As Americans become more informed, they quickly recognize the health risks related to andropause and testosterone deficiency, and learn the benefits of Clomiphene Citrate for men.
Andropause is the time in a guy's life where he no longer produces enough testosterone to meet the body's needs. Though andropause is the most common type of hypogonadism, the condition can result from some different causes.
Video Link: https://vimeo.com/282904105
Video Download: Click Here To Download Video
Video Stream: Click Here To Stream Video
Video Link: https://vimeo.com/282904023
Video Download: Click Here To Download Video
Video Stream: Click Here To Stream Video

For example, many men lack the means to release sufficient testosterone from birth.
Others lose their ability to make enough testosterone because of cancer, radiation, trauma, or other circumstances. For these patients, direct testosterone replacement is the only adequate means to treat low-t.
For most patients, however, there is another option available — clomiphene citrate. Clomiphene citrate is now available for a generic prescription but was initially prescribed by the brand names Clomid and Serophene.
Treating Andropause with Clomiphene Citrate
Most men think that low-t is the direct result of the body's inability to produce its own testosterone.
The truth is that most males retain the ability to create their own testosterone throughout their entire lives — given the appropriate and adequate stimulation.
Andropause is a form of secondary hypogonadism, meaning that the testes still work just fine, they don't receive enough upstream signaling to meet the body's ongoing demand for testosterone, leading to the symptoms of testosterone deficiency.
For these patients, clomiphene citrate can bolster testosterone production back into the healthy adult range.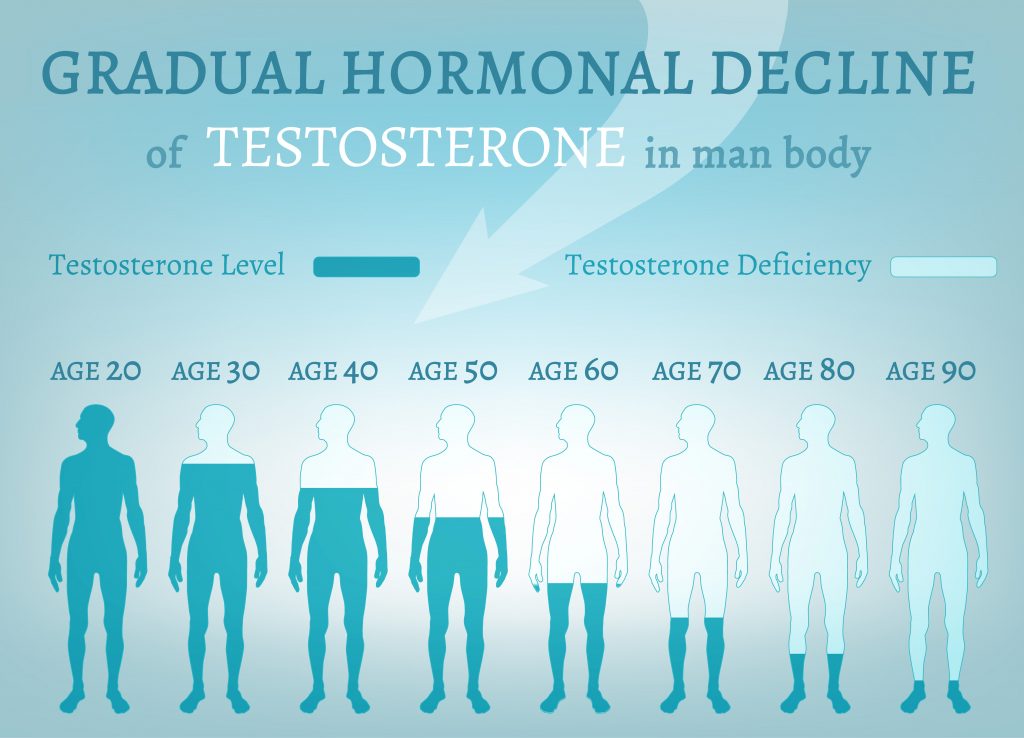
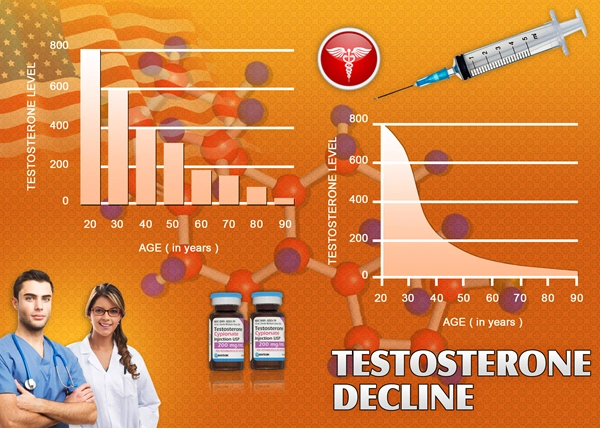
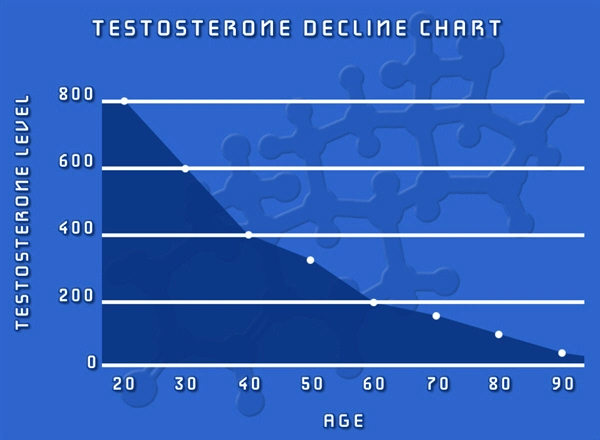
Testosterone Deficiency Risk Correlates Strongly with Age
Because of the way that our bodies work, our ability to make certain hormones declines as we grow older.
Two of the most important hormones that fall into age-related deficiency are testosterone and human growth hormone. The rate of decrease in testosterone is in the same range for all men — 1-2% annually.
Of course, every guy's physiology is different — some males produce more testosterone naturally than others. Many men are more sensitive to hormonal changes than others.
