Introduction
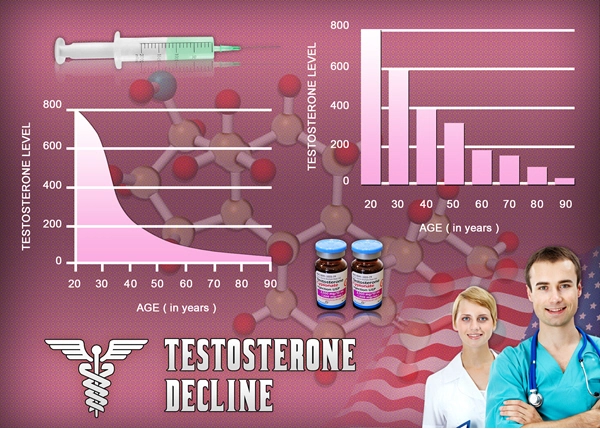
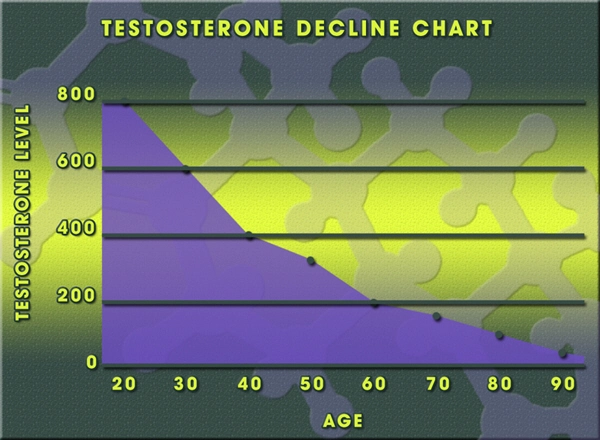
Depo Testosterone, a product of Pfizer, is a widely used injectable form of testosterone cypionate primarily prescribed for testosterone replacement therapy in men with low testosterone levels. This therapy is essential not only for maintaining sexual health but also for its systemic effects on various bodily functions, including erythropoiesis—the process of red blood cell production. This article delves into a comprehensive study involving 300 American males to explore how Depo Testosterone influences erythropoiesis, providing critical insights for healthcare professionals and patients alike.
Study Design and Methodology
The study involved 300 American males aged between 30 and 70 years, all of whom were diagnosed with hypogonadism and were candidates for testosterone replacement therapy. Participants were administered Depo Testosterone injections biweekly, and their hematological parameters were monitored over a period of 12 months. The primary focus was on changes in hemoglobin levels and hematocrit, key indicators of erythropoiesis.
Results: Erythropoiesis and Hemoglobin Levels
The administration of Depo Testosterone was associated with a significant increase in hemoglobin levels across the study population. On average, hemoglobin levels increased by 1.5 g/dL within the first six months of therapy. This elevation in hemoglobin is indicative of enhanced erythropoiesis, a known effect of testosterone. The increase in red blood cell production can be beneficial for patients, particularly those who might have anemia secondary to low testosterone levels.
Hematocrit Changes and Clinical Implications
Alongside hemoglobin, hematocrit levels also rose significantly, with an average increase of 4.5%. While this can improve oxygen-carrying capacity and overall vitality, it is crucial to monitor hematocrit closely, as levels exceeding 54% may predispose patients to conditions such as polycythemia, a state of elevated red blood cell mass that can increase the risk of thrombotic events. The study found that 15% of participants required dose adjustments or temporary cessation of therapy to manage elevated hematocrit levels.
Safety and Monitoring
The safety profile of Depo Testosterone in this study was consistent with existing literature, with the primary concern being the potential for polycythemia. Regular monitoring of hematological parameters is essential to ensure the safe use of testosterone therapy. Patients should be educated about the signs of polycythemia, such as headache, dizziness, and visual disturbances, and should seek medical attention if these symptoms arise.
Patient Profiles and Individual Responses
Individual responses to Depo Testosterone varied, reflecting the diverse nature of the study cohort. Factors such as age, baseline testosterone levels, and comorbidities influenced the degree of erythropoiesis observed. Younger patients and those with lower baseline testosterone levels generally exhibited more pronounced increases in hemoglobin and hematocrit. This underscores the importance of personalized medicine in managing testosterone replacement therapy.
Conclusion
This large-scale study underscores the significant impact of Depo Testosterone on erythropoiesis in American males, highlighting both the benefits and potential risks associated with its use. The increase in hemoglobin and hematocrit levels can enhance patients' quality of life but necessitates careful monitoring to prevent complications such as polycythemia. As testosterone replacement therapy continues to be a cornerstone in managing hypogonadism, understanding its effects on erythropoiesis is crucial for optimizing patient outcomes.
Future Directions
Future research should focus on long-term outcomes of testosterone therapy on erythropoiesis and explore strategies to mitigate the risk of polycythemia. Additionally, studies examining the impact of different testosterone formulations and dosing regimens could provide further insights into optimizing therapy for individual patients.
