It may seem simple, but the process of conception is somewhat complicated even for men. For a man to conceive, some thresholds must be met:
It may seem simple, but the process of conception is somewhat complicated even for men. For a man to conceive, some thresholds must be met:
- A man must have healthy sperm, capable of fertilization. This requires the adequate release of testosterone, as well as other hormones such as luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone.
- That sperm has to be able to mix with semen and pass through the tubes of the vas deferens without obstruction.
- He must produce a sufficient amount of sperm to have a significant chance of conception. The lower a man's sperm count is, the harder it will be for him to get his partner pregnant. If a man produces fewer than 39 million sperm per orgasm or 15 million sperm per milliliter, he is very likely to have issues with conception.
- That sperm must have functional mobility. It is normal that a small portion of sperm will have issues moving correctly, but the higher that this percentage is, the less likely that healthy sperm will make it successfully to the egg.
Video Link: https://vimeo.com/282904822
Video Download: Click Here To Download Video
Video Stream: Click Here To Stream Video
Medical Issues Which Contribute to Male Infertility
Immune Reaction – In some cases, the immune system will attack the sperm  as if it were an unwanted invader, significantly reducing the number of healthy sperm produced by the testes. There are medications that can help prevent this.
as if it were an unwanted invader, significantly reducing the number of healthy sperm produced by the testes. There are medications that can help prevent this.
Issues with Ejaculation – Sometimes, the man will be able to produce sperm effectively, but their bodies are unable to ejaculate regularly. Commonly, this is the result of retrograde ejaculation, a condition in which, during orgasm, sperm flows the wrong way, back into the bladder rather than into the woman. There are specific techniques that can retrieve healthy sperm for conception in this case.
Infection – There are some infections that can slow down or block the production of robust and healthy sperm. Usually, this is the result of scar tissue which can prevent the sperm from passing through the system successfully. These infections can also potentially directly damage the testes.
Varicocele – This is a condition in which the blood vessels which usually drain blood from the testicles swell, preventing them from adequately circulating blood out of the testicles. This increases the core temperature of the testes, which reduces both the mobility and the number of sperm produced by the organs. Via proper medical treatment, this condition can be reversed.
Undescended Testicles – This is a prenatal issue in which one or both testicles did not fall appropriately from the interior of the body. Men are more likely to suffer from fertility issues later in life if they experienced this issue and had to be treated at an early age.
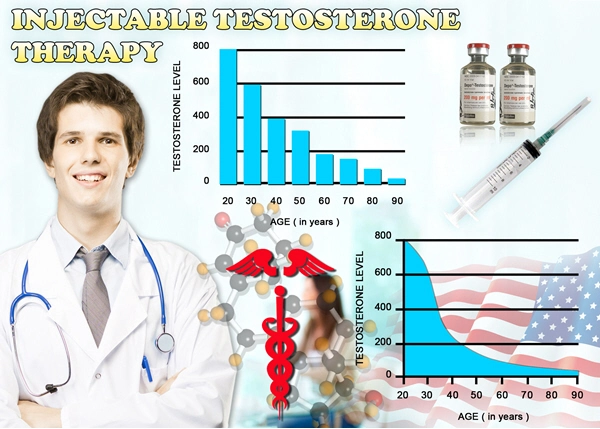
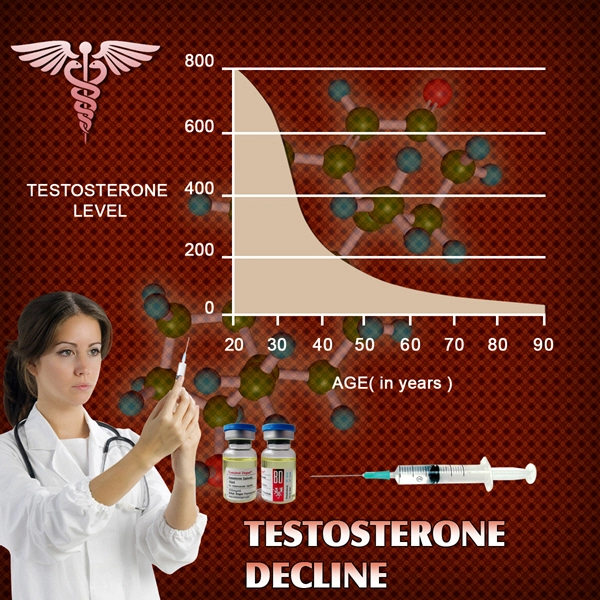
Hormone Imbalances – For the testes to produce sperm, the body needs to be in a state of hormone balance. There are many hormone issues that can impact fertility, including those associated with the adrenal glands, pituitary, thyroid, and hypothalamus. In particular, testosterone deficiency contributes heavily to infertility.