Depending on your health and your lifestyle choices, you could experience symptoms related to low-t as early as thirty years of age. Most men experience problematic symptoms in their forties and fifties, however.
Andropause has long been medicated with excellent results using low-t treatments such as Testosterone Enanthate and Cypionate injections, transdermal patches, and topical gels, but due to certain limitations associated with testosterone therapy, clomiphene citrate may be the preferred option.
Bio-Identical Testosterone Leads to the Suppression of Normal Testosterone and Sperm Production
One of the most notable drawbacks of recombinant testosterone is that regular use of the treatment can impair the natural secretion of testosterone by the testes, as well as testosterone precursor hormones such as luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH).
FSH circulates to the vas deferens and the prostate, primarily promoting sperm output, and LH activates Leydig cells which release testosterone.
For many patients, this isn't a big deal. The goal of testosterone replacement therapy is to boost testosterone levels via medical intervention, and the treatment is more than suitable to meet those needs.
For couples that are looking to have a child, however, testosterone therapy can be a significant roadblock. Both LH and FSH are modulated by testosterone concentrations in the bloodstream. An outside source of testosterone causes LH and FSH production to fall dramatically over time, which significantly impairs fertility.
Testosterone therapy also leads to testicular shrinkage, which many men want to avoid, even if they are not interested in having children.
HCG Supplementation Can Retain Sexual Potency During Testosterone Therapy
There are a couple of different ways to preserve fertility and ward off shrinkage while still receiving the benefits of testosterone optimization. Many doctors write a script for human chorionic gonadotropin to supplement testosterone therapy to maintain fertility and testicular fullness.
HCG injections are also used during testosterone cycling to encourage testicular function while the patient is on break from low-t treatment.
Though this is effective, there are two downsides. For one, this increases the cost of therapy, which may price some patients out of treatment.
The other issue is that the only means to administer therapeutic HCG is via injection, which many patients would prefer to avoid.
