Introduction to Late-Onset Hypogonadism
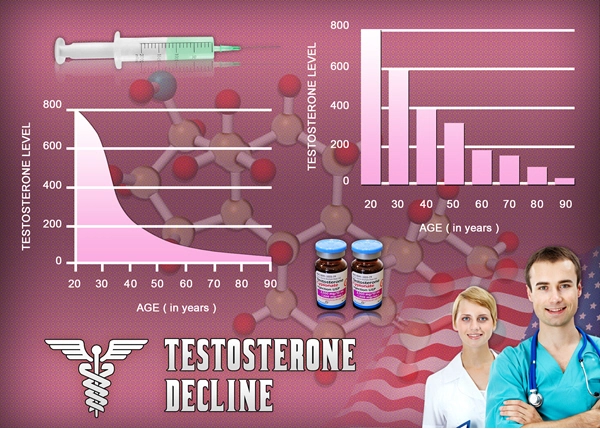
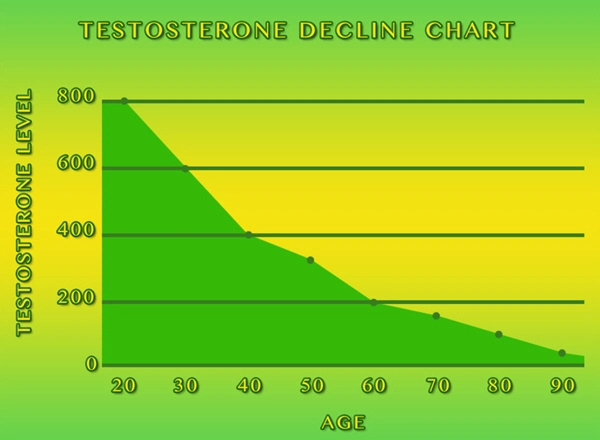
Late-onset hypogonadism (LOH), also known as age-related low testosterone, is a clinical and biochemical syndrome associated with advancing age in men. It is characterized by a deficiency in serum testosterone levels, coupled with symptoms such as reduced libido, erectile dysfunction, decreased muscle mass, increased body fat, and mood disturbances. In the United States, where the aging male population is on the rise, understanding and managing LOH has become increasingly important.
The Prevalence of LOH in American Men
Estimates suggest that LOH affects approximately 20% to 30% of men over the age of 60 in the US. As life expectancy continues to increase, the number of men experiencing symptoms of LOH is expected to grow. This underscores the need for effective strategies to diagnose and treat this condition, ensuring that American men can maintain their quality of life as they age.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of LOH
The symptoms of LOH can be subtle and may be attributed to the normal aging process, which often leads to underdiagnosis. Common symptoms include fatigue, depression, decreased physical performance, and cognitive decline. To diagnose LOH, healthcare providers typically measure serum testosterone levels, often in the morning when levels are highest. A thorough clinical evaluation is also essential to rule out other conditions that may mimic LOH symptoms.
The Importance of a Multidisciplinary Approach
Given the multifaceted nature of LOH, a multidisciplinary approach is crucial for effective management. This involves collaboration among various healthcare professionals, including endocrinologists, urologists, psychologists, and primary care physicians. Each specialist brings a unique perspective and set of skills to the table, ensuring comprehensive care for the patient.
Endocrinological Management
Endocrinologists play a pivotal role in the management of LOH by overseeing hormone replacement therapy (HRT). Testosterone replacement can alleviate many of the symptoms associated with LOH, but it must be carefully monitored to avoid potential side effects such as an increased risk of cardiovascular events or prostate issues. Regular follow-up appointments are essential to adjust dosages and monitor the patient's response to treatment.
Urological Considerations
Urologists are instrumental in addressing the sexual health aspects of LOH, such as erectile dysfunction. They can provide guidance on the use of phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors (PDE5Is) and other treatments that can enhance sexual function. Additionally, urologists can monitor for prostate health, which is crucial given the potential link between testosterone therapy and prostate cancer.
