Introduction
Bodybuilding, a popular sport and fitness regimen among American males, involves rigorous training and a specialized diet aimed at enhancing muscle mass and strength. From a biologist's perspective, the metabolic effects of bodybuilding are profound and multifaceted, impacting various physiological systems. This article delves into the biochemical transformations that occur in the bodies of American men who engage in bodybuilding, highlighting the science behind muscle growth, energy metabolism, and hormonal changes.
Muscle Hypertrophy and Protein Synthesis
The primary goal of bodybuilding is to increase muscle size, a process known as muscle hypertrophy. This is achieved through resistance training, which causes micro-tears in muscle fibers. The body responds by initiating a repair process that involves increased protein synthesis. American males engaging in bodybuilding often consume high-protein diets to support this process. Proteins are broken down into amino acids, which are then used to rebuild and strengthen muscle fibers. Key amino acids like leucine play a crucial role in stimulating the mTOR pathway, which is essential for muscle protein synthesis.
Energy Metabolism and Macronutrient Utilization
Bodybuilding requires a significant amount of energy, leading to alterations in energy metabolism. American males who bodybuilding often follow a diet rich in carbohydrates to fuel their workouts and support glycogen replenishment in muscles. Glycogen, stored in muscles and the liver, serves as a readily available energy source during intense exercise. Additionally, fats are utilized as an energy source, particularly during longer, less intense sessions. The body's ability to switch between carbohydrate and fat metabolism is enhanced in bodybuilders, a phenomenon known as metabolic flexibility.
Hormonal Changes and Anabolic Effects
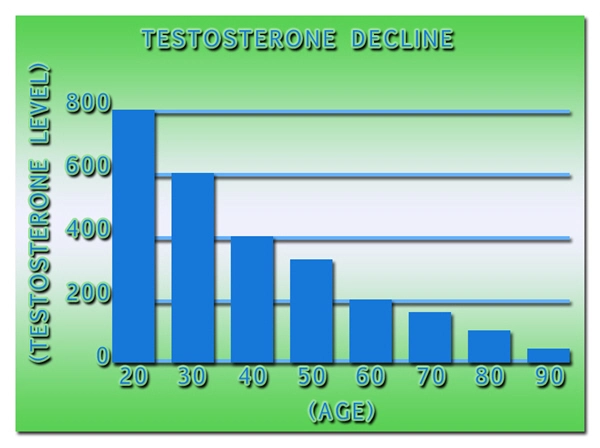
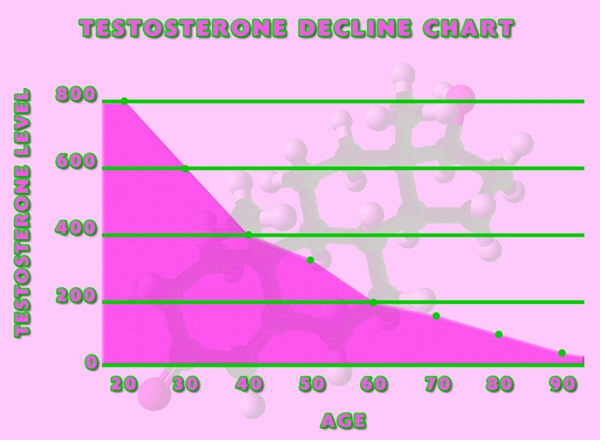
Hormonal changes are a critical aspect of the metabolic effects of bodybuilding. Resistance training stimulates the release of anabolic hormones such as testosterone and growth hormone, which are essential for muscle growth and repair. Testosterone, in particular, plays a significant role in increasing protein synthesis and reducing muscle breakdown. American males who engage in bodybuilding often experience elevated levels of these hormones, contributing to their ability to build muscle mass. Additionally, the stress of intense workouts can lead to increased cortisol levels, which, if not managed properly, can have catabolic effects on muscle tissue.