Oral Clomiphene Citrate Boosts Testosterone Without Needles
For price-conscious patients interested in avoiding needles and retaining normal testicular function, clomiphene citrate is a fantastic option.
Clomiphene citrate costs less than 1/3rd as much as bio-identical testosterone per cycle and still provides results. Clomiphene citrate is delivered via absorption through the mouth tissue and stimulates the testes to produce both testosterone and semen.
Clomiphene First Prescribed as Feminine Fertility Drug
When clomiphene citrate was first utilized as a medication, it was prescribed to women with fertility issues.
Over time, other clinical uses were discovered for clomiphene, and it was found that the treatment was also quite successful as a means to enhance natural testosterone production.
Clomiphene citrate can boost testosterone levels because it belongs to a class of drugs known as selective-estrogen inhibitors.
Specifically, clomiphene citrate can block estrogen from suppressing the production of GnRH (gonadotropin-releasing hormone). GnRH is the precursor hormone responsible for the production of LH and FSH.
In women, GNRH encourages ovulation, which is why clomiphene citrate is used as a fertility drug. In men, the treatment stimulates spermatogenesis and improved testosterone production.
Clomiphene Citrate is an Off-Label Testosterone Boosting Treatment
Like many medical breakthroughs, the use of clomiphene citrate has evolved. The use of clomiphene as male testosterone therapy has not been approved by the Food and Drug Administration, but it is used for that purpose by trained and licensed hormone doctors and specialists across the country.
It's used most frequently by patients looking to boost testosterone levels while maintaining fertility, but it is sometimes used merely as an alternative to bio-identical testosterone.
Testosterone Replacement Therapy Versus Clomiphene Citrate for Low-T
Dependent upon your specific case, your prescribing hormone doctor may recommend bio-identical testosterone therapy, clomiphene citrate, or leave the choice up to you. To make sure that you get the broadest range of options at the best price to you, it pays to be well-informed.
Not all patients with testosterone deficiency will respond adequately to clomiphene. If your low-t is the result of underlying testicular issues, clomiphene will not lead to the desired benefits, and you'll be limited to bio-identical testosterone.
Though testosterone deficiency in children and young adults is frequently the result of a testicular malfunction, andropause can almost universally be treated by clomiphene citrate.
Men that are still interested in having children, but want to experience the benefits of improved testosterone balance will either opt for clomiphene citrate or testosterone with HCG, depending on their budget and the recommendation of their hormone specialist.
Given a choice, many men prefer clomiphene citrate because it can be administered orally, though low-t creams and patches are also easy to use.
On the other hand, most forms of testosterone, aside from testosterone injections, are still patent-protected, making drugs like Testoderm, Androgel, and Androderm more expensive.
Your doctor can help you choose a low-t treatment plan that fits your budget and your needs while keeping your safety and well-being in mind.
Enclomiphene Citrate Soon to Be Available in American Market
Over time, medical treatments are refined and improved upon, and the same is the case for clomiphene citrate.
Currently, enclomiphene citrate is under clinical trial for use as a prescription testosterone enhancer. It appears as though enclomiphene has an improved safety profile and lower risk of side effects than clomiphene with modestly improved efficacy.
That's not to say that you should entirely avoid clomiphene citrate. It still works well, and most patients use the treatment without significant issues.
In reality, enclomiphene is an ingredient of clomiphene citrate, which is a combination of enclomiphene and zuclomiphene. Women respond most effectively to clomiphene citrate, but men appear to get better results from isolated enclomiphene.
Only Use Clomiphene Citrate with a Prescription
Just like bio-identical testosterone, clomiphene should only be used with a legitimate medical prescription as indicated by a physician. Using clomiphene without a prescription can lead to unintended side effects, many of which are similar to the abuse of testosterone therapy.
Side Effects of Clomiphene Citrate
Clomiphene citrate has a low incidence of significant side effects when used as indicated, but as with any medication, it does come with its own set of risks.
One of the most common side effects is mild indigestion, but as the body becomes accustomed to treatment, this symptom usually dissipates quickly.