Tumors – Any tumor that impacts the male reproductive system or the  pituitary can lead to issues with testosterone and sperm production. Treating cancer may restore fertility.
pituitary can lead to issues with testosterone and sperm production. Treating cancer may restore fertility.
Genetic Defects – Some conditions, including Kartagener's syndrome, Kallmann's syndrome, or Klinefelter's syndrome can affect fertility directly.
Celiac disease – Gluten sensitivity can lead to issues with fertility that can be reversed by avoiding gluten.
Surgery – Any surgical procedure which impacts the function of the testes or the ability of sperm to be released during orgasm will limit or block fertility. Sometimes this is purposeful, as is the case with a vasectomy, but other times this can be the result of other, necessary medical procedures.
Issues engaging in healthy sex – Anything that prevents a man from experiencing an erection or orgasm can reduce fertility. This can be psychological, in the case of relationship problems, or it could also be the result of physiological issues that inhibit normal sexual function.
Medications -- Some medications can reduce fertility, including ulcer drugs, anti-fungal medications, and testosterone therapy without additional medicines to encourage sex hormone production.
Sperm duct issues – For sperm to be released during orgasm, it must pass through a series of tubes, including the sperm ducts. If the sperm ducts are malfunctioning (or if they don't exist, in the case of cystic fibrosis and other conditions), this will impair fertility.
Environmental Contributors to Male Infertility
Overheated Testicles – The testes optimally produce sperm at a slightly lower temperature than body temperature. If the testicles are too warm for an extended period for any reason, including the use of hot tubs or laptop computers, this may temporarily suppress fertility.
Radiation – Radiation will temporarily suppress the production of sperm, and radiation poisoning can damage the testes permanently.
Heavy Metals – Heavy metals get absorbed into the body and can directly damage the testes, hindering sperm production.
Chemicals – Some chemicals can reduce the production of testosterone and sperm, including solvents, herbicides, pesticides, xylene, toluene, and benzenes.
Lifestyle Issues Which Contribute to Infertility
Obesity – Fat cells convert testosterone into estrogen, which has a suppressive effect upon sexual function.
Stress – Anxiety diverts resources from testosterone to cortisol production, and it also makes it harder to focus on meaningful sexual activity.
Smoking – Smoking has a statistically significant impact on male fertility.
Work – Certain occupations, especially those that require sedentary, computer work, can increase infertility risk.
Alcohol – Alcohol converts testosterone into estrogen which reduces sperm count and testosterone production in excess and depresses physiological function, which can suppress arousal.
Drug Use – Many drugs suppress testosterone and sperm production, especially opiates and tranquilizers.
Frequent, Long Distance Cycling – There is some evidence that cycling can impede sexual function. For example, riding on the seat for long periods can overheat the testicles. Also, there is evidence that some men experience temporary numbing and erectile dysfunction from such cycling sessions.
Reference
Testosterone replacement in the infertile man
Contact Us Today For A Free Consultation

- FSH LH AND THE REGULATION OF THE REPRODUCTIVE ORGANS [Last Updated On: January 25th, 2024] [Originally Added On: August 23rd, 2013]
- Finally, The First Home Pregnancy Test That Tells You How Pregnant You Are [Last Updated On: January 25th, 2024] [Originally Added On: September 2nd, 2013]
- 'Girls' actress eats her placenta, but doctors say proceed with caution [Last Updated On: January 25th, 2024] [Originally Added On: January 7th, 2015]
- Support Your Fertility With Enclomiphene Citrate (Androxal) Throughout Testosterone Replacement Therapy [Last Updated On: January 17th, 2024] [Originally Added On: May 8th, 2020]
- Male Fertility During Young Adulthood Correlated with Long-Term Health and Wellness [Last Updated On: January 17th, 2024] [Originally Added On: January 10th, 2021]
- Improve Your Semen Quality with Omega-3 Fatty Acids [Last Updated On: August 16th, 2024] [Originally Added On: May 27th, 2021]
Word Count: 973