Introduction
Testosterone, the primary male sex hormone, plays a crucial role in various aspects of men's health, including muscle mass, bone density, and sexual function. In recent years, there has been a growing concern about the prevalence of low testosterone (low T) among American males. This article explores the intricate relationship between reproductive health and testosterone levels, shedding light on how reproductive factors can influence testosterone production and overall well-being.
The Prevalence of Low Testosterone
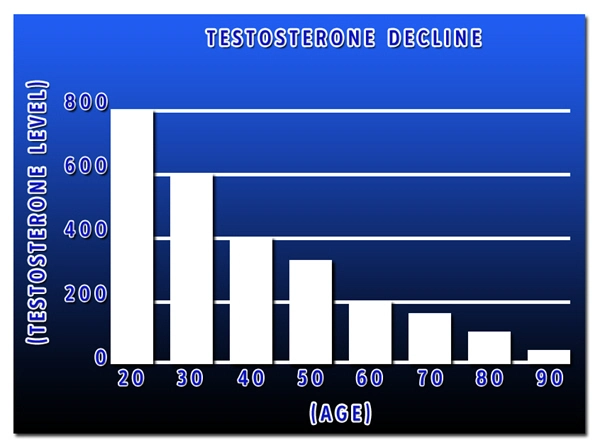
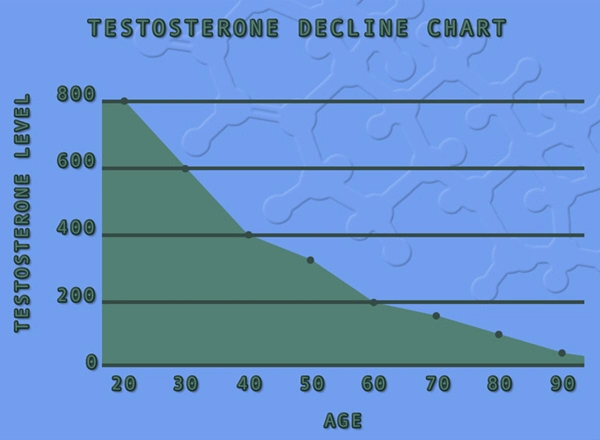
Low testosterone, clinically defined as a total testosterone level below 300 ng/dL, has become increasingly common among American men. Studies suggest that approximately 40% of men aged 45 and older may experience low T. This condition can lead to a range of symptoms, including decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, fatigue, and mood changes. Understanding the factors contributing to low T is essential for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies.
Reproductive Health and Testosterone Production
Reproductive health plays a significant role in testosterone production. The hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis, which regulates testosterone synthesis, is closely linked to reproductive function. Any disruptions in this axis can lead to decreased testosterone levels. Factors such as infertility, hypogonadism, and certain reproductive disorders can directly impact testosterone production.
Infertility and Testosterone Levels
Infertility, affecting approximately 15% of couples in the United States, can have a profound impact on testosterone levels. Men with infertility often exhibit lower testosterone levels compared to fertile men. This association may be due to underlying conditions such as varicocele, a common cause of male infertility, which can impair testicular function and testosterone production. Addressing infertility through appropriate medical interventions can help restore normal testosterone levels and improve overall reproductive health.
Hypogonadism and Its Effects
Hypogonadism, a condition characterized by the body's inability to produce sufficient testosterone, is another significant factor contributing to low T. Primary hypogonadism, resulting from testicular failure, and secondary hypogonadism, caused by dysfunction in the hypothalamus or pituitary gland, can both lead to decreased testosterone levels. Men with hypogonadism often experience a range of symptoms associated with low T, emphasizing the importance of early diagnosis and treatment.
Reproductive Disorders and Testosterone
Certain reproductive disorders, such as Klinefelter syndrome and cryptorchidism, can also impact testosterone levels. Klinefelter syndrome, a genetic condition affecting approximately 1 in 500 to 1,000 newborn males, is characterized by an extra X chromosome, leading to reduced testosterone production. Cryptorchidism, or undescended testicles, can impair testicular function and contribute to low T if not addressed promptly. Identifying and managing these disorders early in life can help mitigate their impact on testosterone levels.
Lifestyle Factors and Reproductive Health
In addition to medical conditions, lifestyle factors can influence reproductive health and testosterone levels. Obesity, a growing concern among American men, is strongly associated with low T. Excess body fat can lead to increased aromatase activity, converting testosterone to estrogen and reducing overall testosterone levels. Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and a balanced diet, can help improve reproductive health and maintain optimal testosterone levels.
The Role of Stress and Mental Health
Stress and mental health also play a crucial role in reproductive health and testosterone production. Chronic stress can disrupt the HPG axis, leading to decreased testosterone levels. Additionally, conditions such as depression and anxiety can contribute to low T. Addressing mental health concerns through therapy, stress management techniques, and, if necessary, medication can help support healthy testosterone levels and overall well-being.