In conclusion, Depo Testosterone plays a vital role in enhancing erythropoiesis in American males with hypogonadism, but its use must be carefully managed to balance benefits and risks. This study provides valuable data that can guide clinical practice and improve patient care in the field of endocrinology.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Depo Testosterone: Enhancing Sexual Health in American Men with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Impacts on Weight Management in American Males with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Psychological Impacts on Mood, Cognition, and Self-Esteem in Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Enhancing American Men's Health and Vitality [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- American Men's Experiences with Depo Testosterone Therapy: Benefits and Challenges [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Enhancing Energy and Vitality in Men with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Enhancing Athletic Performance and Associated Risks in American Male Athletes [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Enhancing Life for American Males with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Impacts on Prostate Health and Cancer Risk in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Benefits, Risks, and Management for Low Testosterone Treatment [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Vital for Men's Health, Challenges in Accessibility and Solutions [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Efficacy and Safety in American Males with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Navigating Insurance Coverage for Depo Testosterone: A Guide for American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Benefits and Considerations for Transgender American Males' HRT [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Treating Delayed Puberty in American Males Effectively [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Benefits and Skin Health Effects in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone Therapy: Future Trends and Impact on American Male Health [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Enhancing Libido and Sexual Function in American Men with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: A Promising Treatment for ED in American Men with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Effects on Blood Sugar Levels in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Benefits vs. Cardiovascular Risks for American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Monitoring, Dosage Adjustment, and Safety for American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Depo-Testosterone's Impact on Sleep Quality in American Men: Insights and Management [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Benefits and Risks for Older American Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Enhancing Life for American Male Cancer Survivors [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Managing Chronic Conditions in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Enhancing American Male Body Composition and Health [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Enhancing Stress Management in American Males with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Vital Therapy for Hypogonadism in American Male Adolescents [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Enhancing Life Quality in American Male Veterans [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Enhancing Endurance in American Male Athletes - Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone and Hair Loss: Risks, Management, and Psychological Impact [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone Pfizer: Enhancing Mood and Well-being in American Males with Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone's Impact on Digestive Health in American Males: Effects and Considerations [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone's Impact on Immune System: Insights for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Enhancing Cognitive Function in American Males with TRT [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: A Promising Adjunct in Diabetes Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Balancing Hormone Therapy and Fertility in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Benefits for Hypogonadism and Potential Eye Health Risks in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Enhancing Life Quality for American Males with HIV/AIDS [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Benefits, Liver Risks, and Monitoring for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone's Impact on Joint Health in American Males: Risks and Benefits [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Enhancing Fertility in American Males with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Pfizer's Injectable HRT for American Males with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Benefits and Risks for American Male Weightlifters [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Treating Anemia in American Men with Pfizer's Injectable Solution [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Effects on Kidney Function and Monitoring in American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Treating Chronic Fatigue Syndrome in American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone's Role in Managing Osteoporosis in American Males: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone's Impact on Respiratory Health in American Males: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: A Promising Treatment for Depression in American Males with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone's Impact on Ear Health in American Males: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: A Potential Treatment for Anxiety in American Males with Low Testosterone [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone's Impact on Dental Health in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Managing Thyroid Disorders in American Males [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Managing Autoimmune Diseases in American Males [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: A Promising Solution for Migraine Management in American Males [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone's Impact on Skin Health in American Males: Benefits and Side Effects [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Uses, Allergic Reactions, and Management for American Males [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: A Promising Treatment for Insomnia in American Males [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: A Promising Option for Chronic Pain Management in American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Benefits for Neurological Disorders in American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Impacts on Cardiovascular Health in American Males [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone's Impact on Gastrointestinal Health in American Males [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Understanding TRT for Hypogonadism in American Males [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Enhancing Respiratory Health in Hypogonadal American Males [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Enhancing Arthritis Management in American Males [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Effects, Risks, and Management in Male Reproductive Health [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone's Impact on Psychiatric Disorders in American Males: A Comprehensive Review [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Benefits and Considerations for American Males with Genetic Disorders [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Managing Musculoskeletal Disorders in American Males [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Potential Dermatological Uses and Considerations in American Males [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Enhancing Metabolic Health in American Males with Pfizer's Therapy [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Enhancing Life for American Males with Renal Disorders [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Depo-Testosterone's Impact on Urological Disorders in American Males: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: A Promising Treatment for Inflammatory Diseases in American Males [Last Updated On: April 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 18th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone's Impact on Hematological Disorders in American Males: Risks and Management [Last Updated On: April 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 20th, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone's Role in Managing Infectious Diseases in American Males [Last Updated On: April 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 21st, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone Enhances Body Composition and Muscle Mass in Hypogonadal Men: Clinical Trial [Last Updated On: April 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 22nd, 2025]
- Depo Testosterone: Effective Hypogonadism Treatment for American Males [Last Updated On: April 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 23rd, 2025]
Word Count: 592