Introduction to Post-Traumatic Hypopituitarism
Post-traumatic hypopituitarism (PTHP) is a condition that can emerge following traumatic brain injury (TBI), affecting the pituitary gland's ability to produce essential hormones. This disorder is particularly relevant to American men, who may experience TBIs due to sports injuries, military service, or accidents. Understanding PTHP is crucial for timely diagnosis and effective management, which can significantly improve quality of life.
The Pathophysiology of PTHP
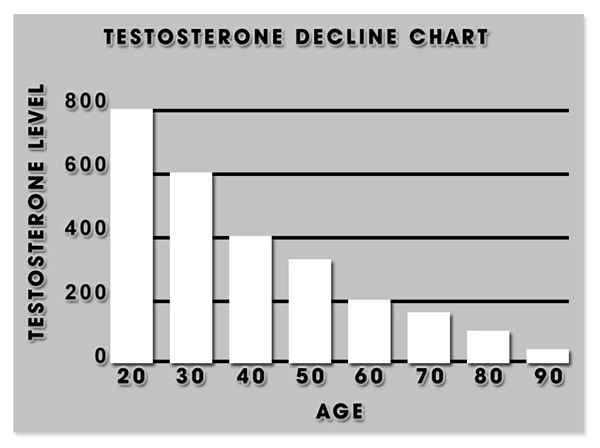
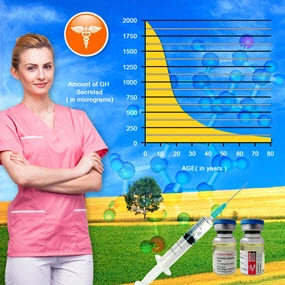
The pituitary gland, often referred to as the "master gland," is responsible for regulating various hormonal functions in the body. When a TBI occurs, the pituitary gland can be damaged, leading to a deficiency in one or more hormones. This can manifest as hypopituitarism, where the gland fails to produce adequate levels of hormones such as growth hormone (GH), thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), luteinizing hormone (LH), and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). The resultant hormonal imbalances can lead to a myriad of symptoms, including fatigue, decreased libido, and metabolic disturbances.
Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis
Men with PTHP may present with a range of symptoms that can be subtle and easily overlooked. Common signs include fatigue, weight gain, decreased muscle mass, and sexual dysfunction. Given the non-specific nature of these symptoms, a high index of suspicion is necessary for diagnosis, especially in men with a history of TBI.
Diagnosis involves a comprehensive endocrine evaluation, which includes blood tests to measure hormone levels and dynamic testing to assess pituitary function. For instance, the insulin tolerance test can evaluate GH and cortisol responses, while the gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) stimulation test can assess LH and FSH secretion. Imaging studies, such as MRI, may also be employed to visualize the pituitary gland and identify any structural abnormalities.
Hormone Replacement Strategies
Once PTHP is confirmed, the cornerstone of management is hormone replacement therapy (HRT), tailored to the specific deficiencies identified. For men with GH deficiency, recombinant human GH can be administered to improve body composition and quality of life. Testosterone replacement is crucial for those with hypogonadism, addressing symptoms such as decreased libido and fatigue. Additionally, cortisol and thyroid hormone replacements are essential for maintaining metabolic homeostasis.
Monitoring and Long-Term Management
Ongoing monitoring is vital to ensure the efficacy of HRT and to adjust dosages as needed. Regular follow-up appointments should include assessments of hormone levels, symptom review, and discussions about any side effects. Long-term management also involves educating patients about their condition and the importance of adherence to treatment regimens.
Psychological and Social Considerations
The impact of PTHP extends beyond physical health, affecting psychological well-being and social functioning. Men may experience depression, anxiety, or difficulties with interpersonal relationships due to the chronic nature of the condition. Therefore, a multidisciplinary approach that includes psychological support and counseling is beneficial. Support groups can also provide a platform for men to share experiences and coping strategies.
