Introduction
Osteoporosis, a condition characterized by weakened bones and an increased risk of fractures, is often associated with aging and predominantly affects women. However, recent research has shed light on the significant impact of low testosterone levels on bone health in American men. This article explores the relationship between low testosterone and the risk of osteoporosis, emphasizing the importance of early detection and management in male patients.
Understanding Osteoporosis in Men
Osteoporosis is not exclusive to women; it poses a substantial health concern for men as well. In the United States, approximately 2 million men are affected by this condition, with an additional 12 million at risk. The consequences of osteoporosis in men can be severe, as they are more likely to suffer fractures and experience higher mortality rates following such incidents compared to women.
The Role of Testosterone in Bone Health
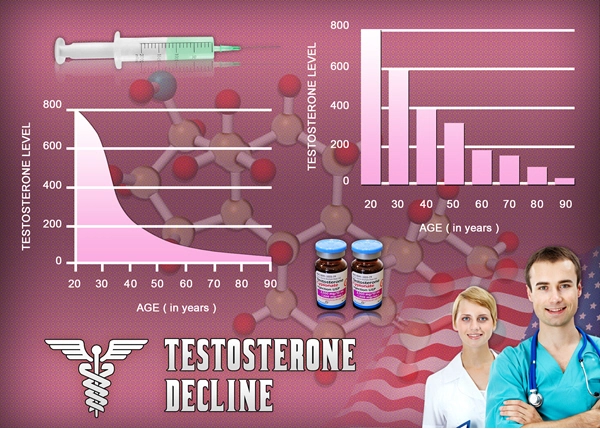
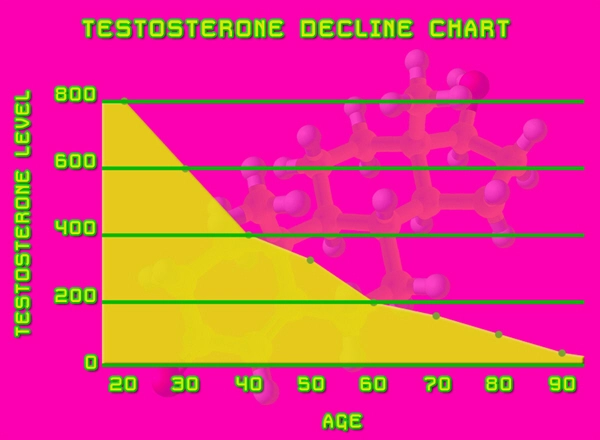
Testosterone, the primary male sex hormone, plays a crucial role in maintaining bone density and strength. It stimulates the activity of osteoblasts, the cells responsible for bone formation, and inhibits the activity of osteoclasts, which break down bone tissue. As men age, their testosterone levels naturally decline, which can lead to a gradual loss of bone mass and an increased risk of osteoporosis.
Low Testosterone and Osteoporosis: The Connection
Numerous studies have established a strong link between low testosterone levels and the development of osteoporosis in men. A study published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism found that men with low testosterone levels had significantly lower bone mineral density compared to those with normal levels. Another study in the Journal of Bone and Mineral Research demonstrated that men with hypogonadism, a condition characterized by low testosterone, had a higher incidence of vertebral fractures.
Risk Factors and Screening
Several factors can contribute to low testosterone levels and an increased risk of osteoporosis in American men. These include aging, obesity, chronic diseases such as diabetes and hypogonadism, and certain medications like glucocorticoids and anticonvulsants. Men with these risk factors should undergo regular screening for both low testosterone and osteoporosis.
The Endocrine Society recommends that men over the age of 65 and those with clinical manifestations of testosterone deficiency should be screened for low testosterone levels. Additionally, the National Osteoporosis Foundation suggests that men over 70, or those between 50 and 69 with risk factors, should undergo bone density testing to assess their risk of osteoporosis.
Treatment and Management
Addressing low testosterone and osteoporosis in men requires a multifaceted approach. Testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) can be an effective treatment for men with hypogonadism, as it has been shown to improve bone mineral density and reduce the risk of fractures. However, TRT should be carefully monitored and managed by a healthcare professional to minimize potential side effects.
In addition to TRT, lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in managing osteoporosis. Regular weight-bearing exercise, a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D, and smoking cessation can all contribute to maintaining bone health. In some cases, medications such as bisphosphonates or denosumab may be prescribed to further reduce the risk of fractures.
