Introduction to Impotence
Impotence, clinically known as erectile dysfunction (ED), is a prevalent condition among American males, affecting millions across various age groups. It is characterized by the inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for satisfactory sexual performance. Understanding the intricate relationship between male anatomy and impotence is crucial for effective management and treatment of this condition.
The Role of the Penis in Erection
The penis plays a central role in the process of achieving an erection. It contains two cylindrical structures called the corpora cavernosa, which run along the top of the penis. When a man is sexually aroused, the arteries supplying blood to these structures dilate, allowing an increased flow of blood. This influx of blood fills the corpora cavernosa, causing the penis to become rigid and erect. The veins that normally drain blood from the penis are compressed during this process, which helps maintain the erection.
Neurological Influence on Erections
The nervous system is a critical component in the erectile process. The brain sends signals through the spinal cord and nerves to the penis, triggering the release of nitric oxide. This chemical causes the smooth muscles in the arteries of the corpora cavernosa to relax, facilitating blood flow. Any disruption in this neural pathway, whether due to psychological stress, neurological disorders, or spinal injuries, can lead to impotence.
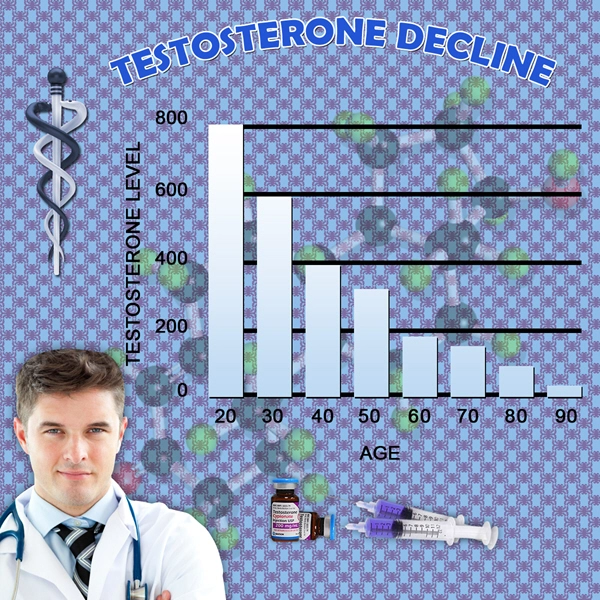
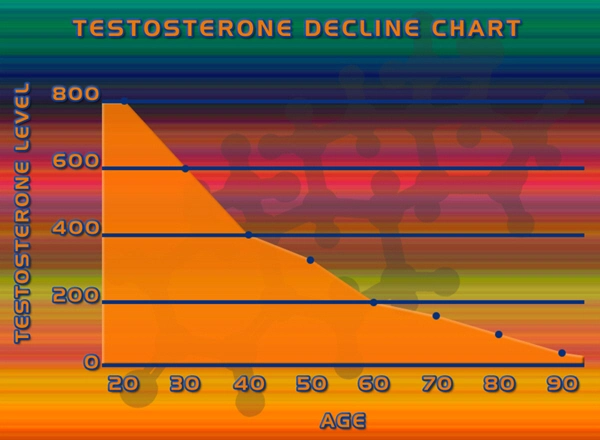
Hormonal Factors and Impotence
Hormones, particularly testosterone, play a significant role in sexual function. Low levels of testosterone can lead to reduced libido and difficulties in achieving an erection. The endocrine system, which regulates hormone production, must function optimally to support sexual health. Conditions such as hypogonadism, where the body does not produce enough testosterone, are directly linked to impotence.
Vascular Health and Its Impact
The health of the vascular system is paramount in maintaining erectile function. Conditions that affect blood flow, such as atherosclerosis, hypertension, and diabetes, can impair the ability to achieve and sustain an erection. Atherosclerosis, for instance, leads to the buildup of plaque in the arteries, reducing blood flow to the penis. Similarly, diabetes can damage blood vessels and nerves, contributing to impotence.
Psychological Aspects of Impotence
Psychological factors, including stress, anxiety, and depression, can significantly influence erectile function. These conditions can create a cycle of performance anxiety, where the fear of not being able to achieve an erection can itself lead to impotence. Addressing these psychological barriers is often essential in the treatment of ED.
