Introduction
Chronic illnesses can have a profound impact on various aspects of health, including sexual function and anatomy. For American males, understanding these effects is crucial for managing their overall well-being. This article delves into the specific issue of penis shrinkage, a concern that can arise from certain chronic conditions, and provides insights into its causes, implications, and potential management strategies.
The Phenomenon of Penis Shrinkage
Penis shrinkage, or penile atrophy, is a condition where the penis appears to decrease in size. This can be a distressing experience for many men, affecting their self-esteem and sexual health. While it is not a common topic of discussion, it is important to address how chronic illnesses can contribute to this phenomenon.
Chronic Illnesses Linked to Penis Shrinkage
Several chronic conditions have been associated with penis shrinkage. Diabetes, for instance, can lead to vascular damage and nerve dysfunction, which may result in reduced blood flow to the penis. This diminished blood flow can cause the penile tissue to shrink over time. Similarly, cardiovascular diseases can impair the circulatory system, further exacerbating the issue.
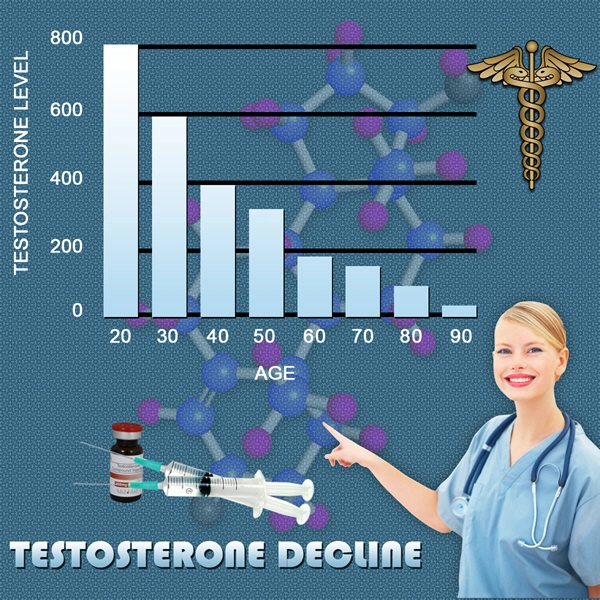
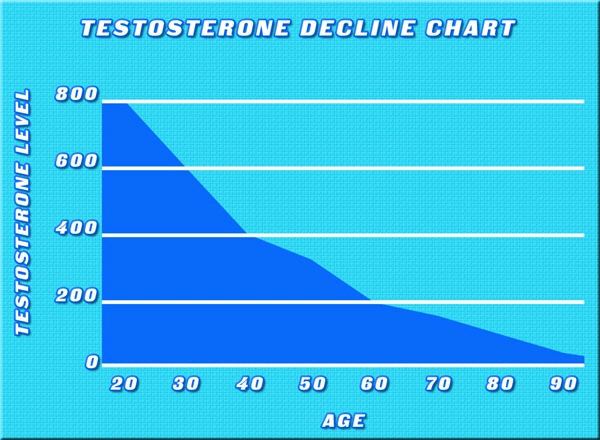
Another condition to consider is Peyronie's disease, which involves the development of fibrous scar tissue inside the penis, leading to curvature and potential shrinkage. Additionally, hormonal imbalances, such as those seen in hypogonadism, can affect testosterone levels, which are crucial for maintaining penile size and function.
Mechanisms Behind the Shrinkage
The mechanisms by which chronic illnesses lead to penis shrinkage are multifaceted. Reduced blood flow, as mentioned, is a primary factor. When the penis does not receive adequate blood supply, the erectile tissue can deteriorate, leading to a decrease in size. Additionally, nerve damage can impair the ability to achieve and maintain an erection, further contributing to the perception of shrinkage.
Inflammation and fibrosis, as seen in conditions like Peyronie's disease, can also cause the penis to contract and shorten. Hormonal changes, particularly a decrease in testosterone, can affect the overall health of penile tissue, leading to atrophy.
Psychological Impact and Coping Strategies
The psychological impact of penis shrinkage should not be underestimated. Many men experience feelings of inadequacy, anxiety, and depression as a result of this condition. It is essential for affected individuals to seek support from healthcare professionals who can provide both medical and psychological assistance.