Some patients may experience an increase in breast tissue known as gynecomastia.
This generally occurs when testosterone levels are too high. Adipose fat cells naturally break down some testosterone and convert it into estrogen.
If these estrogen levels remain too high, the result is gynecomastia. If you experience gynecomastia, it can be mitigated and reversed through the use of Arimidex or similar aromatase inhibitors. Your doctor may also reduce the dose.
If your vision changes during clomiphene citrate treatment, contact your doctor as soon as reasonably possible and discontinue therapy.
Changes in vision are a sign that the pituitary may be growing slightly in response to treatment, pressuring the optic nerve.
Reference
Testosterone versus clomiphene citrate in managing symptoms of hypogonadism in men
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- Andropause Symptoms Treatment - Fixing Male Menopause - Video [Last Updated On: November 25th, 2024] [Originally Added On: July 12th, 2012]
- Andropause: Male Menopause - Video [Last Updated On: November 25th, 2024] [Originally Added On: July 12th, 2012]
- About Andropause - Video [Last Updated On: November 25th, 2024] [Originally Added On: July 12th, 2012]
- MALE MENOPAUSE, MANOPAUSE, OR ANDROPAUSE? - Video [Last Updated On: November 25th, 2024] [Originally Added On: July 12th, 2012]
- Andropause Menopause Symptoms and Solutions Testosterone - Video [Last Updated On: November 25th, 2024] [Originally Added On: July 12th, 2012]
- Treatments for Male Menopause/Andropause/Manopause/Testosterone Deficiency - Video [Last Updated On: December 20th, 2024] [Originally Added On: July 12th, 2012]
- What is testosterone deficiency syndrome/male menopause/.andropause - Video [Last Updated On: November 25th, 2024] [Originally Added On: July 12th, 2012]
- Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome/Andropause - Video [Last Updated On: December 20th, 2024] [Originally Added On: July 12th, 2012]
- John Crisler DO - Andropause [Last Updated On: December 20th, 2024] [Originally Added On: July 12th, 2012]
- Menopause/Andropause [Last Updated On: December 20th, 2024] [Originally Added On: July 12th, 2012]
- Male Andropause: Part 2 - Video [Last Updated On: December 20th, 2024] [Originally Added On: July 12th, 2012]
- Dr. Steven Jepson discusses Andropause - Video [Last Updated On: December 20th, 2024] [Originally Added On: July 12th, 2012]
- Maturitas publishes clinical guide on low-dose vaginal estrogens for vaginal atrophy [Last Updated On: January 10th, 2018] [Originally Added On: September 13th, 2012]
- Testosterone Deficiency in Men - Andropause Symptoms and Treatment - Video [Last Updated On: January 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: November 2nd, 2012]
- Andropause - The Male Menopause - Video [Last Updated On: January 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: November 2nd, 2012]
- SA STGEC ~ Ad Hoc Talk: Andropause (2006) - Video [Last Updated On: January 4th, 2025] [Originally Added On: November 2nd, 2012]
- The Cosmetic Medic Stamford CT - Video [Last Updated On: January 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: November 2nd, 2012]
- Testosterone Roundtable -- Overview of Low Testosterone (Part 1) - Video [Last Updated On: January 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: November 2nd, 2012]
- Naturally Increase Testosterone Levels - Video [Last Updated On: February 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: November 26th, 2012]
- Patients Medical Welcomes Dr. Marcia A. Harris, Holistic Gynecologist and Anti-Aging Physician [Last Updated On: May 4th, 2015] [Originally Added On: December 2nd, 2012]
- ALCAT Pioneer, Roger Deutsch, to Address "Food Induced Inflammation and Aging" at Vienna's Prestigious December ... [Last Updated On: May 4th, 2015] [Originally Added On: December 5th, 2012]
- Andropause: Changes in Aging Men - Video [Last Updated On: February 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: December 10th, 2012]
