Introduction to Secondary Hypogonadism
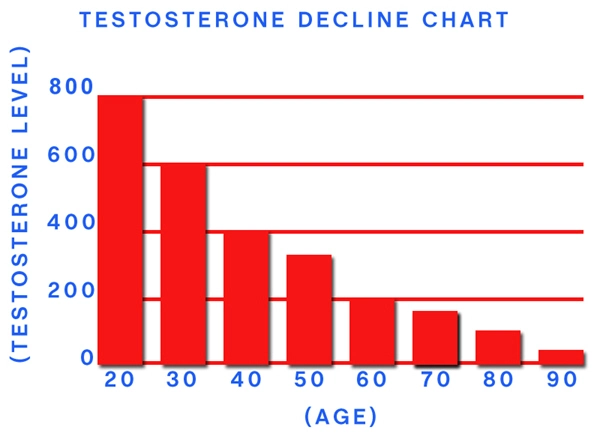
Secondary hypogonadism, a condition characterized by the inadequate production of testosterone due to dysfunctions in the hypothalamus or pituitary gland, is increasingly prevalent among American males. This condition not only affects sexual health but also impacts overall well-being, including muscle mass, bone density, and mood. Understanding the role of lifestyle in the development and management of secondary hypogonadism is crucial for effective prevention and treatment.
Lifestyle Factors Contributing to Secondary Hypogonadism
Several lifestyle factors have been identified as significant contributors to the development of secondary hypogonadism. Obesity, for instance, is a well-documented risk factor. Excess body fat can lead to increased levels of estrogen, which in turn can suppress the production of testosterone. A study published in the *Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism* found that men with a body mass index (BMI) over 30 had significantly lower testosterone levels compared to those with a normal BMI.
In addition to obesity, chronic stress and poor sleep quality are also implicated in the pathogenesis of secondary hypogonadism. Stress triggers the release of cortisol, which can interfere with the normal functioning of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis. Similarly, inadequate sleep disrupts the circadian rhythm, further exacerbating hormonal imbalances. A meta-analysis in *Sleep Medicine Reviews* highlighted that men who slept less than 7 hours per night had a 29% higher risk of developing low testosterone levels.
The Role of Diet and Exercise
Diet and exercise play pivotal roles in mitigating the risk of secondary hypogonadism. A diet rich in nutrients that support testosterone production, such as zinc, vitamin D, and omega-3 fatty acids, can be beneficial. Foods like oysters, fatty fish, and fortified cereals are excellent sources of these nutrients. Conversely, a diet high in processed foods and sugars can contribute to obesity and insulin resistance, both of which are detrimental to testosterone levels.
Regular physical activity, particularly resistance training, has been shown to boost testosterone production. A study in the *Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research* demonstrated that men who engaged in regular weightlifting experienced significant increases in testosterone levels. Moreover, exercise helps in maintaining a healthy weight, reducing stress, and improving sleep quality, all of which are crucial for hormonal balance.
Alcohol and Substance Use
Alcohol consumption and substance abuse are other lifestyle factors that can adversely affect testosterone levels. Chronic alcohol use can lead to liver damage, which in turn impairs the metabolism of hormones. Additionally, alcohol can directly suppress the HPG axis, leading to decreased testosterone production. A review in *Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research* noted that men who consumed more than 21 drinks per week had significantly lower testosterone levels.
Similarly, the use of anabolic steroids and other performance-enhancing drugs can lead to secondary hypogonadism. These substances can cause the body to stop producing its own testosterone, leading to long-term hormonal imbalances. It is essential for American males to be aware of these risks and seek professional guidance if considering the use of such substances.
Strategies for Prevention and Management
Preventing and managing secondary hypogonadism requires a multifaceted approach that addresses lifestyle factors. Adopting a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress, and ensuring adequate sleep are all essential components of a healthy lifestyle that can support optimal testosterone levels. For those already diagnosed with secondary hypogonadism, working closely with healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan is crucial. This may include hormone replacement therapy, lifestyle modifications, or a combination of both.
Conclusion
Secondary hypogonadism is a significant health concern for American males, with lifestyle playing a critical role in its development and management. By understanding and addressing the various lifestyle factors that contribute to this condition, men can take proactive steps to maintain their hormonal health and overall well-being. Awareness and education are key to empowering individuals to make informed choices that support a healthy and balanced life.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Cardiovascular Health and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: February 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: Importance of Regular Check-ups for Early Detection and Management [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Genetic Insights into Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Diagnosis and Treatment [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Exercise Regimens for Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Sleep: Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Stress-Induced Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Energy and Treatment Options in American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Body Composition in American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Comprehensive Support for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Mental Health and Treatment Approaches in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Cognitive Function in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Understanding Impacts and Managing Prostate Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Testing, and Treatment for American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Immune System and Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Mood Disorders: Impact and Clinical Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Diabetes: Prevalence, Link, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Hair Loss: Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options for American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Exploring Alternative Therapies for Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Anemia: Causes, Symptoms, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Fat Distribution in American Men: Risks and Management [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Kidney Function in American Males: Symptoms, Treatment, and Management [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Causes, and Management Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Support [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Skin Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Nutrition's Role in Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Key Nutrients and Dietary Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Understanding Its Profound Social Impact on American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Bone Density in American Men: Diagnosis and Management [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Environmental Factors and Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: Impacts and Interventions [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Fatigue: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Thyroid Function's Impact on Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Diagnosis and Management [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Libido and Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Sleep Disorders and Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Health and Treatment Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Cognitive Function in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts, Mental Health Needs, and Integrated Care Solutions for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Psychological Impact on American Men: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Stress, Strategies, and Support for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Autoimmune Diseases: A Rising Concern in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Exercise Boosts Testosterone and Alleviates Secondary Hypogonadism Symptoms in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Emotional Well-being in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Liver Health: Impacts and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Physical Performance and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Cardiovascular Risks in American Males: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Muscle Strength in American Men: Diagnosis and Treatment [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Symptoms, Monitoring, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Mood and Treatment in American Men [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Comprehensive Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Hormonal Therapy, and Lifestyle Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Energy, Vitality, and Treatment Options for American Men [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Weight Management and Holistic Health Strategies [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: The Crucial Role of Diet and Nutrients [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Enhancing Quality of Life [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Men's Relationships and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: The Critical Impact of Sleep Deprivation [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: A Holistic Approach for American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Mental Clarity in American Men [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Community Support's Vital Role in Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Emotional Resilience in American Men [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: A Holistic Approach for American Men [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Understanding and Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Personalized Care [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Mental Health in American Males: Diagnosis and Treatment [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Causes, and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Muscle, Bone, and Cardiovascular Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Self-Esteem in American Men: Causes and Management [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Understanding, Diagnosing, and Enhancing Vitality in American Men [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Nutrition's Role in Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Understanding Causes, Symptoms, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Importance of Regular Health Check-ups for American Males [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Lifestyle Factors and Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts and Prevention Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Emotional Impact and Comprehensive Management in American Men [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
Word Count: 632