Psychological Support
The psychological impact of LOH should not be underestimated. Symptoms such as depression and mood swings can significantly affect a man's quality of life. Psychologists and counselors can offer support through cognitive-behavioral therapy and other interventions, helping patients cope with the emotional challenges of LOH.
Primary Care and Lifestyle Interventions
Primary care physicians are often the first point of contact for men experiencing symptoms of LOH. They can initiate the diagnostic process and coordinate care with other specialists. Additionally, primary care providers can emphasize the importance of lifestyle interventions, such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, and adequate sleep, which can mitigate some of the symptoms of LOH.
The Role of Patient Education
Educating patients about LOH is a critical component of a multidisciplinary approach. Men need to understand the potential benefits and risks of testosterone therapy, as well as the importance of adhering to treatment plans and lifestyle recommendations. Patient education can empower men to take an active role in managing their health.
Conclusion: A Collaborative Path Forward
Late-onset hypogonadism presents a significant challenge for American men, but with a multidisciplinary approach, it can be effectively managed. By fostering collaboration among healthcare professionals and prioritizing patient education, we can improve outcomes for men with LOH, helping them lead healthier and more fulfilling lives as they age.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Exploring Alternatives to TRT for Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 9th, 2025]
- Nutrition's Role in Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Future of Late-Onset Hypogonadism Treatment: Innovations and Personalized Approaches [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on Mood, Energy, and Quality of Life in American Men [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Genetic Insights into Late-Onset Hypogonadism in Aging American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Effects on Muscle Mass and Treatment Options in American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Prevalence, Economic Impact, and Management Challenges in American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Preventing Complications of Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men: Strategies and Insights [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on Fertility and Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Exercise as a Key Strategy for Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Early Detection and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Hormone Replacement Therapy for Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Benefits, Risks, and Guidelines [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Understanding and Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men Over 40 [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Emotional Challenges and Support for American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Stress Exacerbates Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males: Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Understanding Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impacts and Management in Aging Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Exploring the Link Between Late-Onset Hypogonadism and Diabetes in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Understanding Symptoms, Impacts, and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on Sleep and Holistic Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism's Cognitive Impact in American Men: Awareness and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Understanding TRT Benefits and Risks in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Understanding Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Impact, and Management for American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options for American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Dietary Strategies to Manage Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Understanding Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Prevalence, Symptoms, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Prevalence, Risks, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Diagnosing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Testing, and Challenges in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Overcoming Stigma and Enhancing Men's Health in America [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Understanding Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Impact, and Management for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Early Intervention Benefits for Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males: Importance of Monitoring and Management [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Advocating for Better Late-Onset Hypogonadism Care: A Call to Action for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Understanding, Managing, and Maintaining Independence in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Advanced Technology Enhances LOH Diagnosis in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment for Aging Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatments, and Lifestyle Management for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Understanding Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on Intimate Relationships and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Cultural Perceptions and Management of Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Understanding Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Myths, Facts, and Management for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Legal Aspects of Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Rights in the U.S. [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Holistic Treatment of Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males: A Comprehensive Approach [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: The Crucial Role of Mental Health Professionals [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Community Support Enhances Management of Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Family Support Crucial for American Males with Late-Onset Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impacts and Strategies for Career Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Financial Implications and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on Self-Esteem and Treatment Options for American Men [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Peer Support Enhances Life Quality for American Males with Late-Onset Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Lifestyle Strategies for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Navigating Insurance Coverage for Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Diagnosis and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Understanding Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Treatment, and Lifestyle Management for American Males [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Research Advances in Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Lifestyle Impact [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Social Impact, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Strategies for Mental Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Stress, Nutrition, and Holistic Approaches for American Men [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men: Advocacy and Personalized Care [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Nutritionists' Role in Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Exercise Strategies to Combat Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Prevalence, Impact, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Understanding and Managing Emotional Impacts in Men Over 40 [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
- Endocrinologists' Vital Role in Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in Aging American Males [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Lifestyle and Medical Interventions for American Men [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Comprehensive Care Strategies [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Holistic Management Strategies for Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact and Strategies for American Men's Sexual Health [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact, Research, and Future Directions in American Men's Health [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Community Resources and Support for American Men [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on American Men's Professional Lives and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Therapists' Vital Role in Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
Word Count: 610