Introduction
Prostate cancer remains one of the most prevalent cancers among American males, with significant impacts on health and quality of life. Recent research has increasingly focused on the role of endocrinology in the development and progression of this disease. Understanding the intricate relationship between hormonal levels and prostate health can lead to better prevention strategies and more effective treatments. This article delves into the latest findings on how hormones influence prostate cancer risk and progression in American men.
The Role of Androgens in Prostate Cancer
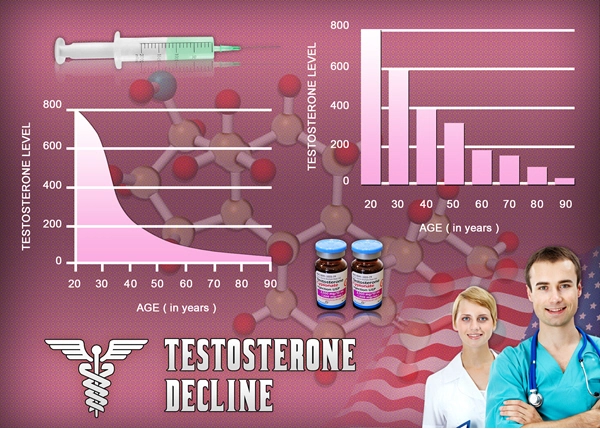
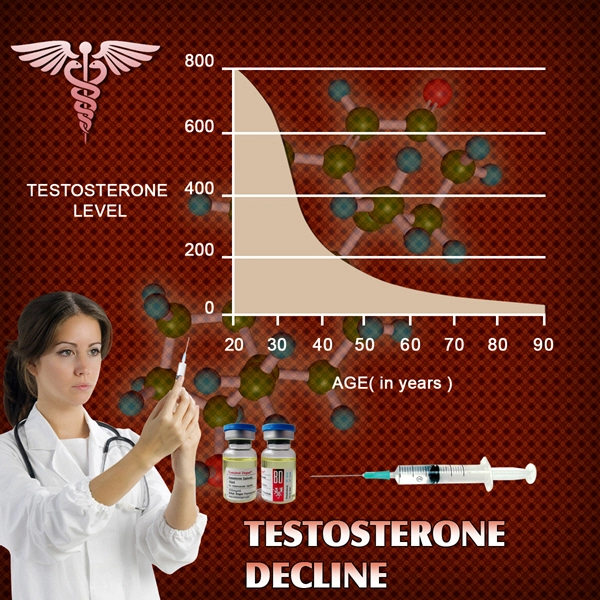
Androgens, primarily testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT), are crucial in the development and function of the prostate gland. These hormones are known to stimulate the growth of prostate cells, which can lead to benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and, in some cases, prostate cancer. Studies have shown that men with higher levels of circulating androgens may have an increased risk of developing prostate cancer. Conversely, treatments that reduce androgen levels, such as androgen deprivation therapy (ADT), are commonly used to manage advanced prostate cancer by slowing tumor growth.
Estrogen and Prostate Health
While androgens are the primary focus in prostate cancer research, estrogens also play a significant role. Estrogen levels in men can influence prostate health, as these hormones can interact with androgen receptors and affect cell proliferation. Some research suggests that a higher estrogen-to-testosterone ratio may be associated with an increased risk of aggressive prostate cancer. This finding underscores the need for a balanced hormonal profile to maintain prostate health.
The Impact of Insulin and IGF-1
Insulin and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) are other hormonal factors that have been linked to prostate cancer. High levels of insulin, often associated with metabolic syndrome and diabetes, can promote cell proliferation and inhibit apoptosis, potentially increasing the risk of cancer development. Similarly, elevated IGF-1 levels have been correlated with an increased risk of prostate cancer. These findings highlight the importance of metabolic health in the prevention and management of prostate cancer.