Coping strategies may include engaging in open communication with partners, seeking therapy to address emotional concerns, and exploring treatment options that can help manage the underlying chronic illness. Support groups can also be beneficial, offering a space to share experiences and gain insights from others facing similar challenges.
Medical Interventions and Management
Managing penis shrinkage involves addressing the underlying chronic illness. For conditions like diabetes, maintaining good blood sugar control through diet, exercise, and medication can help prevent further vascular damage. Similarly, managing cardiovascular health through lifestyle changes and medical treatment can improve blood flow to the penis.
In cases of Peyronie's disease, treatments such as medications, injections, or surgery may be considered to reduce the fibrous tissue and restore penile length. For hormonal imbalances, hormone replacement therapy can be an effective solution to restore testosterone levels and support penile health.
Conclusion
Penis shrinkage is a complex issue that can arise from various chronic illnesses. Understanding the underlying causes and mechanisms is crucial for American males seeking to manage this condition. By addressing the root causes and seeking appropriate medical and psychological support, men can improve their overall sexual health and quality of life. It is important to approach this topic with sensitivity and to encourage open dialogue to ensure that those affected receive the care and support they need.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Penile Atrophy: Recognizing Early Signs and Importance of Timely Intervention for American Males [Last Updated On: February 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 22nd, 2025]
- Unveiling the Facts: Penis Size Transformation [Last Updated On: February 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 25th, 2025]
- Size Perception: Unveiling the Phenomenon of Penis Shrinkage and Its Root Causes [Last Updated On: February 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 26th, 2025]
- Embracing Natural Progression: Understanding the Impacts of Age on Male Physicality [Last Updated On: February 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 27th, 2025]
- Deciphering the Enigma: Linking Hormonal Balance, Health and Penile Size Variations [Last Updated On: February 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 28th, 2025]
- Examining the Dynamic Relationship: Body Weight, Dietary Habits, and Male Genital Proportions [Last Updated On: February 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 28th, 2025]
- Addressing the Elephant in the Room: Understanding and Discussing Penis Shrinkage [Last Updated On: March 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 1st, 2025]
- Understanding the Stress-Penis Health Nexus: An Objective Exploration [Last Updated On: March 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 2nd, 2025]
- Unveiling Andropause: Understanding Male Menopause and Its Effects on Penile Size [Last Updated On: March 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 2nd, 2025]
- Comprehensive Overview of Testosterone: Roles in Muscle Growth, Fat Distribution, Bone Density, and Age-Related Changes [Last Updated On: March 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 3rd, 2025]
- Expectations After Prostate Surgery: Physical and Psychological Impacts [Last Updated On: March 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 4th, 2025]
- Exploring the Impact of Exercise on Male Sexual Health and Erectile Function [Last Updated On: March 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 5th, 2025]
- Exploring the Impact of Vascular Health on Penis Size and Erectile Function [Last Updated On: March 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 6th, 2025]
- Unveiling the Truth: Genetics, Lifestyle, and the Phenomenon of Penis Shrinkage in American Males [Last Updated On: March 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 6th, 2025]
- Impact of Smoking and Alcohol on Male Sexual Health: Lifestyle Factors Unveiled [Last Updated On: March 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 7th, 2025]
- Understanding Penis Size Concerns: Myths, Causes, and Real Solutions for Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 8th, 2025]
- Comprehensive Insights into Chronic Illnesses Impacting Male Genital Health: A Holistic Approach [Last Updated On: March 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 9th, 2025]
- Unveiling the Link Between Diabetes and Reduced Size: A Metabolic Perspective [Last Updated On: March 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 12th, 2025]
- Unveiling the Truth: The Impact of Environmental Toxins on Male Genital Health [Last Updated On: March 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 13th, 2025]
- A Global Insight into Penile Shrinkage: Understanding and Addressing a Universal Concern Among Men [Last Updated On: March 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 15th, 2025]
- Weight Loss Reverses Penis Shrinkage: Evidence and Benefits for American Males [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Obesity's Impact on Male Genital Health: Understanding Penis Shrinkage and Solutions [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Inflammation and Oxidative Stress: Key Factors in Penis Shrinkage and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Hypertension's Impact on Penile Size: Understanding Shrinkage in American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Natural Remedies for Preventing Penile Shrinkage: Herbs, Supplements, and Lifestyle [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Hormonal Imbalances and Penis Shrinkage: Understanding Endocrine Disruptions in Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Understanding Penile Aging: Size Changes, Causes, and Health Maintenance Tips [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Diet and Nutrition Strategies to Combat Penis Shrinkage in American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Chronic Stress, Cortisol, and Penile Health: Understanding and Managing the Impact [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Sedentary Lifestyles and Penis Shrinkage: Impacts and Preventive Measures for