Introduction
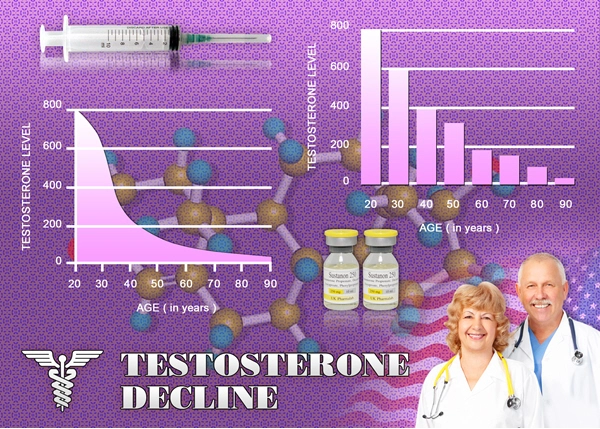
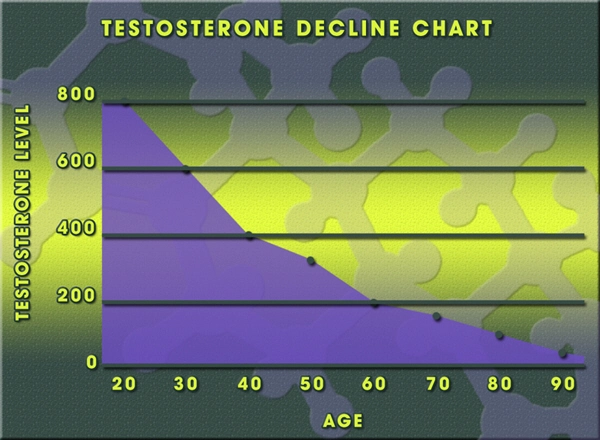
Low testosterone, or hypogonadism, is a prevalent condition among American males, affecting their quality of life and overall health. While many factors contribute to this condition, the role of rheumatological health is often overlooked. Rheumatological disorders, which include conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus, can have a significant impact on testosterone levels. This article delves into the intricate relationship between rheumatological health and low testosterone, offering insights and strategies for management tailored to American males.
Understanding Rheumatological Disorders
Rheumatological disorders encompass a range of autoimmune and inflammatory conditions that primarily affect the joints and connective tissues. Conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) are characterized by chronic inflammation, which can extend beyond the musculoskeletal system and influence systemic health, including hormonal balance. The chronic inflammatory state associated with these disorders can lead to a cascade of physiological changes, one of which is the alteration of testosterone levels.
The Impact of Rheumatological Disorders on Testosterone
Chronic inflammation, a hallmark of rheumatological disorders, can disrupt the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis, which is crucial for testosterone production. Inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-?) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) have been shown to inhibit testosterone synthesis. Moreover, the stress and pain associated with these conditions can further exacerbate the hormonal imbalance, leading to decreased testosterone levels.
Clinical Evidence Linking Rheumatological Health and Low Testosterone
Several studies have highlighted the association between rheumatological disorders and hypogonadism. For instance, research published in the *Journal of Rheumatology* found that men with RA had significantly lower testosterone levels compared to healthy controls. Similarly, a study in *Arthritis & Rheumatology* reported that men with SLE exhibited a higher prevalence of hypogonadism. These findings underscore the need for rheumatologists and endocrinologists to collaborate in managing patients with rheumatological conditions.
Strategies for Managing Low Testosterone in Rheumatological Patients
Managing low testosterone in the context of rheumatological disorders requires a multifaceted approach. Here are some strategies tailored for American males:
1. **Anti-inflammatory Medications**: Medications such as disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) and biologics can help reduce systemic inflammation, potentially improving testosterone levels. Regular monitoring of hormone levels is essential to assess the effectiveness of these treatments.
2. **Lifestyle Modifications**: Engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy diet, and managing stress can contribute to overall well-being and may help mitigate the impact of rheumatological disorders on testosterone levels. American males are encouraged to incorporate these lifestyle changes into their daily routines.
3. **Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT)**: In cases where low testosterone persists despite other interventions, TRT may be considered. However, this should be done under the guidance of a healthcare professional, as it carries potential risks and side effects. Regular follow-up and monitoring are crucial to ensure the safety and efficacy of TRT.