Conclusion
The relationship between reproductive health and testosterone levels in American males is complex and multifaceted. Factors such as infertility, hypogonadism, reproductive disorders, lifestyle choices, and mental health can all impact testosterone production. By understanding these connections, men can take proactive steps to maintain optimal reproductive health and testosterone levels. Regular check-ups, early intervention for reproductive issues, and a healthy lifestyle can all contribute to better overall health and well-being. As research continues to uncover the intricacies of this relationship, it is essential for men to prioritize their reproductive health to ensure a vibrant and fulfilling life.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Environmental Toxins and Testosterone: Impacts and Mitigation Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 9th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone in American Males: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on Muscle Mass and Strength in American Males [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Vitamin D's Role in Managing Low Testosterone in American Men: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Chronic Illness Impact on Low Testosterone in American Males: Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Managing Low Testosterone in Aging Men: Symptoms, Treatments, and Lifestyle Strategies [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Economic Burden of Low Testosterone on American Healthcare System [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Diabetes: Dual Challenges Impacting American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Alcohol Consumption and Its Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Zinc's Role in Boosting Testosterone Levels in American Men: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Mood Disorders: Impact and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Low Testosterone in American Men: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Strategies [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Smoking's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Men: Risks and Recovery [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on Osteoporosis Risk in American Men: Detection and Management [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Prostate Health: Risks, Therapy, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Hair Loss: Understanding the Link and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on Cognitive Function in American Men: Insights and Interventions [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Shift Work's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Men: Health Implications and Mitigation [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on Immune Health in American Males: Insights and Management [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Optimizing Testosterone Levels: Dietary Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Low Testosterone in American Men: Symptoms, Impact, and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Environmental Estrogens: A Hidden Cause of Low Testosterone in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on Skin Health in American Men: Causes and Management [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Weight Loss Boosts Testosterone: A Guide for American Males with Low T [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Herbal Supplements for Low Testosterone: Benefits, Limitations, and Efficacy in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Managing Low Testosterone in Aging Men: Symptoms, Treatments, and Lifestyle Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Heart Disease: Risks, Mechanisms, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Chronic Stress Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Men: Causes and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on Emotional Wellbeing in American Men: Insights and Guidance [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Depression: Understanding the Link and Its Impact on American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Sleep Apnea's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males: Insights and Solutions [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Medications Impacting Testosterone Levels: Insights for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Metabolic Syndrome: Implications for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Chronic Pain's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Genetic Factors in Low Testosterone Among American Males: Insights and Implications [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Increased Thyroid Disorder Risk in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Insulin Resistance: Exploring the Link in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Exercise Boosts Testosterone: A Guide for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Libido: Impacts, Diagnosis, and Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on Body Composition in American Males: Challenges and Management [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Skin Health: Dermatological Impacts and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Chronic Inflammation and Low Testosterone: Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Nutrition's Impact on Testosterone: Deficiencies and Dietary Solutions for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Respiratory Health's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone's Role and Managing Low Levels in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Anemia Risk in American Men: Insights and Management [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Autoimmune Diseases in American Men: Insights and Management [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Liver Health Crucial for Testosterone Balance in American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Gut Health and Testosterone: Optimizing Hormonal Balance in American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Increased Kidney Disease Risk in American Men [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Dental Health's Role in Managing Low Testosterone in American Males [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Neurological Risks in American Men: Implications and Interventions [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Increased Eye Disorder Risk in American Men [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on Musculoskeletal Health in American Men: Risks and Interventions [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- ENT Health's Crucial Role in Maintaining Testosterone Levels in American Men [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Levels Increase Infectious Disease Risk in American Men: Emerging Evidence [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Hematological Risks in American Men: Screening and Treatment Insights [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Managing Low Testosterone: Endocrine Health and Holistic Approaches for American Males [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Immunological Health's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males: A Holistic Approach [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Cancer's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Men: Challenges and Management [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Increased Psychiatric Disorders in American Men: Implications and Treatments [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Urological Health: Risks, Links, and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Testosterone Levels and Wound Healing in American Males: A Bidirectional Impact Study [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Increased Vascular Disorder Risk in American Men [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Rheumatological Disorders and Low Testosterone: Insights and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on Surgical Risks in American Men: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Trauma's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males: Mechanisms and Management [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Genetic Disorders: Risks and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Developmental Health Impacts on Testosterone Levels in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone in American Men Linked to Increased Congenital Disorder Risk in Offspring [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone in American Men Linked to Pediatric Disorders in Offspring [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Occupational Health Impacts on Testosterone Levels in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Increased Allergic Reactions in American Men: Emerging Evidence [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Anesthetic Health and Its Impact on Low Testosterone in American Males [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Risks in Aging American Men: Health Impacts and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Neonatal Health's Long-term Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- Prenatal Health's Impact on Adult Male Testosterone Levels and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- Managing Low Testosterone: Diagnosis, Treatment Options, and Lifestyle Strategies [Last Updated On: April 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 22nd, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Higher Type 2 Diabetes Risk in American Males [Last Updated On: April 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 22nd, 2025]
- Low Testosterone in American Men: Symptoms, Risks, and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: April 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 22nd, 2025]
Word Count: 649