Lifestyle and Its Effect on Impotence
Lifestyle choices play a crucial role in the development and management of impotence. Factors such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and a sedentary lifestyle can exacerbate the risk of ED. Smoking, for example, can damage blood vessels and reduce blood flow to the penis. Regular physical activity, a balanced diet, and cessation of smoking can improve overall vascular health and reduce the likelihood of impotence.
Medical Interventions and Treatments
Various medical interventions are available for treating impotence. Oral medications such as sildenafil (Viagra), tadalafil (Cialis), and vardenafil (Levitra) are commonly prescribed to enhance blood flow to the penis. For those who do not respond to oral medications, other treatments such as penile injections, vacuum erection devices, and surgical implants may be considered. It is important for individuals to consult with healthcare professionals to determine the most appropriate treatment based on their specific health needs.
Conclusion: Empowering Men Through Knowledge
Understanding the anatomy and physiological processes involved in impotence is essential for American males seeking to address this condition. By recognizing the various factors that contribute to ED, men can take proactive steps towards improving their sexual health. Through a combination of lifestyle modifications, psychological support, and medical interventions, impotence can be effectively managed, enhancing overall quality of life.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Innovations in Impotence Treatment: A New Era for American Males' Sexual Health [Last Updated On: February 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 23rd, 2025]
- Dissecting the Hushed Truth: Comprehensive Grasp on the Facets of Impotence [Last Updated On: February 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 25th, 2025]
- Unveiling the Frontiers of Male Sexual Health: Advanced Therapies for Erectile Dysfunction [Last Updated On: February 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 26th, 2025]
- Unveiling Masculine Strength: Finding the Path from Powerless to Potent [Last Updated On: February 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 26th, 2025]
- Unveiling Silent Torment: Navigating the Path of Impotence [Last Updated On: February 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 27th, 2025]
- Understanding Impotence: A Deep Dive into the Science of Desire [Last Updated On: February 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 28th, 2025]
- Subverting Traditions: Reinventing Masculinity Beyond the Shadow of Impotence [Last Updated On: February 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 28th, 2025]
- Disentangling Misconceptions and Unveiling the Truth about Erectile Dysfunction [Last Updated On: March 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 1st, 2025]
- Revolutionizing Impotence Management: A Deep Dive into Alternative Therapies for American Males [Last Updated On: March 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 1st, 2025]
- The Undeniable Link: Sexuality and Men's Mental Health [Last Updated On: March 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 2nd, 2025]
- Understanding Erectile Dysfunction: Causes, Stigma, and Advanced Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 3rd, 2025]
- Linking Erectile Dysfunction to Cardiovascular Health Risks [Last Updated On: March 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 4th, 2025]
- Understanding Testosterone's Role in Male Sexual Health and Impotence Management [Last Updated On: March 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 5th, 2025]
- Exploring the Impact of Stress and Anxiety on Erectile Dysfunction in Men [Last Updated On: March 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 6th, 2025]
- Understanding and Addressing Erectile Dysfunction's Impact on Relationships: A Comprehensive Guide [Last Updated On: March 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 7th, 2025]
- Comprehensive Guide to Male Impotence: Causes, Treatments, and Success Stories [Last Updated On: March 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 8th, 2025]
- Impotence: Psychological, Relational, and Medical Insights for Men and Partners [Last Updated On: March 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 9th, 2025]
- Understanding and Overcoming Impotence: A Comprehensive Guide for American Males [Last Updated On: March 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 12th, 2025]
- Revitalizing Masculine Vigor: A Comprehensive Guide to Overcoming Impotence Through Lifestyle Changes [Last Updated On: March 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 13th, 2025]
- Navigating Emotional Recovery: The Impact of Counseling on Impotence in American Men [Last Updated On: March 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 15th, 2025]
- Understanding and Overcoming Impotence: A Guide to Rebuilding Intimacy and Sexual Health [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Impotence and Aging: Understanding and Managing ED in American Males [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Impotence in American Males: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Emotional Support Strategies [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Impotence to Triumph: Men's Stories of Overcoming Erectile Dysfunction [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Understanding Impotence: Causes, Treatments, and Importance of Male Sexual Health [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Impotence: Economic and Emotional Impacts on American Men's Well-being [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Impotence: Understanding, Treating, and Overcoming Stigma in American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Telemedicine Revolutionizes Impotence Care for American Men: Benefits, Challenges, and Future [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Medication-Induced Impotence: Causes, Mechanisms, and Solutions for American Men [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Harnessing Positivity to Combat Impotence: A Mental Health Perspective [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Natural