Hormonal Imbalances and Prostate Cancer Progression
Hormonal imbalances can not only contribute to the development of prostate cancer but also influence its progression. For instance, the transition from androgen-sensitive to castration-resistant prostate cancer is a critical stage where hormonal therapies often become less effective. Understanding the mechanisms behind this transition is vital for developing new treatment strategies. Research into the role of other hormones, such as cortisol and thyroid hormones, is also ongoing, as these may influence cancer progression and response to treatment.
Lifestyle Factors and Hormonal Regulation
Lifestyle factors play a significant role in hormonal regulation and, consequently, prostate health. Diet, exercise, and stress management can all impact hormone levels. For example, a diet high in red meat and dairy products has been linked to higher androgen levels, while a diet rich in fruits and vegetables may help maintain hormonal balance. Regular physical activity can also help regulate insulin and IGF-1 levels, reducing the risk of prostate cancer. Additionally, managing stress through techniques such as meditation and yoga can help maintain a healthy hormonal profile.
Conclusion
The link between endocrinology and prostate cancer in American males is a complex and multifaceted issue. Hormones such as androgens, estrogens, insulin, and IGF-1 all play significant roles in the development and progression of prostate cancer. Understanding these relationships can lead to more effective prevention and treatment strategies. By maintaining a healthy lifestyle and monitoring hormonal levels, American men can take proactive steps to reduce their risk of prostate cancer and improve their overall health. As research continues to unravel the hormonal puzzle, the hope is that new insights will lead to better outcomes for those affected by this prevalent disease.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Hormonal Imbalances and Sleep Disorders: Impact on American Men's Health and Interventions [Last Updated On: March 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 7th, 2025]
- Vitamin D's Crucial Role in Endocrine Health for American Males [Last Updated On: March 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 16th, 2025]
- Endocrinology's Role in Managing Chronic Fatigue in American Males [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Dietary Strategies for Enhancing Endocrine Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Endocrinology's Impact on Weight Management for American Males: Hormones and Strategies [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Hormonal Changes in Aging American Men: Impacts and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Endocrine Health and Cancer Risk in American Men: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Autoimmune Endocrine Disorders in Males: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Strategies [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- PCOS in Transgender Men: Diagnosis, Management, and Holistic Care Approaches [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Endocrine Disruptors: Impact on American Male Health and Mitigation Strategies [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Lifestyle Impacts on Endocrine Health: A Guide for American Men [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Hormonal Optimization in Sports: Enhancing Performance Ethically for American Male Athletes [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Male Infertility and Endocrinology: Understanding Hormonal Impacts on Fertility [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Gout in American Males: Endocrine Influences and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Endocrinology's Impact on Sexual Health in American Males: Hormones, Dysfunction, and Holistic Care [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Hormonal Imbalances and Kidney Health: Critical Insights for American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Endocrine Health and Mental Well-being: A Comprehensive Guide for American Males [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Alcohol's Impact on Endocrine System in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Hormonal Influences on Joint Health in American Men: A Comprehensive Guide [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Hormonal Impacts on Men's Immune Health in the U.S.: Insights and Strategies [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Endocrine-Neurological Interplay in American Men: Diagnosis, Management, and Future Research [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hormonal Imbalances and Their Role in Managing Male Depression in America [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Managing Endocrine Disorders in American Men with Autoimmune Diseases: A Comprehensive Guide [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hormonal Dynamics and Skin Health in American Men: Androgens, Acne, Aging, and Lifestyle [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Endocrine Health and Prostate Cancer: Insights for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Managing Endocrine Disorders and Heart Disease in American Men: Strategies and Insights [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Exercise Impacts on Endocrine Function in American Males: Hormonal Health Benefits [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Endocrine Disorders in Men: Impact on Skin Health and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Managing Type 2 Diabetes in American Men: Endocrine Insights and Strategies [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Endocrine System and Liver Health in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Endocrine and Gastrointestinal Health Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Hormonal Influences on Muscle Health in American Males: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Endocrine Health's Impact on Respiratory Function in American Males: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Exploring ADHD and Endocrinology: Hormonal Imbalances and New Treatment Avenues [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Exploring Endocrinological Interventions for PTSD in American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Endocrinology's Role in Managing Insomnia Among American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Endocrinology's Vital Role in Treating Male Eating Disorders in the U.S. [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Stress Impact on Male Endocrine Health: Hormones and Holistic Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Smoking's Impact on Endocrine Health in American Men: Testosterone, Thyroid, and More [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Hormonal Imbalances and Hearing Loss in American Males: Causes and Prevention [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hormonal Imbalances and Foot Health: A Guide for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Caffeine's Impact on Endocrine Health in American Males: Cortisol, Insulin, Testosterone, Thyroid [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Endocrine Health and Vision: Insights for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hormonal Fluctuations and Oral Health in American Men: Insights and Recommendations [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Hormonal Hair Loss in American Men: Causes, Treatments, and Future Research [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Hormonal Imbalances and Male Anxiety: Endocrinological Insights and Treatments in the USA [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Sleep's Impact on Endocrine Health: Key Hormones and Practical Sleep Improvement Tips for American Males [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Endocrine System's Impact on Digestive Health in American Males: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Nutrition's Impact on Endocrine Health in American Males: Key Nutrients and Diets [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Endocrine Health and Nail Changes in American Males: A Vital Connection [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Endocrinological Approaches Enhance Bipolar Disorder Treatment in American Men [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Endocrine Disorders and Eye Health: Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: March 31st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 31st, 2025]
- Endocrine Health and Hand Conditions in American Males: Insights and Management [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Endocrine Disorders and Ear Health: A Comprehensive Guide for American Men [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Hormonal Fluctuations and Nasal Health in American Men: Symptoms and Management [Last Updated On: April 1st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 1st, 2025]
- Hydration's Crucial Role in Endocrine Health for American Males [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Endocrine Health and Throat Conditions in American Males: Hormonal Impacts and Management [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Schizophrenia in Males: The Role of Endocrinology in Treatment and Management [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Managing Endocrine Disorders in American Men with Lung Conditions: An Endocrinological Approach [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Dietary Supplements' Impact on Endocrine Health in American Males: A Comprehensive Analysis [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Hormonal Balance and Heart Health: A Guide for American Men [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Exploring Hormonal Influences on Autism in American Males: Endocrine Insights and Therapies [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Endocrine System's Impact on Blood Health in American Males: Hormones, Disorders, and Management [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Mental Health's Impact on Endocrine Function in American Males: An Integrated Approach [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Exploring Endocrine Approaches to Treating OCD in American Males [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Endocrine and Nerve Health in American Males: Hormones, Disorders, and Lifestyle Impact [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 11th, 2025]
- Managing Endocrine Disorders in American Men with Kidney Disease: A Comprehensive Guide [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Hormonal Balance and Brain Health in American Men: Endocrinology Insights [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- Hormonal Influences on Skin Health in American Men: A Comprehensive Guide [Last Updated On: April 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 15th, 2025]
- Managing Endocrine Disorders in Men with Muscle Conditions: A Comprehensive Guide [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Exploring Endocrine Therapy for Managing ADD Symptoms in American Males [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Endocrinology's Crucial Role in Treating Male Eating Disorders in the USA [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Endocrine Disorders and Heart Health: Management Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Lifestyle Choices Impact Endocrine Health in American Males: Diet, Exercise, Stress, Sleep, Substance Abuse [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Aging and Endocrine Function in American Males: Impacts and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Endocrine Health and Liver Function: Impacts on American Males' Wellness [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Hormonal Influences on Bone Health in Aging American Men [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Endocrine Health's Impact on Joint Function in American Males: Hormonal Connections [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2025]
- Endocrinology's Impact on Male Health: Hormones, Aging, and Wellness [Last Updated On: April 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 21st, 2025]
- Thyroid Health in American Men: Understanding Disorders, Symptoms, and Management [Last Updated On: April 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 22nd, 2025]
Word Count: 601