American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Penile Measurement Techniques and Understanding Shrinkage Factors [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Understanding Penis Size: Measurement, Factors, and Shrinkage Management [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Penis Shrinkage and ED: Causes, Overlap, and Treatment Options for American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Prostate Health and Its Impact on Penis Size: Understanding and Managing Changes [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Understanding Penis Shrinkage: Causes, When to See a Urologist, and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Understanding Penile Shrinkage: Causes, Prevention, and Health Tips for American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- HRT's Role in Preventing Penis Shrinkage: Benefits and Risks for American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Relationship Dynamics and Penis Size Perception: Understanding Shrinkage and Its Impacts [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Medications Linked to Penile Shrinkage: Causes, Risks, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Understanding Penile Atrophy: Causes, Symptoms, and Importance of Urological Exams [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Preventing Penis Shrinkage: Lifestyle Tips for American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Understanding Penile Shrinkage: Causes, Impacts, and Breaking the Stigma in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Understanding Penile Atrophy: Causes, Effects, and Treatments for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Smoking and Penis Shrinkage: Cessation Strategies and Genital Health Recovery [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Sleep Disorders and Penis Shrinkage: Impacts on American Males' Sexual Health [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Environmental Pollution's Impact on Male Reproductive Health and Penis Size in America [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Peyronie's Disease: Understanding Penis Shrinkage and Treatment Options for American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Anti-Inflammatory Diets: A Strategy to Prevent Penis Shrinkage in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Sleep's Impact on Sexual Health: Preventing Penile Shrinkage in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Weight Loss and Penis Size: Understanding Changes in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Meditation and Stress Reduction: Key to Preventing Penis Shrinkage in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Coping with Perceived Penis Shrinkage: Psychological Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Metabolic Syndrome Linked to Penis Shrinkage in American Males: Causes and Prevention [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Genetic Variability and Its Impact on Penis Size and Shrinkage [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Innovative Treatments for Penis Shrinkage: Stem Cells, Shockwave, and Pharmacological Advances [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Boost Testosterone Naturally: Diet, Exercise, and Lifestyle to Prevent Penis Shrinkage [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Inflammation's Role in Penis Shrinkage: Cellular Mechanisms and Prevention Strategies [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Cardiovascular Fitness: Key to Preventing Penile Shrinkage in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- American Men's Experiences with Penile Atrophy: Causes, Treatment, and Coping Strategies [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Guide to Accurate Penis Measurement and Understanding Shrinkage for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Preventing Penile Shrinkage: Enhancing Vascular Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Androgens' Crucial Role in Preventing Penile Shrinkage Among American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Managing Penis Shrinkage in Aging Men: Causes, Impacts, and Interventions [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Regular Exercise: A Key to Preventing Age-Related Penile Shrinkage in Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Emerging Therapies Revolutionize Treatment of Penis Shrinkage in American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Managing Penile Atrophy: Causes, Diagnosis, and Effective Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Alcohol Consumption and Penis Size: The Importance of Moderation in American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Penis Size and Sexual Health: Function, Sensation, and Holistic Well-being [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Vascular Surgery: A Hopeful Solution for Penis Shrinkage in American Males [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Chronic Diseases and Penis Shrinkage: Insights and Management Strategies for Men [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Superfoods Boost Vascular Health, Prevent Penis Shrinkage in American Males [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Psychological Support for American Men with Perceived Penis Shrinkage: Strategies and Insights [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Andropause and Penis Shrinkage: Understanding and Managing Male Aging Symptoms [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Understanding and Managing Penis Shrinkage: Causes, Effects, and Support for American Males [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Hypertension Medications and Penile Shrinkage: Insights for American Males [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Chronic Stress and Penile Health: Understanding Impacts and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Supplements and Penis Health: Evaluating Efficacy and Risks [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Hormonal Health and Penis Size: Understanding and Prevention Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Male Genital Health: Importance of Regular Check-Ups for Preventing Penis Shrinkage [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Postoperative Penile Shrinkage: Causes, Management, and Recovery Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
Word Count: 598