4. **Collaborative Care**: Given the complex interplay between rheumatological health and testosterone levels, a collaborative approach involving rheumatologists, endocrinologists, and primary care physicians is vital. This ensures comprehensive care and personalized treatment plans for American males affected by these conditions.
Conclusion
The relationship between rheumatological health and low testosterone is a critical aspect of men's health that warrants attention. American males with rheumatological disorders should be aware of the potential impact on their hormonal balance and seek appropriate medical care. By understanding this link and implementing targeted strategies, it is possible to improve quality of life and manage the challenges posed by low testosterone effectively.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Environmental Toxins and Testosterone: Impacts and Mitigation Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 9th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone in American Males: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on Muscle Mass and Strength in American Males [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Vitamin D's Role in Managing Low Testosterone in American Men: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Chronic Illness Impact on Low Testosterone in American Males: Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Managing Low Testosterone in Aging Men: Symptoms, Treatments, and Lifestyle Strategies [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Economic Burden of Low Testosterone on American Healthcare System [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Diabetes: Dual Challenges Impacting American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Alcohol Consumption and Its Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Zinc's Role in Boosting Testosterone Levels in American Men: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Mood Disorders: Impact and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Low Testosterone in American Men: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Strategies [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Smoking's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Men: Risks and Recovery [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on Osteoporosis Risk in American Men: Detection and Management [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Prostate Health: Risks, Therapy, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Hair Loss: Understanding the Link and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on Cognitive Function in American Men: Insights and Interventions [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Shift Work's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Men: Health Implications and Mitigation [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on Immune Health in American Males: Insights and Management [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Optimizing Testosterone Levels: Dietary Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Low Testosterone in American Men: Symptoms, Impact, and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Environmental Estrogens: A Hidden Cause of Low Testosterone in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on Skin Health in American Men: Causes and Management [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Weight Loss Boosts Testosterone: A Guide for American Males with Low T [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Herbal Supplements for Low Testosterone: Benefits, Limitations, and Efficacy in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Managing Low Testosterone in Aging Men: Symptoms, Treatments, and Lifestyle Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Heart Disease: Risks, Mechanisms, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Chronic Stress Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Men: Causes and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on Emotional Wellbeing in American Men: Insights and Guidance [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Depression: Understanding the Link and Its Impact on American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Sleep Apnea's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males: Insights and Solutions [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Medications Impacting Testosterone Levels: Insights for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Metabolic Syndrome: Implications for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Chronic Pain's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Genetic Factors in Low Testosterone Among American Males: Insights and Implications [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Increased Thyroid Disorder Risk in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Insulin Resistance: Exploring the Link in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Exercise Boosts Testosterone: A Guide for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Libido: Impacts, Diagnosis, and Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on Body Composition in American Males: Challenges and Management [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Skin Health: Dermatological Impacts and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Chronic Inflammation and Low Testosterone: Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Nutrition's Impact on Testosterone: Deficiencies and Dietary Solutions for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Respiratory Health's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone's Role and Managing Low Levels in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Anemia Risk in American Men: Insights and Management [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Autoimmune Diseases in American Men: Insights and Management [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Liver Health Crucial for Testosterone Balance in American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Gut Health and Testosterone: Optimizing Hormonal Balance in American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Increased Kidney Disease Risk in American Men [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Dental Health's Role in Managing Low Testosterone in American Males [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Neurological Risks in American Men: Implications and Interventions [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Increased Eye Disorder Risk in American Men [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on Musculoskeletal Health in American Men: Risks and Interventions [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- ENT Health's Crucial Role in Maintaining Testosterone Levels in American Men [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Reproductive Health's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Levels Increase Infectious Disease Risk in American Men: Emerging Evidence [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Hematological Risks in American Men: Screening and Treatment Insights [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Managing Low Testosterone: Endocrine Health and Holistic Approaches for American Males [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Immunological Health's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males: A Holistic Approach [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Cancer's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Men: Challenges and Management [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Increased Psychiatric Disorders in American Men: Implications and Treatments [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Urological Health: Risks, Links, and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Testosterone Levels and Wound Healing in American Males: A Bidirectional Impact Study [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Increased Vascular Disorder Risk in American Men [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on Surgical Risks in American Men: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Trauma's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males: Mechanisms and Management [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
Word Count: 556