Introduction to Primary Hypogonadism
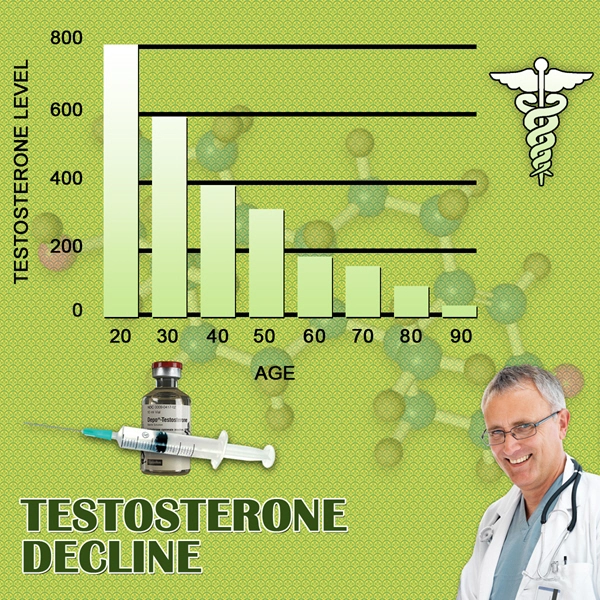
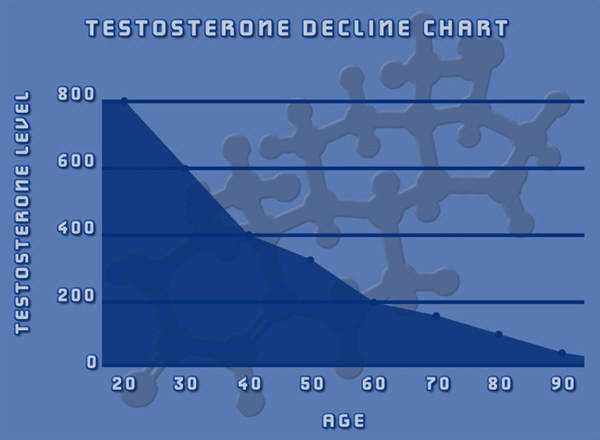
Primary hypogonadism, also known as testicular failure, is a condition where the testes do not produce sufficient levels of testosterone, the primary male sex hormone. This can lead to a variety of symptoms including decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, infertility, and reduced muscle mass. In American males, understanding the genetic underpinnings of this condition is crucial for effective diagnosis and management.
The Role of Genetic Testing
Genetic testing has become a pivotal tool in diagnosing primary hypogonadism. By analyzing an individual's DNA, healthcare providers can identify specific genetic mutations that may be responsible for the condition. This is particularly important for American males, as certain genetic variations may be more prevalent within different ethnic groups in the U.S.
Common Genetic Mutations
Several genes have been linked to primary hypogonadism. Mutations in the Klinefelter syndrome gene, for instance, result in an extra X chromosome (XXY), which is a common cause of the condition. Other genes such as NR5A1 and DHH are also implicated in testicular development and function. Understanding these genetic factors can help tailor treatment plans to the individual's specific needs.
Benefits of Genetic Testing
Genetic testing offers several benefits for American males with suspected primary hypogonadism. Firstly, it can confirm the diagnosis, which is essential for initiating appropriate treatment. Secondly, it can provide insights into the prognosis and potential complications of the condition. Lastly, genetic testing can inform family planning decisions, as it can identify carriers of genetic mutations that may be passed on to future generations.
The Testing Process
The process of genetic testing for primary hypogonadism typically involves a simple blood draw or saliva sample. The sample is then sent to a laboratory where it is analyzed for specific genetic mutations. Results are usually available within a few weeks, and a genetic counselor can help interpret the findings and discuss the implications.
Challenges and Considerations
While genetic testing is a powerful diagnostic tool, it is not without challenges. The cost of testing can be a barrier for some American males, although insurance coverage may be available in certain cases. Additionally, the emotional impact of receiving a genetic diagnosis should not be underestimated. It is important for individuals to have access to genetic counseling and support services to help them navigate the results.