- Rhein Test Kit - Avante Medical Center - Video [Last Updated On: February 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: December 10th, 2012]
- AM Northwest Appearance - Andropause - Video [Last Updated On: February 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: December 10th, 2012]
- Lessons in Menopause for Men - Video [Last Updated On: December 15th, 2012] [Originally Added On: December 15th, 2012]
- AAG Health Publishes Testosterone and HGH Discussion-Blog [Last Updated On: May 4th, 2015] [Originally Added On: December 26th, 2012]
- Understanding Andropause: Erectile Dysfunction - Part Two - Video [Last Updated On: February 26th, 2013] [Originally Added On: February 26th, 2013]
- Airing March 2 and 3: BBC World News 30-Minute Segment on Andropause/Aging with Dr. Jeff Life, Healthy Aging Expert ... [Last Updated On: February 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 28th, 2013]
- Andropause - Great Android App For Men - Vigor - Stamina - Video [Last Updated On: February 28th, 2013] [Originally Added On: February 28th, 2013]
- Eastday-Survey finds 1m locals suffer from andropause [Last Updated On: May 4th, 2015] [Originally Added On: May 22nd, 2013]
- What Is Andropause?Diagnosis,Symptoms,Treatment [Last Updated On: March 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: July 2nd, 2013]
- Andropause - Video [Last Updated On: July 2nd, 2013] [Originally Added On: July 2nd, 2013]
- Andropause Glossary - Video [Last Updated On: July 2nd, 2013] [Originally Added On: July 2nd, 2013]
- Andropause Symptoms - Video [Last Updated On: July 2nd, 2013] [Originally Added On: July 2nd, 2013]
- Understanding Andropause: Erectile Dysfunction - Part One - Video [Last Updated On: July 2nd, 2013] [Originally Added On: July 2nd, 2013]
- Understanding Andropause - Video [Last Updated On: July 2nd, 2013] [Originally Added On: July 2nd, 2013]
- Andropause video - Video [Last Updated On: July 8th, 2013] [Originally Added On: July 8th, 2013]
- ANDROPAUSE SOLUTION "OSS-TEST" TOP BEST NATURAL TESTOSTERONE BOOSTER - Video [Last Updated On: August 3rd, 2013] [Originally Added On: August 3rd, 2013]
- Natural relief for andropause [Last Updated On: December 2nd, 2017] [Originally Added On: October 10th, 2013]
- Andropause - Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, Diagnosis - Seniors ... [Last Updated On: January 7th, 2018] [Originally Added On: November 3rd, 2013]
- Andropause - Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, Diagnosis - Men's Health ... [Last Updated On: December 31st, 2017] [Originally Added On: November 3rd, 2013]
- Andropause Specialist [Last Updated On: January 21st, 2018] [Originally Added On: November 10th, 2013]
- Understanding Andropause [Last Updated On: October 24th, 2015] [Originally Added On: November 10th, 2013]
- Andropause - Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, Diagnosis - Men's ... [Last Updated On: January 20th, 2018] [Originally Added On: November 18th, 2013]
- Andropause | Male Menopause | Male Menopause Symptoms | Male ... [Last Updated On: November 25th, 2018] [Originally Added On: November 18th, 2013]
- Symptoms of andropause - Men's health [Last Updated On: November 25th, 2018] [Originally Added On: November 21st, 2013]
- Andropause In Men [Last Updated On: December 9th, 2017] [Originally Added On: November 23rd, 2013]
- Andropause - Male Menopause - Androgen Replacement Therapy [Last Updated On: January 13th, 2018] [Originally Added On: November 25th, 2013]
- Andropause 2013 - Reviewed and Ranked - Independent Reviews on ... [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: November 25th, 2013]
- Andropause, Facts, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Testosterone Treatment [Last Updated On: January 18th, 2018] [Originally Added On: November 27th, 2013]
- Symptoms of Andropause (Male Menopause): Low Testosterone, Low ... [Last Updated On: December 13th, 2017] [Originally Added On: November 27th, 2013]
- Discovery Health "Andropause: Dealing With Male Menopause" [Last Updated On: December 5th, 2017] [Originally Added On: November 27th, 2013]
