Introduction
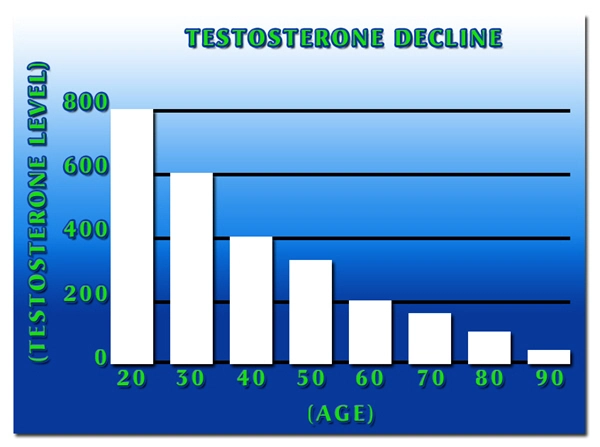
Testosterone, the primary male sex hormone, plays a crucial role in regulating various physiological processes, including muscle mass, bone density, and libido. Recent studies have highlighted a concerning trend: a decline in testosterone levels among American males. While various factors contribute to this phenomenon, occupational health emerges as a significant yet often overlooked determinant. This article delves into the impact of occupational health on testosterone levels, with a particular focus on the implications for men experiencing low testosterone.
Occupational Stress and Testosterone
Occupational stress is a pervasive issue that can significantly affect testosterone levels. Chronic stress, often resulting from demanding work environments, triggers the release of cortisol, a stress hormone that can inhibit testosterone production. American males working in high-stress professions, such as finance, law, or emergency services, are particularly vulnerable to this effect. Prolonged exposure to stress can lead to a sustained decrease in testosterone, contributing to symptoms of low testosterone, such as fatigue, reduced libido, and mood disturbances.
Shift Work and Circadian Rhythm Disruption
Shift work, prevalent in industries like healthcare, transportation, and manufacturing, disrupts the body's natural circadian rhythms. This disruption can have a detrimental impact on testosterone levels. Research indicates that men working night shifts or rotating shifts experience lower testosterone levels compared to those working regular daytime hours. The misalignment of sleep-wake cycles and the suppression of melatonin production, which is crucial for maintaining healthy testosterone levels, are key factors in this association. American males engaged in shift work should be aware of these risks and consider strategies to mitigate the impact on their hormonal health.
Physical Demands and Testosterone
The physical demands of certain occupations can also influence testosterone levels. Jobs that require heavy lifting, intense physical exertion, or prolonged standing can lead to increased testosterone production in the short term. However, chronic overexertion without adequate recovery can result in overtraining syndrome, which is associated with decreased testosterone levels. American males in physically demanding professions, such as construction, firefighting, or professional sports, must balance their physical activity with sufficient rest to maintain optimal testosterone levels.
Exposure to Environmental Toxins
Occupational exposure to environmental toxins, such as heavy metals, pesticides, and endocrine-disrupting chemicals, poses another threat to testosterone levels. These substances can interfere with the endocrine system, leading to hormonal imbalances. Industries with high exposure risks include agriculture, mining, and chemical manufacturing. American males working in these sectors should be vigilant about protective measures and regular health screenings to monitor their testosterone levels and overall hormonal health.
Strategies for Maintaining Healthy Testosterone Levels
To mitigate the impact of occupational health on testosterone levels, American males can adopt several strategies. Firstly, managing stress through techniques like mindfulness, exercise, and adequate sleep can help maintain healthy cortisol levels and support testosterone production. Secondly, for those engaged in shift work, maintaining a consistent sleep schedule and creating a dark, quiet sleep environment can help preserve circadian rhythms. Thirdly, balancing physical activity with rest and recovery is crucial for those in physically demanding jobs. Finally, minimizing exposure to environmental toxins through the use of personal protective equipment and adhering to safety protocols can reduce the risk of hormonal disruption.