Aphrodisiacs: Exploring Their Role in Managing Impotence in American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Restorative Sleep: A Key to Enhancing Sexual Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Diabetes and Erectile Dysfunction: Prevalence, Mechanisms, and Management Strategies in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Overcoming Impotence: Understanding Causes, Treatments, and Emotional Impact [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Global Cultural Perspectives on Impotence and Sexual Health: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Strategies for American Men to Overcome Impotence and Enhance Seduction [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Innovative Gadgets and Techniques Revolutionizing ED Treatment [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Psychological Approaches to Combat Impotence in American Men: Mind-Body Connection [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Impotence in American Men: Understanding, Overcoming, and Redefining Sexual Health [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Work Stress and Impotence: Understanding and Managing the Connection in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- From Ancient Remedies to Modern Advances: Treating Impotence in American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Impotence and Endocrine Disorders: Insights and Guidance for American Men [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Navigating Insurance Coverage for Impotence: A Comprehensive Guide for American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Obesity, Diet, and Impotence: A Comprehensive Guide for American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Lifestyle Choices Impacting Male Sexual Health: Diet, Exercise, and More [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Erectile Dysfunction: Causes, Emerging Research, and Innovative Treatments in the U.S. [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Impotence in American Males: Understanding Impacts and Pathways to Renewed Intimacy [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Counseling Strategies to Rebuild Self-Esteem in Men with Impotence [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Breaking the Taboo: Understanding and Addressing Erectile Dysfunction in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- PDE5 Inhibitors: Revolutionizing ED Treatment and Enhancing Quality of Life [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Navigating the Emotional Impact of Impotence: Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Exercise: A Vital Strategy for Managing Impotence in American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Debunking Impotence Myths: Understanding and Treating Erectile Dysfunction in American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Acupuncture as a Complementary Treatment for Impotence in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Exploring Injection and Device Therapies for Impotence: Beyond Oral Medications [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Physical Therapy Enhances Sexual Health, Treats Impotence in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Impotence: Unveiling Emotional, Financial Burdens and Seeking Solutions for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Supporting Partners Through Impotence: A Guide to Understanding and Recovery [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Essential Nutrients for Combating Impotence in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Overcoming Impotence: A Holistic Approach to Men's Sexual Wellness [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Exploring Secondary Causes of Impotence Beyond Medication in American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Smoking, Alcohol, and Impotence: Impacts and Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Impotence: Navigating Psychological Impacts and Enhancing Intimate Relationships in American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Chronic Stress and Impotence: Understanding Links and Managing Effects [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Understanding Impotence: Biochemical, Hormonal, and Psychological Factors in American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Effective Strategies for Managing Impotence in American Men [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Overcoming Impotence: American Men's Journeys to Sexual Health and Confidence [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Impotence, Depression, and Anxiety: Integrated Treatment Approaches for American Men [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Impotence: Redefining Masculinity and Addressing Social Impact in America [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Innovative Technologies Revolutionizing Erectile Dysfunction Treatment and Management [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Prostate Health and Impotence: A Comprehensive Guide for American Men [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Impotence: Understanding ED's Impact on Relationships and Masculinity in American Men [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Future of Impotence Treatment: Innovations and Personalized Approaches [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Surgical Options for Impotence: Types, Procedures, and Recovery Insights [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Environmental Toxins and Male Impotence: Understanding Risks and Mitigation Strategies [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Breaking the Silence: Strategies for American Men to Discuss Impotence [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Lifestyle Hacks to Combat Impotence in American Men: Diet, Exercise, and More [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Innovative Drug Therapies Revolutionizing Impotence Treatment in American Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Holistic Self-Care Strategies for American Men to Overcome Impotence [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Chronic Illness and Impotence: Understanding Links and Managing Challenges [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
Word Count: 617