Introduction to Secondary Hypogonadism and Diabetes
Secondary hypogonadism, a condition characterized by the inadequate production of testosterone due to dysfunctions in the hypothalamus or pituitary gland, has been increasingly linked to metabolic disorders such as diabetes. For American males, understanding this connection is crucial not only for managing symptoms but also for preventing the progression of these intertwined health issues.
The Prevalence of Secondary Hypogonadism Among American Men
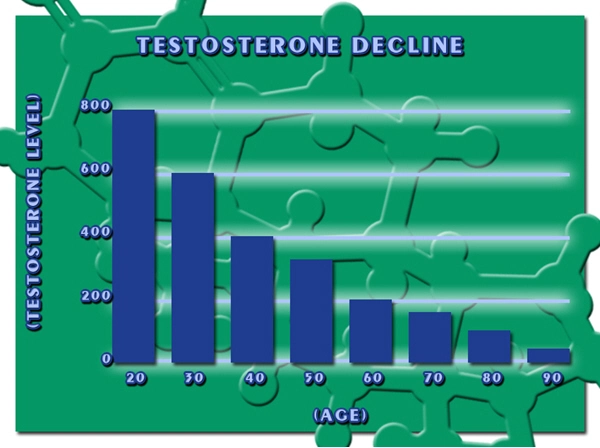
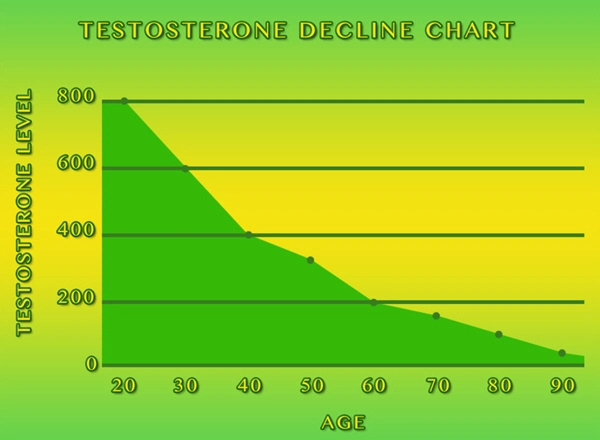
In the United States, secondary hypogonadism affects a significant portion of the male population. Studies indicate that approximately 5% to 6% of men may suffer from this condition, with prevalence increasing with age. This statistic is particularly alarming when considering the parallel rise in diabetes cases, which now affects over 34 million Americans, many of whom are men.
Understanding the Pathophysiological Link
The relationship between secondary hypogonadism and diabetes is multifaceted. Insulin resistance, a hallmark of type 2 diabetes, can lead to increased fat mass and obesity, which in turn can disrupt the normal function of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis. This disruption can result in decreased testosterone levels, thereby contributing to or exacerbating secondary hypogonadism.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Men experiencing secondary hypogonadism may notice a range of symptoms, including decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, fatigue, and mood changes. These symptoms can be particularly distressing and may be compounded by the effects of diabetes, such as neuropathy and vascular complications. Diagnosis typically involves measuring serum testosterone levels, alongside assessing luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) levels to differentiate secondary from primary hypogonadism.
Treatment Approaches
Effective management of secondary hypogonadism in diabetic men involves a dual approach: addressing the underlying hormonal imbalance and managing diabetes. Testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) can be beneficial in restoring testosterone levels and improving symptoms. However, it must be administered cautiously in diabetic patients due to potential risks such as worsening insulin resistance. Lifestyle modifications, including diet and exercise, play a critical role in managing both conditions. Weight loss, in particular, can improve insulin sensitivity and potentially reverse hypogonadism.
The Importance of Regular Screening
Given the intertwined nature of secondary hypogonadism and diabetes, regular screening for both conditions is essential for American males, especially those over the age of 40 or with risk factors such as obesity. Early detection and intervention can significantly improve quality of life and prevent the progression of both diseases.
Impact on Quality of Life
The combined effects of secondary hypogonadism and diabetes can severely impact a man's quality of life. Fatigue, reduced sexual function, and mood disturbances can affect personal relationships and professional productivity. Addressing these conditions comprehensively can lead to significant improvements in overall well-being.
Future Research Directions
Ongoing research is crucial to better understand the mechanisms linking secondary hypogonadism and diabetes. Future studies may focus on identifying genetic predispositions, developing targeted therapies, and exploring the long-term effects of testosterone replacement in diabetic men. Such research will be vital in tailoring treatments to improve outcomes for American males affected by these conditions.
Conclusion
The connection between secondary hypogonadism and diabetes presents a complex challenge for American men. By recognizing the symptoms, seeking timely diagnosis, and engaging in comprehensive management strategies, men can mitigate the impact of these conditions on their health and quality of life. As research continues to evolve, the hope is that more effective and personalized treatments will become available, offering new hope for those affected by these intertwined health issues.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Cardiovascular Health and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: February 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: Importance of Regular Check-ups for Early Detection and Management [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Genetic Insights into Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Diagnosis and Treatment [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Exercise Regimens for Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Sleep: Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Stress-Induced Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Energy and Treatment Options in American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Body Composition in American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Comprehensive Support for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Mental Health and Treatment Approaches in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Cognitive Function in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Understanding Impacts and Managing Prostate Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Testing, and Treatment for American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Immune System and Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Mood Disorders: Impact and Clinical Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Hair Loss: Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options for American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Exploring Alternative Therapies for Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Anemia: Causes, Symptoms, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Fat Distribution in American Men: Risks and Management [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Kidney Function in American Males: Symptoms, Treatment, and Management [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Causes, and Management Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Support [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Skin Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Nutrition's Role in Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Key Nutrients and Dietary Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Understanding Its Profound Social Impact on American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Bone Density in American Men: Diagnosis and Management [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Environmental Factors and Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: Impacts and Interventions [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Lifestyle Impact on Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Prevention and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Fatigue: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Thyroid Function's Impact on Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Diagnosis and Management [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Libido and Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Sleep Disorders and Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Health and Treatment Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Cognitive Function in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts, Mental Health Needs, and Integrated Care Solutions for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Psychological Impact on American Men: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Stress, Strategies, and Support for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Autoimmune Diseases: A Rising Concern in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Exercise Boosts Testosterone and Alleviates Secondary Hypogonadism Symptoms in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Emotional Well-being in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Liver Health: Impacts and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Physical Performance and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Cardiovascular Risks in American Males: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Muscle Strength in American Men: Diagnosis and Treatment [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Symptoms, Monitoring, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Mood and Treatment in American Men [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Comprehensive Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Hormonal Therapy, and Lifestyle Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Energy, Vitality, and Treatment Options for American Men [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Weight Management and Holistic Health Strategies [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: The Crucial Role of Diet and Nutrients [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Enhancing Quality of Life [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Men's Relationships and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: The Critical Impact of Sleep Deprivation [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: A Holistic Approach for American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Mental Clarity in American Men [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Community Support's Vital Role in Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Emotional Resilience in American Men [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: A Holistic Approach for American Men [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Understanding and Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Personalized Care [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Mental Health in American Males: Diagnosis and Treatment [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Causes, and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Muscle, Bone, and Cardiovascular Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Self-Esteem in American Men: Causes and Management [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Understanding, Diagnosing, and Enhancing Vitality in American Men [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Nutrition's Role in Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Understanding Causes, Symptoms, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Importance of Regular Health Check-ups for American Males [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Lifestyle Factors and Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts and Prevention Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Emotional Impact and Comprehensive Management in American Men [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
Word Count: 553