Conclusion: Empowering Men with PTHP
Post-traumatic hypopituitarism presents unique challenges for American men, but with comprehensive evaluation and tailored hormone replacement strategies, it is possible to manage the condition effectively. By raising awareness and improving diagnostic and treatment protocols, healthcare providers can empower men with PTHP to lead fulfilling lives despite their diagnosis. As research continues to evolve, the future holds promise for even more refined approaches to managing this complex endocrine disorder.
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Clomiphene Citrate Therapy in Men: Enhancing Endocrine Function in Secondary Hypogonadism [Last Updated On: February 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 20th, 2025]
- Comprehensive Endocrine Evaluation Essential for Diagnosing Fatigue in American Men [Last Updated On: March 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 2nd, 2025]
- Exploring hCG Monotherapy and Exogenous Testosterone in Young Men with Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism: A Focus on Testicular Function [Last Updated On: March 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 5th, 2025]
- The Crucial Link Between Insulin Resistance and Male Hormonal Imbalances: Effective Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 7th, 2025]
- The Crucial Link: Vitamin D's Impact on Androgen Metabolism and Hormone Replacement Therapy [Last Updated On: March 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 8th, 2025]
- The Critical Balance: Cortisol and Testosterone's Impact on Men's Health and Hormones [Last Updated On: March 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 9th, 2025]
- Exploring Neurosteroid Modulation as a Pioneering Treatment for Stress-Induced Endocrine Disorders in American Men [Last Updated On: March 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 12th, 2025]
- Exploring the Therapeutic Potential of Selective Androgen Receptor Modulators (SARMs) in Male Endocrine Disorders [Last Updated On: March 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 13th, 2025]
- Exploring the Role of Oxytocin in Male Endocrinology: From Physiology to Therapeutic Potential [Last Updated On: March 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 15th, 2025]
- Precision Medicine Revolutionizes HRT for Male Endocrine Disorders in American Males [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals: Impact on Male Health and Holistic Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Adipokines and Male Endocrine Health: Mechanisms, Impacts, and Therapeutic Prospects [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Chronobiology's Role in Male Hormone Secretion and Endocrinology for American Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Trace Elements' Impact on Hormone Metabolism in American Men: Zinc, Selenium, Magnesium [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Gut Microbiome's Role in Men's Steroid Hormone Metabolism and Health [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Thyroid-Testicular Axis: Impact on Male Health and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- Somatostatin Analogues: Versatile Applications in Male Endocrinology and Beyond [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Inflammaging and Male Hormonal Health: Strategies for Endocrine Optimization [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Mitochondrial Health and Male Hormones: Therapeutic Targets for Age-Related Decline [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- Metabolomics Revolutionizing Male Endocrine Health Diagnostics and Treatment [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- OSA in American Men: Exploring Endocrine Effects Beyond Testosterone [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Ghrelin Modulation Enhances Weight Management in Hypogonadal American Men on TRT [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Energy Balance and Reproductive Function in American Men: Neuroendocrine Integration and Clinical Implications [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- NAFLD's Impact on Male Endocrine and Reproductive Health: A Comprehensive Overview [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Male Hormonal Health and Cognitive Function: The Impact of Hormone Replacement Therapy [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Pharmacogenomics Revolutionizes Hormone Therapy in Men: Tailoring Treatment to Genetic Profiles [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- SHBG's Role in Male Hormonal Health: Regulation, Diagnosis, and Therapeutic Implications [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Luteinizing Hormone Dynamics: Diagnosis and Treatment in Male Endocrinology [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Managing Polycythemia in Men on Testosterone Therapy: Monitoring and Strategies [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Hormone Optimization and Lifestyle Strategies to Combat Sarcopenia in Aging Males [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Epigenetic Changes from HRT in American Men: Longitudinal Insights and Clinical Implications [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Leptin Resistance in American Men: Endocrine Effects and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Endocrine Reserve Testing: Diagnosis and Management of Hormonal Imbalances in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Optimizing Bone Health: BMD Monitoring Protocols for Men on HRT in the USA [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Managing Male Climacteric Syndrome: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Multidisciplinary Treatment Approaches [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Exercise and Endocrinology in Men: Hormonal Dynamics and HRT Implications [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Navigating Prostate Health During Testosterone Replacement Therapy: Risks and Monitoring