Future Directions in Genetic Research
Ongoing research into the genetics of primary hypogonadism continues to uncover new insights. Advances in genetic sequencing technologies are making it possible to identify rare mutations that were previously undetectable. For American males, this means that the future of diagnosis and treatment for primary hypogonadism is likely to become even more personalized and effective.
Conclusion
Genetic testing for primary hypogonadism is a valuable resource for American males seeking to understand and manage their condition. By identifying specific genetic mutations, healthcare providers can offer targeted treatments and support. As research progresses, the role of genetics in the management of primary hypogonadism will only become more significant, offering hope for improved outcomes and quality of life.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Primary Hypogonadism: Understanding, Overcoming Stigma, and Seeking Support in American Males [Last Updated On: February 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 21st, 2025]
- Exercise and Nutrition: Managing Primary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options for American Men [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Obesity and Primary Hypogonadism: A Vicious Cycle in American Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Management, and Advocacy for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in Aging Men: Symptoms, Treatment, and Lifestyle Management [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Navigating Challenges with Robust Support Networks [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Navigating the Emotional Journey of Primary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Diet and Nutrition Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Impact on Work and Strategies for Enhanced Productivity in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Current Treatments and Future Innovations for American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Financial Impact of Primary Hypogonadism on American Men: Costs and Planning [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Testosterone's Role and Replacement Therapy Benefits [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism and Diabetes: Dual Challenge in American Men's Health Management [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Innovative Treatments for Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Body Image and Masculinity in American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Holistic Management [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Diagnosis, Challenges, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- American Males' Resilience and Mental Fortitude in Managing Primary Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Community Support Enhances Life for Men with Primary Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Navigating U.S. Healthcare [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Family Support Crucial for American Males with Primary Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Holistic Management and Treatment Strategies [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism's Impact on Muscle Mass in American Males: Diagnosis and Management [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Impact on Sleep Quality and Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Integrating Mental Health for Holistic Care in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Males: Causes, Impacts, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Understanding, Managing, and Supporting American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Males: Causes, Effects, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Males: Importance of Regular Medical Check-ups [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism's Impact on Social Life and Relationships in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Impacts on American Men's Self-Esteem and Well-being [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Support [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Peer Support's Vital Role in Managing Primary Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Understanding, Impact, and Advocacy for Better Care [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Diagnosis, Challenges, and Multidisciplinary Management [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Variability, Impact, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism's Impact on Career Aspirations in American Males: Insights and Strategies [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Males: Awareness, Impact, and Urgent Action Needed [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism's Impact on Physical Activity in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: TRT Benefits, Risks, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Understanding, Impact, and Early Intervention for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Treatment, Healthcare, and Insurance Navigation in the U.S. [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Nutritionists' Vital Role in Managing Primary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Emotional Impacts and Holistic Management Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options for American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Exercise Physiology's Crucial Role in Managing Primary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Addressing Emotional Support Needs in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Symptoms, Management, and Continuous Monitoring [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Impacts and Family Planning Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Endocrinologists' Vital Role in Managing Primary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Overcoming Psychological Barriers to Primary Hypogonadism Treatment in American Males [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Managing Stress and Anxiety in American Men [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Symptoms, Prevalence, and Lifestyle Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Social Impacts on American Males' Relationships and Professional Life [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Financial Assistance and Support Options for American Men [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Males: The Vital Role of Patient Education [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Males: Challenges and Strategies for Treatment Adherence [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Holistic Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Technology's Role in Managing Primary Hypogonadism for American Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Support Groups: Vital for Managing Primary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Treatment, and Healthcare Navigation for American Men [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Multidisciplinary Care [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Impacts on Health, Emotions, and Daily Life in American Males [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Mental Health Apps: Support for American Males with Primary Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Impact, Advocacy, and Workplace Support for American Men [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Importance of Regular Follow-ups for American Men [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Dietitians' Role in Managing Primary Hypogonadism with Tailored Nutrition Plans for American Males [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism: Overcoming Travel Challenges for American Males [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism's Impact on American Men's Hobbies and Well-being [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Physical Therapy's Role in Managing Primary Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Managing Primary Hypogonadism: A Comprehensive Healthcare Team Approach for American Men [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Managing Primary Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism in American Men: Personalized Care and Treatment Strategies [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Primary Hypogonadism's Impact on Educational Achievement in American Males [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
Word Count: 499