Introduction to Secondary Hypogonadism
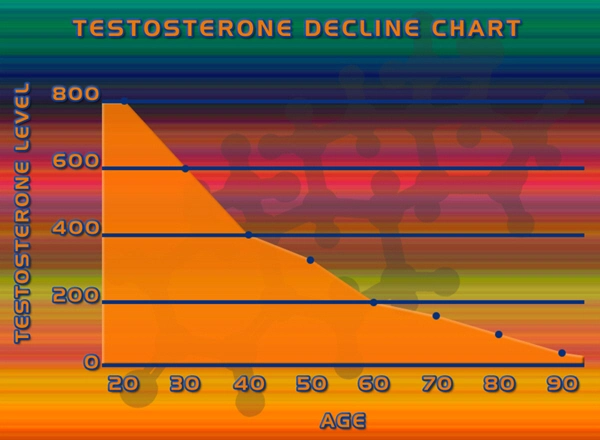
Secondary hypogonadism, also known as hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, is a condition characterized by the inadequate production of testosterone due to a dysfunction in the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis. This condition affects a significant number of American men, leading to symptoms such as decreased libido, fatigue, and mood disturbances. Traditional treatments often involve testosterone replacement therapy (TRT), but recent interest has surged in exploring alternative therapies that may offer benefits with fewer side effects.
Understanding the Causes and Symptoms
Secondary hypogonadism can arise from various causes, including pituitary disorders, genetic conditions, and chronic illnesses. Symptoms often manifest subtly and can be mistaken for general aging or lifestyle-related issues. Common signs include reduced sexual desire, erectile dysfunction, decreased muscle mass, and increased body fat. Recognizing these symptoms early is crucial for effective management and improving quality of life.
Traditional Treatment Approaches
The conventional approach to treating secondary hypogonadism has been testosterone replacement therapy. TRT can effectively alleviate symptoms and restore testosterone levels to normal ranges. However, it is not without its drawbacks, including potential side effects such as sleep apnea, increased risk of cardiovascular events, and suppression of natural testosterone production. These concerns have prompted researchers and clinicians to seek alternative therapies that might mitigate these risks.
Emerging Alternative Therapies
Several alternative therapies are being explored for their potential in managing secondary hypogonadism. One promising approach is the use of selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) like clomiphene citrate. SERMs work by stimulating the body's own production of testosterone, thus avoiding the suppression of natural hormone production seen with TRT. Studies have shown that clomiphene can effectively increase testosterone levels and improve symptoms in men with secondary hypogonadism.
Another alternative is human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), which mimics luteinizing hormone and stimulates the testes to produce testosterone. hCG has been used successfully in men with hypogonadism, particularly those who wish to preserve fertility, as it does not suppress spermatogenesis like TRT.
Lifestyle Interventions and Natural Supplements
In addition to pharmacological alternatives, lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in managing secondary hypogonadism. Regular exercise, particularly resistance training, has been shown to boost testosterone levels naturally. A balanced diet rich in nutrients like zinc and vitamin D can also support healthy testosterone production.
Natural supplements such as fenugreek and ashwagandha have gained popularity for their potential to enhance testosterone levels. While the evidence is not as robust as for pharmaceutical interventions, some studies suggest these supplements may offer modest benefits, particularly when combined with lifestyle changes.
The Role of Psychological Support
The psychological impact of secondary hypogonadism should not be underestimated. Men experiencing symptoms may suffer from decreased self-esteem and depression. Psychological support, including counseling and support groups, can be invaluable in helping men cope with the emotional aspects of the condition. Integrating mental health support with medical treatment can lead to better overall outcomes.
Future Directions in Research
Ongoing research continues to explore new avenues for treating secondary hypogonadism. Gene therapy and stem cell research hold promise for future treatments that could address the root causes of the condition. Additionally, personalized medicine approaches, which tailor treatments to individual genetic profiles, may offer more effective and safer options for managing hypogonadism.
Conclusion
Secondary hypogonadism presents a significant challenge for many American men, but the landscape of treatment options is evolving. Alternative therapies, including SERMs, hCG, and lifestyle interventions, offer hope for managing this condition with fewer side effects than traditional TRT. As research progresses, the future looks promising for developing more effective and personalized treatments for secondary hypogonadism, ultimately improving the quality of life for affected men.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Cardiovascular Health and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: February 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: Importance of Regular Check-ups for Early Detection and Management [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Genetic Insights into Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Diagnosis and Treatment [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Exercise Regimens for Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Sleep: Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Stress-Induced Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Energy and Treatment Options in American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Body Composition in American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Comprehensive Support for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Mental Health and Treatment Approaches in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Cognitive Function in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Understanding Impacts and Managing Prostate Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Testing, and Treatment for American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Immune System and Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Mood Disorders: Impact and Clinical Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Diabetes: Prevalence, Link, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Hair Loss: Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options for American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Anemia: Causes, Symptoms, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Fat Distribution in American Men: Risks and Management [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Kidney Function in American Males: Symptoms, Treatment, and Management [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Understanding Secondary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Causes, and Management Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Support [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Skin Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Nutrition's Role in Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Key Nutrients and Dietary Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Understanding Its Profound Social Impact on American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Bone Density in American Men: Diagnosis and Management [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Environmental Factors and Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men: Impacts and Interventions [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Lifestyle Impact on Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Prevention and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Fatigue: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Thyroid Function's Impact on Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Diagnosis and Management [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Libido and Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Sleep Disorders and Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Health and Treatment Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Cognitive Function in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts, Mental Health Needs, and Integrated Care Solutions for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Psychological Impact on American Men: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Stress, Strategies, and Support for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Autoimmune Diseases: A Rising Concern in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Exercise Boosts Testosterone and Alleviates Secondary Hypogonadism Symptoms in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Emotional Well-being in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Liver Health: Impacts and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Physical Performance and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism and Cardiovascular Risks in American Males: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Muscle Strength in American Men: Diagnosis and Treatment [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Symptoms, Monitoring, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Mood and Treatment in American Men [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Comprehensive Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Hormonal Therapy, and Lifestyle Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impact on Energy, Vitality, and Treatment Options for American Men [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Weight Management and Holistic Health Strategies [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: The Crucial Role of Diet and Nutrients [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Enhancing Quality of Life [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Men's Relationships and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: The Critical Impact of Sleep Deprivation [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: A Holistic Approach for American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Mental Clarity in American Men [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Community Support's Vital Role in Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Emotional Resilience in American Men [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Managing Secondary Hypogonadism: A Holistic Approach for American Men [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Impacts and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Understanding and Managing Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism in American Males: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Personalized Care [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Secondary Hypogonadism's Impact on Mental Health in American Males: Diagnosis and Treatment [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
Word Count: 592