Conclusion
The relationship between occupational health and testosterone levels is a critical consideration for American males, particularly those experiencing symptoms of low testosterone. By understanding the various occupational factors that can influence testosterone production, men can take proactive steps to safeguard their hormonal health. Employers also play a vital role in creating work environments that support the well-being of their male employees. Through a combination of individual efforts and workplace initiatives, American males can better manage the impact of their occupations on their testosterone levels and overall health.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Environmental Toxins and Testosterone: Impacts and Mitigation Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 9th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone in American Males: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on Muscle Mass and Strength in American Males [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Vitamin D's Role in Managing Low Testosterone in American Men: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Chronic Illness Impact on Low Testosterone in American Males: Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Managing Low Testosterone in Aging Men: Symptoms, Treatments, and Lifestyle Strategies [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Economic Burden of Low Testosterone on American Healthcare System [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Diabetes: Dual Challenges Impacting American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Alcohol Consumption and Its Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Zinc's Role in Boosting Testosterone Levels in American Men: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Mood Disorders: Impact and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Low Testosterone in American Men: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Strategies [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Smoking's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Men: Risks and Recovery [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on Osteoporosis Risk in American Men: Detection and Management [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Prostate Health: Risks, Therapy, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Hair Loss: Understanding the Link and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on Cognitive Function in American Men: Insights and Interventions [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Shift Work's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Men: Health Implications and Mitigation [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on Immune Health in American Males: Insights and Management [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Optimizing Testosterone Levels: Dietary Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Low Testosterone in American Men: Symptoms, Impact, and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Environmental Estrogens: A Hidden Cause of Low Testosterone in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on Skin Health in American Men: Causes and Management [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Weight Loss Boosts Testosterone: A Guide for American Males with Low T [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Herbal Supplements for Low Testosterone: Benefits, Limitations, and Efficacy in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Managing Low Testosterone in Aging Men: Symptoms, Treatments, and Lifestyle Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Heart Disease: Risks, Mechanisms, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Chronic Stress Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Men: Causes and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on Emotional Wellbeing in American Men: Insights and Guidance [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Depression: Understanding the Link and Its Impact on American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Sleep Apnea's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males: Insights and Solutions [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Medications Impacting Testosterone Levels: Insights for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Metabolic Syndrome: Implications for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Chronic Pain's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Genetic Factors in Low Testosterone Among American Males: Insights and Implications [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Increased Thyroid Disorder Risk in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Insulin Resistance: Exploring the Link in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Exercise Boosts Testosterone: A Guide for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Libido: Impacts, Diagnosis, and Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on Body Composition in American Males: Challenges and Management [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Skin Health: Dermatological Impacts and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Chronic Inflammation and Low Testosterone: Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Nutrition's Impact on Testosterone: Deficiencies and Dietary Solutions for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Respiratory Health's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone's Role and Managing Low Levels in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Anemia Risk in American Men: Insights and Management [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Autoimmune Diseases in American Men: Insights and Management [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Liver Health Crucial for Testosterone Balance in American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Gut Health and Testosterone: Optimizing Hormonal Balance in American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Increased Kidney Disease Risk in American Men [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Dental Health's Role in Managing Low Testosterone in American Males [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Neurological Risks in American Men: Implications and Interventions [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Increased Eye Disorder Risk in American Men [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on Musculoskeletal Health in American Men: Risks and Interventions [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- ENT Health's Crucial Role in Maintaining Testosterone Levels in American Men [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Reproductive Health's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Levels Increase Infectious Disease Risk in American Men: Emerging Evidence [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Hematological Risks in American Men: Screening and Treatment Insights [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Managing Low Testosterone: Endocrine Health and Holistic Approaches for American Males [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Immunological Health's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males: A Holistic Approach [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Cancer's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Men: Challenges and Management [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Increased Psychiatric Disorders in American Men: Implications and Treatments [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Urological Health: Risks, Links, and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Testosterone Levels and Wound Healing in American Males: A Bidirectional Impact Study [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Increased Vascular Disorder Risk in American Men [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Rheumatological Disorders and Low Testosterone: Insights and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on Surgical Risks in American Men: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Trauma's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males: Mechanisms and Management [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Genetic Disorders: Risks and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Developmental Health Impacts on Testosterone Levels in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone in American Men Linked to Increased Congenital Disorder Risk in Offspring [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone in American Men Linked to Pediatric Disorders in Offspring [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Increased Allergic Reactions in American Men: Emerging Evidence [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Anesthetic Health and Its Impact on Low Testosterone in American Males [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Risks in Aging American Men: Health Impacts and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Neonatal Health's Long-term Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- Prenatal Health's Impact on Adult Male Testosterone Levels and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
Word Count: 609