Conclusion
The link between low testosterone and osteoporosis in American men is a growing concern that warrants increased awareness and proactive management. By understanding the role of testosterone in bone health and recognizing the risk factors associated with low testosterone and osteoporosis, healthcare providers can implement early screening and intervention strategies. Through a combination of testosterone replacement therapy, lifestyle modifications, and appropriate medications, men can take control of their bone health and reduce their risk of osteoporosis-related complications. As research continues to unravel the complexities of this relationship, it is essential for men to prioritize their bone health and work closely with their healthcare providers to maintain optimal testosterone levels and strong, healthy bones.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Environmental Toxins and Testosterone: Impacts and Mitigation Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 9th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone in American Males: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on Muscle Mass and Strength in American Males [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Vitamin D's Role in Managing Low Testosterone in American Men: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Chronic Illness Impact on Low Testosterone in American Males: Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Managing Low Testosterone in Aging Men: Symptoms, Treatments, and Lifestyle Strategies [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Economic Burden of Low Testosterone on American Healthcare System [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Diabetes: Dual Challenges Impacting American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Alcohol Consumption and Its Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Zinc's Role in Boosting Testosterone Levels in American Men: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Mood Disorders: Impact and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Low Testosterone in American Men: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Strategies [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Smoking's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Men: Risks and Recovery [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Prostate Health: Risks, Therapy, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Hair Loss: Understanding the Link and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on Cognitive Function in American Men: Insights and Interventions [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Shift Work's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Men: Health Implications and Mitigation [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on Immune Health in American Males: Insights and Management [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Optimizing Testosterone Levels: Dietary Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Low Testosterone in American Men: Symptoms, Impact, and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Environmental Estrogens: A Hidden Cause of Low Testosterone in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on Skin Health in American Men: Causes and Management [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Weight Loss Boosts Testosterone: A Guide for American Males with Low T [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Herbal Supplements for Low Testosterone: Benefits, Limitations, and Efficacy in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Managing Low Testosterone in Aging Men: Symptoms, Treatments, and Lifestyle Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Heart Disease: Risks, Mechanisms, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Chronic Stress Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Men: Causes and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on Emotional Wellbeing in American Men: Insights and Guidance [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Depression: Understanding the Link and Its Impact on American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Sleep Apnea's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males: Insights and Solutions [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Medications Impacting Testosterone Levels: Insights for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Metabolic Syndrome: Implications for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Chronic Pain's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Genetic Factors in Low Testosterone Among American Males: Insights and Implications [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Increased Thyroid Disorder Risk in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Insulin Resistance: Exploring the Link in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Exercise Boosts Testosterone: A Guide for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Libido: Impacts, Diagnosis, and Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on Body Composition in American Males: Challenges and Management [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Skin Health: Dermatological Impacts and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Chronic Inflammation and Low Testosterone: Strategies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Nutrition's Impact on Testosterone: Deficiencies and Dietary Solutions for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Respiratory Health's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone's Role and Managing Low Levels in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Anemia Risk in American Men: Insights and Management [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Autoimmune Diseases in American Men: Insights and Management [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Liver Health Crucial for Testosterone Balance in American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Gut Health and Testosterone: Optimizing Hormonal Balance in American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Increased Kidney Disease Risk in American Men [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Dental Health's Role in Managing Low Testosterone in American Males [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Neurological Risks in American Men: Implications and Interventions [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Increased Eye Disorder Risk in American Men [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on Musculoskeletal Health in American Men: Risks and Interventions [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- ENT Health's Crucial Role in Maintaining Testosterone Levels in American Men [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Reproductive Health's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Levels Increase Infectious Disease Risk in American Men: Emerging Evidence [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Hematological Risks in American Men: Screening and Treatment Insights [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Managing Low Testosterone: Endocrine Health and Holistic Approaches for American Males [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Immunological Health's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males: A Holistic Approach [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Cancer's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Men: Challenges and Management [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Increased Psychiatric Disorders in American Men: Implications and Treatments [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Urological Health: Risks, Links, and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Testosterone Levels and Wound Healing in American Males: A Bidirectional Impact Study [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Increased Vascular Disorder Risk in American Men [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Rheumatological Disorders and Low Testosterone: Insights and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone's Impact on Surgical Risks in American Men: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Trauma's Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males: Mechanisms and Management [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone and Genetic Disorders: Risks and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Developmental Health Impacts on Testosterone Levels in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone in American Men Linked to Increased Congenital Disorder Risk in Offspring [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone in American Men Linked to Pediatric Disorders in Offspring [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Occupational Health Impacts on Testosterone Levels in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Linked to Increased Allergic Reactions in American Men: Emerging Evidence [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Anesthetic Health and Its Impact on Low Testosterone in American Males [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Low Testosterone Risks in Aging American Men: Health Impacts and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Neonatal Health's Long-term Impact on Testosterone Levels in American Males [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- Prenatal Health's Impact on Adult Male Testosterone Levels and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
Word Count: 619