifestyle Changes
In addition to medical treatments, lifestyle modifications can play a significant role in managing secondary hypogonadism. Maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing stress can help improve testosterone levels and overall well-being. Men are encouraged to adopt a balanced diet rich in nutrients that support hormonal health, such as zinc and vitamin D. Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption and smoking can also contribute to better health outcomes.
The Importance of Education and Awareness
Educating American men about secondary hypogonadism is vital for early detection and effective management of the condition. Public health campaigns, educational resources, and open discussions with healthcare providers can help increase awareness and encourage men to seek help if they experience symptoms. By fostering a better understanding of secondary hypogonadism, men can take proactive steps to protect their health and well-being.
Conclusion
Secondary hypogonadism is a prevalent condition that can significantly impact the lives of American men. Through education, early diagnosis, and appropriate treatment, men can manage this condition effectively and maintain a high quality of life. It is essential for men to be aware of the symptoms, seek medical advice when necessary, and engage in lifestyle practices that support hormonal health. By addressing secondary hypogonadism head-on, men can continue to lead healthy, fulfilling lives.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Cardiovascular Health and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: February 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: Importance of Regular Check-ups for Early Detection and Management [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Genetic Insights into Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Diagnosis and Treatment [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Exercise Regimens for Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Sleep: Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Stress-Induced Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Energy and Treatment Options in American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Body Composition in American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Comprehensive Support for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Mental Health and Treatment Approaches in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Cognitive Function in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Understanding Impacts and Managing Prostate Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Testing, and Treatment for American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Immune System and Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Mood Disorders: Impact and Clinical Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Diabetes: Prevalence, Link, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Hair Loss: Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options for American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Exploring Alternative Therapies for Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Anemia: Causes, Symptoms, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Fat Distribution in American Men: Risks and Management [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Kidney Function in American Males: Symptoms, Treatment, and Management [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Causes, and Management Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Support [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Skin Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Nutrition's Role in Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Key Nutrients and Dietary Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Understanding Its Profound Social Impact on American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Bone Density in American Men: Diagnosis and Management [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Environmental Factors and Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: Impacts and Interventions [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Lifestyle Impact on Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Prevention and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Fatigue: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Thyroid Function's Impact on Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Diagnosis and Management [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Libido and Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Sleep Disorders and Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Health and Treatment Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Cognitive Function in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts, Mental Health Needs, and Integrated Care Solutions for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Psychological Impact on American Men: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Stress, Strategies, and Support for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Autoimmune Diseases: A Rising Concern in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Exercise Boosts Testosterone and Alleviates Secondary Hypogonadism Symptoms in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Emotional Well-being in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Liver Health: Impacts and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Physical Performance and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Cardiovascular Risks in American Males: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Muscle Strength in American Men: Diagnosis and Treatment [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Symptoms, Monitoring, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Mood and Treatment in American Men [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Comprehensive Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Hormonal Therapy, and Lifestyle Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Energy, Vitality, and Treatment Options for American Men [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Weight Management and Holistic Health Strategies [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: The Crucial Role of Diet and Nutrients [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Enhancing Quality of Life [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Men's Relationships and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: The Critical Impact of Sleep Deprivation [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: A Holistic Approach for American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Mental Clarity in American Men [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Community Support's Vital Role in Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Emotional Resilience in American Men [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: A Holistic Approach for American Men [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Understanding and Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Personalized Care [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Mental Health in American Males: Diagnosis and Treatment [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Causes, and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Muscle, Bone, and Cardiovascular Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Self-Esteem in American Men: Causes and Management [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Understanding, Diagnosing, and Enhancing Vitality in American Men [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Nutrition's Role in Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Understanding Causes, Symptoms, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Importance of Regular Health Check-ups for American Males [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Lifestyle Factors and Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts and Prevention Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Emotional Impact and Comprehensive Management in American Men [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
Word Count: 519