Introduction to Late-Onset Hypogonadism
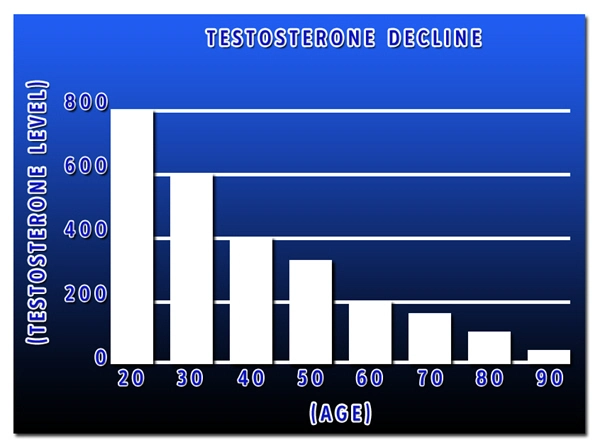
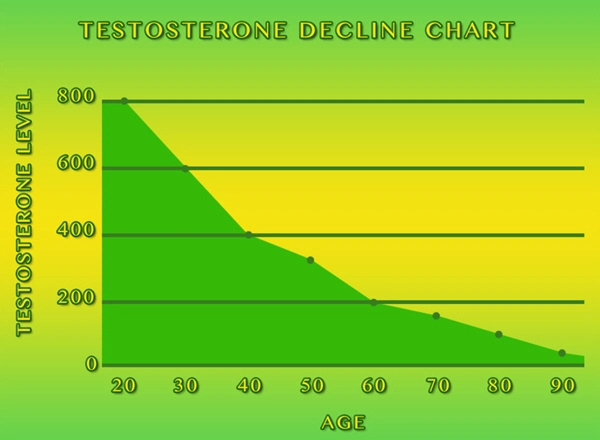
Late-onset hypogonadism (LOH), also known as age-related low testosterone, is a clinical and biochemical syndrome characterized by a deficiency in serum testosterone levels in conjunction with specific signs and symptoms. As men age, testosterone levels naturally decline, but for some, this drop can lead to significant health issues. LOH is increasingly recognized as a prevalent condition among American men, particularly those over the age of 40, with a profound impact on their quality of life and healthcare economics.
Prevalence and Diagnosis of LOH
The prevalence of LOH is estimated to affect between 2% to 6% of men in their 40s, increasing to 20% to 30% in men over 60. Diagnosis involves a combination of clinical symptoms, such as reduced libido, erectile dysfunction, fatigue, and mood disturbances, alongside biochemical confirmation of low testosterone levels. Accurate diagnosis is crucial, as it guides appropriate treatment and mitigates the economic burden on healthcare systems.
Economic Impact on Healthcare
The economic implications of LOH are multifaceted. Firstly, the direct costs associated with diagnosis and treatment are significant. These include laboratory tests, physician consultations, and medications, such as testosterone replacement therapy (TRT). According to recent studies, the annual cost of TRT alone can range from $500 to $1,500 per patient, depending on the formulation and dosage.
Beyond direct costs, LOH contributes to indirect economic burdens. Untreated or inadequately managed LOH can lead to a range of comorbidities, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and osteoporosis, which further escalate healthcare expenditures. Moreover, the impact on workforce productivity due to symptoms like fatigue and depression cannot be overlooked. Men with LOH may experience reduced work efficiency, increased absenteeism, and higher rates of early retirement, all of which have substantial economic repercussions.
Challenges in Managing LOH
Managing LOH presents several challenges that exacerbate its economic impact. One major issue is the variability in clinical guidelines and diagnostic criteria, which can lead to overdiagnosis or underdiagnosis. This inconsistency not only affects patient outcomes but also drives up healthcare costs due to unnecessary treatments or delayed interventions.