- Global Toronto's News at Noon Andropause aka "manopause" - Video [Last Updated On: November 27th, 2013] [Originally Added On: November 27th, 2013]
- San Diego Dermatologist Discusses Male Menopause | Andropause Expert in San Diego - Video [Last Updated On: December 7th, 2017] [Originally Added On: December 9th, 2013]
- The American Academy of Anti-Aging Medicine (A4M) Concludes Largest Event in Anti-Aging, Regenerative and Aesthetic ... [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: December 19th, 2013]
- Andropause Symptoms - Male Menopause Symptoms [Last Updated On: December 16th, 2017] [Originally Added On: December 27th, 2013]
- What Is Andropause? | eHow - eHow | How to Videos, Articles ... [Last Updated On: January 20th, 2018] [Originally Added On: December 30th, 2013]
- Drug companies are pushing that new-man feeling Low T, high stakes [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: January 16th, 2014]
- Andropause - Male Menopause - Androgen Replacement Therapy ... [Last Updated On: December 24th, 2017] [Originally Added On: January 16th, 2014]
- Male Menopause Symptoms, Treatments, Causes, and More [Last Updated On: January 15th, 2018] [Originally Added On: January 16th, 2014]
- Can you reverse the aging process? [Last Updated On: April 11th, 2025] [Originally Added On: January 17th, 2014]
- Yourwellness Magazine Explores Male Menopause [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: January 19th, 2014]
- Antiaging Medicine and Research, India Will Highlight “Hormones and Aging in Medical Practice” During 5th Indomedicon ... [Last Updated On: April 14th, 2025] [Originally Added On: January 24th, 2014]
- Care needed when controlling cholesterol [Last Updated On: October 23rd, 2020] [Originally Added On: January 27th, 2014]
- Symptoms of Andropause (Male Menopause): Low Testosterone ... [Last Updated On: October 11th, 2020] [Originally Added On: January 30th, 2014]
- Antiaging Medicine and Research, India Will Highlight Hormones and Aging in Medical Practice During 5th Indomedicon ... [Last Updated On: October 24th, 2020] [Originally Added On: January 31st, 2014]
- The truth about low testosterone and 'male menopause' [Last Updated On: October 31st, 2020] [Originally Added On: January 31st, 2014]
- Surge or shrink [Last Updated On: November 1st, 2020] [Originally Added On: February 11th, 2014]
- How Does Andropause Affect Men? - Video [Last Updated On: November 10th, 2020] [Originally Added On: February 14th, 2014]
- Andropause | Male Menopause | Male Menopause Symptoms ... [Last Updated On: November 25th, 2018] [Originally Added On: February 15th, 2014]
- NuMale Medical - Low Testosterone -- Andropause - Video [Last Updated On: October 21st, 2020] [Originally Added On: February 21st, 2014]
- Boost Your Sex Drive: Solutions For Impotence, Erectile Dysfunction And Low Libido [Last Updated On: May 4th, 2015] [Originally Added On: February 27th, 2014]
- HowStuffWorks "Andropause: Dealing With Male Menopause" [Last Updated On: October 16th, 2020] [Originally Added On: March 7th, 2014]
- The Truth About Andropause: Male Menopause - Explained by Hormone Expert, Dr. Ken G. Knott, MD - Video [Last Updated On: November 20th, 2020] [Originally Added On: March 7th, 2014]
- What Is Andropause? It's Symptoms In Men & Treatment ... [Last Updated On: November 11th, 2020] [Originally Added On: March 14th, 2014]
- Andropause Low Testosterone A Drug Free Natural Approach UnitedMulticare com - Video [Last Updated On: October 9th, 2020] [Originally Added On: March 15th, 2014]
- Low Testosterone (Andropause). What is it? - Video [Last Updated On: October 30th, 2020] [Originally Added On: March 15th, 2014]
- Male menopause is a reality [Last Updated On: October 13th, 2020] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2014]
- Anatomy Menopause Andropause - Video [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2014] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2014]
- Menopause & Andropause - Video [Last Updated On: November 7th, 2020] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2014]
Word Count: 1546