Introduction
Secondary hypogonadism, a condition characterized by the inadequate production of testosterone due to dysfunctions in the hypothalamus or pituitary gland, has become a significant health concern among American males. This article delves into the multifaceted genetic and environmental factors that contribute to the onset and progression of this condition, offering insights into its complex etiology and potential avenues for prevention and treatment.
Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism
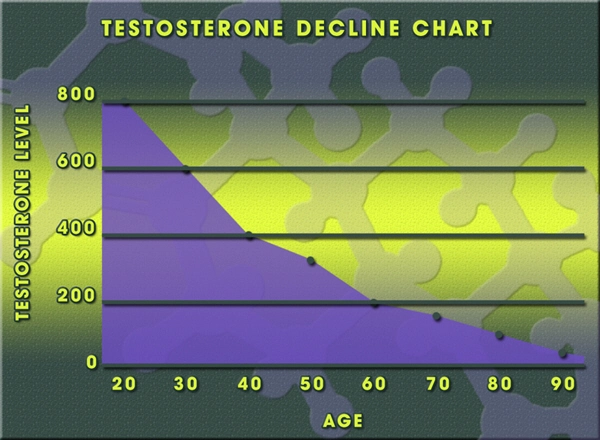
Secondary hypogonadism, also known as hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, is a condition where the testes are normal but do not produce sufficient testosterone due to a malfunction in the brain's signaling pathways. The hypothalamus and pituitary gland, which are responsible for regulating hormone production, fail to stimulate the testes effectively, leading to reduced testosterone levels and associated symptoms such as decreased libido, fatigue, and muscle loss.
Genetic Factors
Genetic predispositions play a crucial role in the development of secondary hypogonadism. Mutations in genes such as KAL1, FGFR1, and PROK2 have been identified as significant contributors to the condition. These genes are involved in the development and function of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis, and their mutations can disrupt the normal signaling processes necessary for testosterone production. Additionally, chromosomal abnormalities, such as Kallmann syndrome, can lead to congenital forms of secondary hypogonadism, highlighting the importance of genetic screening and counseling for at-risk individuals.
Environmental Influences
Environmental factors also significantly impact the prevalence and progression of secondary hypogonadism in American males. Exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs), found in pesticides, plastics, and certain industrial chemicals, can interfere with hormone regulation and contribute to the development of hypogonadism. Moreover, lifestyle factors such as obesity, chronic stress, and substance abuse, including excessive alcohol consumption and opioid use, have been linked to altered hormone levels and increased risk of secondary hypogonadism. Addressing these environmental and lifestyle factors through public health initiatives and personal lifestyle changes can play a vital role in mitigating the risk of developing this condition.
Diagnosis and Management
Diagnosing secondary hypogonadism involves a comprehensive evaluation of symptoms, hormone levels, and imaging studies to assess the function of the hypothalamus and pituitary gland. Once diagnosed, treatment typically involves hormone replacement therapy to restore testosterone levels and alleviate symptoms. However, addressing the underlying genetic or environmental causes is crucial for long-term management. Genetic counseling can help individuals understand their risk and take preventive measures, while lifestyle modifications and environmental interventions can reduce exposure to harmful substances and promote overall health.
Conclusion
Secondary hypogonadism in American males is a complex condition influenced by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Understanding these influences is essential for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies. By integrating genetic screening, lifestyle modifications, and environmental awareness into healthcare practices, we can better manage and potentially reduce the incidence of secondary hypogonadism, improving the quality of life for affected individuals. As research continues to uncover the intricacies of this condition, it is imperative that healthcare providers and patients alike remain vigilant and proactive in addressing its multifaceted causes.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Cardiovascular Health and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: February 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: Importance of Regular Check-ups for Early Detection and Management [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Genetic Insights into Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Diagnosis and Treatment [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Exercise Regimens for Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Sleep: Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Stress-Induced Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Energy and Treatment Options in American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Body Composition in American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Comprehensive Support for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Mental Health and Treatment Approaches in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Cognitive Function in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Understanding Impacts and Managing Prostate Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Testing, and Treatment for American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Immune System and Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Mood Disorders: Impact and Clinical Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Diabetes: Prevalence, Link, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Hair Loss: Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options for American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Exploring Alternative Therapies for Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Anemia: Causes, Symptoms, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Fat Distribution in American Men: Risks and Management [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Kidney Function in American Males: Symptoms, Treatment, and Management [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Causes, and Management Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Support [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Skin Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Nutrition's Role in Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Key Nutrients and Dietary Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Understanding Its Profound Social Impact on American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Bone Density in American Men: Diagnosis and Management [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Environmental Factors and Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: Impacts and Interventions [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Lifestyle Impact on Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Prevention and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Fatigue: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Thyroid Function's Impact on Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Diagnosis and Management [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Libido and Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Sleep Disorders and Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Health and Treatment Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Cognitive Function in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts, Mental Health Needs, and Integrated Care Solutions for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Psychological Impact on American Men: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Stress, Strategies, and Support for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Autoimmune Diseases: A Rising Concern in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Exercise Boosts Testosterone and Alleviates Secondary Hypogonadism Symptoms in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Emotional Well-being in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Liver Health: Impacts and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Physical Performance and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Cardiovascular Risks in American Males: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Muscle Strength in American Men: Diagnosis and Treatment [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Symptoms, Monitoring, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Mood and Treatment in American Men [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Comprehensive Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Hormonal Therapy, and Lifestyle Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Energy, Vitality, and Treatment Options for American Men [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Weight Management and Holistic Health Strategies [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: The Crucial Role of Diet and Nutrients [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Enhancing Quality of Life [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Men's Relationships and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: The Critical Impact of Sleep Deprivation [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: A Holistic Approach for American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Mental Clarity in American Men [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Community Support's Vital Role in Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Emotional Resilience in American Men [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: A Holistic Approach for American Men [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Understanding and Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Personalized Care [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Mental Health in American Males: Diagnosis and Treatment [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Causes, and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Muscle, Bone, and Cardiovascular Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Self-Esteem in American Men: Causes and Management [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Understanding, Diagnosing, and Enhancing Vitality in American Men [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Nutrition's Role in Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Understanding Causes, Symptoms, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Importance of Regular Health Check-ups for American Males [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Lifestyle Factors and Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts and Prevention Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Emotional Impact and Comprehensive Management in American Men [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: Symptoms, Impacts, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 21st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Health and Importance of Early Detection in Men [Last Updated On: April 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 21st, 2025]
Word Count: 488