Nutrient Timing and Meal Frequency
The timing and frequency of meals are crucial considerations for American males involved in bodybuilding. Consuming protein and carbohydrates immediately after a workout can enhance muscle recovery and glycogen replenishment. This practice, known as nutrient timing, is based on the principle that muscles are more receptive to nutrients in the post-exercise window. Furthermore, frequent meals throughout the day help maintain a positive nitrogen balance, which is essential for continuous muscle growth and repair.
Impact on Insulin Sensitivity and Glucose Metabolism
Regular resistance training, as practiced in bodybuilding, can improve insulin sensitivity. This is particularly beneficial for American males, as it can reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Improved insulin sensitivity means that muscles can more effectively take up glucose from the bloodstream, leading to better glucose metabolism. Bodybuilders often experience enhanced glucose uptake in muscles, which supports their high energy demands during workouts.
Conclusion
The metabolic effects of bodybuilding on American males are extensive and complex, involving changes in muscle protein synthesis, energy metabolism, hormonal balance, nutrient timing, and glucose metabolism. Understanding these biochemical processes can help American men optimize their bodybuilding regimens for maximum muscle growth and overall health. As the science of bodybuilding continues to evolve, it remains a fascinating area of study that underscores the intricate relationship between exercise, diet, and metabolism.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Bodybuilding: A Therapeutic Strategy Against Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome in American Males [Last Updated On: February 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 21st, 2025]
- Exploring the Synergy Between Bodybuilding and Diabetes Management: A Comprehensive Guide for American Males [Last Updated On: February 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 27th, 2025]
- Exploring the Inspiring Ties: Physical Fitness and Mental Health Enhancement [Last Updated On: March 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 2nd, 2025]
- Integrating Physical Therapy Insights into Bodybuilding: Enhancing Benefits and Minimizing Risks [Last Updated On: March 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 3rd, 2025]
- Effective Nutritional Strategies for Optimal Bodybuilding Results [Last Updated On: March 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 4th, 2025]
- Exploring Bodybuilding: Impacts on Health, Hormones, and Body Composition in American Males [Last Updated On: March 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 5th, 2025]
- Exploring Bodybuilding's Role in Cardiovascular Health and Disease Prevention [Last Updated On: March 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 6th, 2025]
- Orthopedic Risks in Bodybuilding: Strategies for Prevention and Long-Term Musculoskeletal Health [Last Updated On: March 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 7th, 2025]
- The Hidden Dangers of Anabolic Steroids: Impact on Health and Fitness Goals [Last Updated On: March 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 8th, 2025]
- Unveiling the Nexus of Longevity and Bodybuilding: Insights from Geriatric Medicine [Last Updated On: March 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 9th, 2025]
- Optimizing Hormonal Dynamics in Bodybuilding: Strategies for Muscle Growth and Health [Last Updated On: March 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 9th, 2025]
- Sculpting More Than Muscle: The Psychological Benefits of Bodybuilding for American Males [Last Updated On: March 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 12th, 2025]
- Exploring the Impact of Bodybuilding on Sleep Patterns and Quality in American Males [Last Updated On: March 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 13th, 2025]
- Harnessing the Power of Bodybuilding: A Therapeutic Approach to Managing Chronic Pain in American Males [Last Updated On: March 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 15th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding: A Promising Strategy for Hypertension Management in American Males [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Health Risks of Competitive Bodybuilding: Steroids, Nutrition, and Psychological Impacts [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding Boosts Immune Health: A Guide for American Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding: A Holistic Approach to Managing Stress and Anxiety in American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding's Impact on Endocrine System: Hormonal Health in American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding's Role in Enhancing Addiction Recovery for American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Body Building Myths Debunked: Health Facts for American Males [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Integrating Bodybuilding into Post-Surgery Rehabilitation for American Males: A Physician's Guide [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Preventing Bodybuilding Injuries: Techniques, Recovery, and Nutrition for American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Bodybuilding's Role in Combating Lifestyle Diseases in American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Bodybuilding: A Promising Intervention for Osteoporosis in American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Asthma and Bodybuilding: Safety, Benefits, and Tailored Programs for American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Debunking Menstrual Cycle Myths in Bodybuilding: A Scientific Perspective for American Males [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Holistic Health and Bodybuilding: Enhancing American Males' Well-being [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Orthostatic Hypotension Risks and Prevention for American Male Bodybuilders [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Essential Vitamins and Supplements for American Male Bodybuilders: A Medical Review [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Bodybuilding