Additionally, the long-term safety and efficacy of TRT remain subjects of ongoing research and debate. While TRT can significantly improve symptoms and quality of life for many men, potential side effects and the need for continuous monitoring add to the economic burden. Healthcare providers must balance the benefits of treatment against these costs, ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently.
Strategies for Mitigating Economic Impact
To address the economic challenges posed by LOH, a multifaceted approach is necessary. Enhanced education and awareness among healthcare professionals and the public can lead to earlier diagnosis and more effective management, potentially reducing long-term healthcare costs. Standardization of diagnostic and treatment protocols can also streamline care and reduce variability in practice.
Furthermore, investment in research to better understand the long-term effects of LOH and TRT can inform more cost-effective treatment strategies. Policymakers and healthcare systems should consider the broader economic implications of LOH, advocating for preventive measures and integrated care models that address both the physical and psychological aspects of the condition.
Conclusion
Late-onset hypogonadism represents a significant health and economic challenge for American men. By understanding its prevalence, economic impact, and the challenges in its management, stakeholders can develop strategies to mitigate its burden. Through improved diagnosis, treatment, and research, it is possible to enhance the quality of life for men with LOH while reducing the economic strain on healthcare systems.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Exploring Alternatives to TRT for Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 9th, 2025]
- Nutrition's Role in Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Future of Late-Onset Hypogonadism Treatment: Innovations and Personalized Approaches [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on Mood, Energy, and Quality of Life in American Men [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Genetic Insights into Late-Onset Hypogonadism in Aging American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Effects on Muscle Mass and Treatment Options in American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Preventing Complications of Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men: Strategies and Insights [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on Fertility and Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Exercise as a Key Strategy for Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Early Detection and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Hormone Replacement Therapy for Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Benefits, Risks, and Guidelines [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Understanding and Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men Over 40 [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Emotional Challenges and Support for American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Stress Exacerbates Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males: Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Understanding Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impacts and Management in Aging Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Exploring the Link Between Late-Onset Hypogonadism and Diabetes in American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Understanding Symptoms, Impacts, and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on Sleep and Holistic Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism's Cognitive Impact in American Men: Awareness and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Understanding TRT Benefits and Risks in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Understanding Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Impact, and Management for American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options for American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Dietary Strategies to Manage Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Understanding Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Prevalence, Symptoms, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Prevalence, Risks, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Diagnosing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Testing, and Challenges in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Overcoming Stigma and Enhancing Men's Health in America [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Understanding Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Impact, and Management for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Early Intervention Benefits for Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males: Importance of Monitoring and Management [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: A Multidisciplinary Approach for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Advocating for Better Late-Onset Hypogonadism Care: A Call to Action for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Understanding, Managing, and Maintaining Independence in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Advanced Technology Enhances LOH Diagnosis in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment for Aging Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatments, and Lifestyle Management for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Understanding Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on Intimate Relationships and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Cultural Perceptions and Management of Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Understanding Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Myths, Facts, and Management for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Legal Aspects of Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Rights in the U.S. [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Holistic Treatment of Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males: A Comprehensive Approach [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: The Crucial Role of Mental Health Professionals [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Community Support Enhances Management of Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Family Support Crucial for American Males with Late-Onset Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impacts and Strategies for Career Management in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Financial Implications and Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Impact on Self-Esteem and Treatment Options for American Men [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Peer Support Enhances Life Quality for American Males with Late-Onset Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Lifestyle Strategies for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Navigating Insurance Coverage for Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Diagnosis and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Understanding Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Treatment, and Lifestyle Management for American Males [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Research Advances in Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Lifestyle Impact [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Social Impact, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management in American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Strategies for Mental Health in American Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Stress, Nutrition, and Holistic Approaches for American Men [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men: Advocacy and Personalized Care [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Nutritionists' Role in Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Exercise Strategies to Combat Late-Onset Hypogonadism in American Men [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Prevalence, Impact, and Management in American Men [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Managing Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment for American Men [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Understanding and Managing Emotional Impacts in Men Over 40 [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
Word Count: 557