Guidelines [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Pituitary Incidentalomas in Men: Evaluation, Management, and Long-term Monitoring [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Biomarkers in Male Endocrinology: Growth Factors and Cytokines' Clinical Applications [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Androgen Receptor Sensitivity: Enhancing Personalized Hormone Therapy in Men's Health [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Vasopressin's Therapeutic Roles in Male Endocrinology and Health [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Managing HPT Axis Recovery in American Men Post-Testosterone Therapy: Endocrinological Approaches [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Diurnal Hormone Patterns: Optimizing Endocrinology for American Males [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Endocrine Sequelae in Male TBI Patients: Long-Term Management and Follow-Up Strategies [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- ECS's Role in Male Reproductive Health: Insights for American Men [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Subclinical Endocrinopathies in Men: Diagnosis, Thresholds, and Treatment Strategies [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Inhibin B: Key Biomarker for Assessing Male Fertility and Endocrine Health [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Aging Men's Endocrine Changes: Impacts on Fertility and Offspring Health [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Opioid-Induced Endocrinopathy in Men: Mechanisms, Symptoms, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Multimarker Approach to Cardiometabolic Risk in Men on Hormone Replacement Therapy [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Endocrine Frailty in Aging Men: Hormonal Decline and Multimodal Intervention Strategies [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Male Sex Hormones and Autoimmune Disease Management in American Men: Endocrinology Insights [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- HRT and Telomere Length: Implications for Aging and Longevity in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- INSL3: A Stable Biomarker for Leydig Cell Function in Male Reproductive Health [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Neuropeptide Y: Key Regulator in Male Endocrine and Metabolic Health [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Bioavailable Hormones: Key to Effective Male Endocrinology Treatment in American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Managing Endocrine Disruption in Men Post-Chemotherapy: Strategies and Support [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Genetic Insights into Male Hypogonadism: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Counseling [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- AMH's Emerging Role in Adult Male Endocrinology and Reproductive Health [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- Hyperparathyroidism's Impact on Male Reproductive Health: Diagnosis and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Radiation-Induced Hypopituitarism in Men: Diagnosis, Hormone Deficiency Patterns, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- Hemochromatosis in American Men: Endocrine Effects, Screening, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- CKD's Impact on Male Endocrine Function: Adaptations and Therapeutic Strategies [Last Updated On: April 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 4th, 2025]
- Managing Male Sexual Desire Disorders: Endocrine Focus and Treatment Options for American Men [Last Updated On: April 6th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 6th, 2025]
- Osteoporosis in Men: Endocrine Evaluation, Hormone Therapy, and Dietary Management [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Adrenal Incidentalomas in Men: Evaluation, Management, and Long-term Follow-up Strategies [Last Updated On: April 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 7th, 2025]
- Cushing's Syndrome in Men: Clinical Features, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Hormonal Imbalances and Their Impact on Male Stress Urinary Incontinence [Last Updated On: April 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 8th, 2025]
- Hormone Replacement Therapy: Enhancing Male Fertility Through Endocrinology [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Enhancing Endocrine Resilience in American Men: Strategies and Biological Insights [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Growth Hormone and IGF-1: Enhancing Male Athletic Performance and Health [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Endocrine Management of Hormone Therapy for Transgender Men: Protocols and Monitoring [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Androgen Action: Mechanisms, Prostate Health, and Targeted Therapies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Advancements in Male Hormonal Contraception: Impact and Future Prospects [Last Updated On: April 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 13th, 2025]
- AI-Driven Precision Endocrinology: Personalizing Hormone Therapy for Men [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 14th, 2025]
- Enhancing Male Endocrinology Care with Patient-Reported Outcome Measures in American Men [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Quality Indicators in Male Endocrine Care: Development, Implementation, and Impact on American Men's Health [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Integrative Endocrinology: Holistic Hormone Therapy for American Men's Health [Last Updated On: April 16th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 16th, 2025]
- Wearable Tech Revolutionizes Hormone Monitoring and HRT for American Men [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
- Cost-Effectiveness of Hormone Replacement Therapy Strategies for American Men [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2025]
Word Count: 539