Reduces Colon Cancer Risk in American Males: Fitness and Health Benefits [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Bodybuilding and Kidney Health: Safe Practices for American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Bodybuilding and Dementia Risk: Exploring Cognitive Benefits for American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Bodybuilding Enhances Lung Health: Exercises, Nutrition, and Monitoring for American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Bodybuilding and Gut Health: Optimizing Performance for American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Bodybuilding's Impact on Young Males: Benefits, Risks, and Growth Considerations [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding and Heart Health: Risks and Cardiologist's Insights for American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Genetic Factors in Bodybuilding: Muscle Growth, Strength, and Recovery Optimization [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding: A Natural Approach to Managing Arthritis in American Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Liquid Diets for Bodybuilders: Medical Critique and Risks [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding Boosts Cognitive Health: A Holistic Approach for American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding Enhances Mental Resilience in American Men: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding's Role in Managing Mood Disorders: A Holistic Approach for American Males [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding: A Comprehensive Anti-Aging Strategy for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Injury Prevention Strategies for American Male Bodybuilders: A Holistic Approach [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding Enhances Postnatal Recovery for American Fathers: Physical and Mental Benefits [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Body Building Enhances Life Quality for Parkinson's Patients: A Holistic Approach [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Sickle Cell Disease and Body Building: Benefits, Risks, and Safe Practices for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Combatting Sarcopenia: Bodybuilding Strategies for American Men's Muscle Health [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding's Psychological Impact on American Teenage Males: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding: A Holistic Approach to Managing Chronic Degenerative Diseases in American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding's Impact on Prostate Health: Risks and Benefits for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Body Building Benefits for American Men with COPD: Enhancing Life Quality [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding as a Recovery Strategy for American Males Post-Chemotherapy [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hydration Guidelines for American Male Bodybuilders: Enhancing Performance and Recovery [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Male Menopause and Body Building: Strategies for Muscle Growth and Health [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding Boosts Immune Health in American Males: Mechanisms and Benefits [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding Boosts Metabolism: Benefits and Risks for American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding: A Strategic Approach to Prevent Musculoskeletal Disorders in American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding as a Strategy for Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding as a Therapeutic Strategy for Managing PTSD in American Males [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Essential Safety Measures for American Male Bodybuilders: Techniques and Precautions [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding Boosts Bone Density: Optimizing Regimen for American Males' Skeletal Health [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Body Building and Heart Health: Benefits, Risks, and Safe Practices for American Males [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Medically Supervised Bodybuilding: Safe, Effective Weight Management for American Males [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Bodybuilding's Impact on Hormones in American Males: Benefits and Risks [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Bodybuilding and Longevity: Balancing Health Benefits and Risks for American Males [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Bodybuilding Boosts Cardiovascular Health: A Comprehensive Guide for American Males [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Flexibility in Bodybuilding: Enhancing Performance and Health for American Males [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Stretching Essentials for Bodybuilding: Enhancing Growth, Preventing Injuries [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding Success: The Critical Role of Gut Health in American Males [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding: A Clinically Proven Stress Management Strategy for American Males [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding and Back Pain: Chiropractic Strategies for Prevention and Management [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding Benefits for American Males with ADHD: Focus, Discipline, and Well-being [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Structured Bodybuilding: Preventing Low Back Pain in American Males [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding Enhances Joint Replacement Recovery in American Males [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Vegetarian Bodybuilding: Optimizing Protein Intake for Muscle Growth [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Safe Bodybuilding During Pregnancy: Guidelines for American Males Supporting Partners [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Bodybuilding: A Promising Approach to Managing Sciatica in American Males [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Overexertion Risks in Bodybuilding: Health Impacts and Safe Practices for American Males [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
Word Count: 579